Solvent Effects on Protonation Constants of Betanin in Different Aqueous Solutions of Methanol at T = 25 ºC
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.29356/jmcs.v63i2.789Keywords:
Protonation Constants, Methanol, Spectrophotometric, Potentiometric, Solvent.Abstract
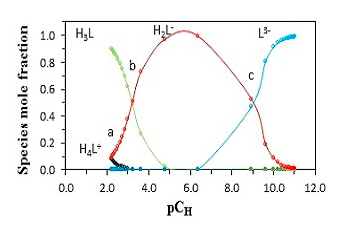
Abstract. The protonation constants of the betanin (pKa1, pKa2, and pKa3) were determined in mixed solvent of water and methanol containing 0, 10, 20, 30, 40, 50, 60, 70, and 80 % (v/v) methanol, using a combination of the spectrophotometric and potentiometric methods at T = 25 ºC and constant ionic strength (0.1 mol.dm-3 NaClO4). The obtained protonation constants were analyzed using Kamlet, Abboud, and Taft parameters. KAT parameters are α (hydrogen-bond donor acidity), β (hydrogen-bond acceptor basicity), and π* (dipolarity/polarizability). In this study, a good linear relationship was obtained between protonation constants (on the logarithmic scale) and dielectric constant (ɛ) of the water-methanol mixed solvents. It was found that the dual-parameter correlation between log10K,s and π*, β give us the best result in various volume fractions of methanol for water-methanol mixed solvent. Finally, the results are discussed in terms of the effect of the solvent on the protonation constants.
Resumen. Las constantes de protonación de la betanina (pKa1, pKa2 y pKa3) se determinaron en un disolvente mixto de agua y metanol que contenía metanol al 0, 10, 20, 30, 40, 50, 60, 70 y 80% (v / v), utilizando una combinación de los métodos espectrofotométricos y potenciométricos a T = 25 ºC y fuerza iónica constante (0,1 mol.dm-3 NaClO4). Las constantes de protonación obtenidas se analizaron utilizando los parámetros de Kamlet, Abboud y Taft. Los parámetros KAT son α (acidez del donante de enlaces de hidrógeno), β (basicidad del aceptor de enlaces de hidrógeno) y π* (dipolaridad / polarizabilidad). En este estudio, se obtuvo una buena relación lineal entre las constantes de protonación (en la escala logarítmica) y la constante dieléctrica (ɛ) de los disolventes mixtos agua-metanol. Se encontró que la correlación de doble parámetro entre log10K, s y π*, β nos da el mejor resultado en varias fracciones de volumen de metanol para el disolvente mixto agua-metanol. Finalmente, los resultados se discuten en términos del efecto del solvente en las constantes de protonación.
Downloads
References
SRaupp, D. D.; Rodrigues, E.; Rockenbach, I. I.; Carbonar, A.; Campos, P. F. D.; Borsato. A. L. V. Food Sci. Technol. (Campinas). 2011, 31, 688. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1590/S0101-20612011000300021
Slavov, A.; Karagyozov, V.; Denev, P.; Kratchanova, M.; Kratchanov, C. Czech J. Food Sci. 2013, 31, 139. DOI: https://doi.org/10.17221/61/2012-CJFS
Sapers, G.M.; Hornstein, G.S. J. Food Sci. 1979, 44, 1245. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2621.1979.tb03490.x
Hendry, G.A.R.; Houghton, J.D. Natural Food Colorants. Second edition, Blackie, 1996. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4615-2155-6
Delgado-Vargas, F.; Jiménez, A.R.; Paredes-López, O. CRC Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2000, 40, 173. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1080/10408690091189257
Hendry, G.; Houghton, G. Natural Food Colorants, Blackie Bublication, 1992, London.
Saguy, I.; Kopelman, I.J.; Mizrahi, S. J. Food Sci. 1978, 43, 124. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2621.1978.tb09750.x
Gharib, F.; Farkhad-Ali, N. J. Phys. Theor. Chem. 2015, 12, 19.
Reichardt. S. Solvents and solvent effects in organic chemistry. 2004, 3rded.; VCH: New York,.
Mayer. U. Pure Appl. Chem. 1979, 51, 1697. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1351/pac197951081697
Krygowski, T.M.; Fawcett. W.R. J. Chem. 1976, 54, 2383.
Taft, R.W.; Abbound, J.M.; Abraham. M.H. J. Solution Chem. 1985, 14, 153. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00647061
Svoboda, P.; Pytela, O.; Vecera. M. Chem. Commun. 1983, 48, 3287. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1135/cccc19833287
Gutmann, V.; Wychera, E. Inorg. Nucl. Chem. Lett. 1966, 2, 257. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/0020-1650(66)80056-9
Kamlet, M.J.; Abboud, J.M.; Abraham, M.H.; Taft, R.W. J. Org. Chem. 1983, 48, 2877. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/jo00165a018
Pehrsson, L.; Ingman, L.; Johansson, A. Talanta, 1976, 23, 769. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/0039-9140(76)80086-0
Gameiro, P.; Reis, S.; Lima, J.L.F.C.; Castro. B.D.E. Anal. Chim. Acta, 2000, 405, 167. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/S0003-2670(99)00641-8
Ferrer, J.S.; Couallier, E.; Rakib, M.; Durand, G. Electrochim. Acta. 2007, 52, 5773. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2007.02.058
Gharib, F.; Farajtabar, F.; Farahani, A.M.; Bahmani, F. J. Chem. Eng. Data. 2010, 55, 327. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/je900352f
Nilsson, T. Lantbrukshoegskolans Annaler, 1970, 36, 179. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/0029-554X(70)90315-0
Beck, M.T.; Nagypal, I. Chemistry of Complex Equilibria. 1990, Ellis Harwood, New York.
Leggett, D.J. Computational Methods for the Determination of Formation Constants, 1985, Plenum Press, New York. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4684-4934-1
Meloun, M.; Javurek, M.; Havel, J. Talanta. 1986, 33, 513. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/0039-9140(86)80263-6
Tutone, M.; Lauria, A.; Almerico, A. Interdisciplinary Sciences: Computational Life Sciences, 2016, 8, 177. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12539-015-0101-3
Barbosa, J.; Barron, D.; Beltran, J.L.; Buti, S. Talanta. 1998, 45, 817. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/S0039-9140(97)00167-7
Barbosa, J.; Toro, I.; Sanz-Nebot, V. Anal. Chim. Acta. 1997, 347, 295. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/S0003-2670(97)00163-3
Taft, R.W.; Abboud, J.L.M.; Kamlet, M.J. J. Org. Chem. 1984, 49, 2001. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/jo00185a034
Soleimani, F.; Gharib, F. J. Solution Chem. 2014, 43, 763. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10953-014-0161-8
Shamel, A.; Saghiri, A.; Jaberi, F.; Farajtabar, A.; Mofidi, F.; Khorrami, S.A.; Gharib. F. J. Solution Chem. 2012, 41, 1020. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10953-012-9845-0
Jabbari, M.; Gharib. F. J. Mol. Liq. 2012, 168, 36. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2012.02.001
Jabbari, M.; Gharib. F. J. Solution Chem. 2011, 40, 561. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10953-011-9667-5
Farajtabar, A.; Jaberi, F.; Gharib, F. Spectrochim. Acta A. 2011, 83, 213. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.saa.2011.08.020
Billo. E.J. Excel for Chemists: A Comprehensive Guide. Wiley, Weinheim. 2001. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/0471220582
Maleki, N.; Haghighi, B.; Safavi, A. Microchem. J. 1999, 62, 229. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1006/mchj.1998.1665
Akerlof, G. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1932, 54, 4125. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/ja01350a001
Moyano, F.; Biasutti, M.A. Silber, J.J.; Correa, N.M. J. Phys. Chem. B., 2006, 110, 11838. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/jp057208x

Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
License
Authors who publish with this journal agree to the following terms:
- Authors retain copyright and grant the journal right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution License that allows others to share the work with an acknowledgement of the work's authorship and initial publication in this journal.
- Authors are able to enter into separate, additional contractual arrangements for the non-exclusive distribution of the journal's published version of the work (e.g., post it to an institutional repository or publish it in a book), with an acknowledgement of its initial publication in this journal.









