Facile Synthesis of Silver-salicylic acid (modified)/TiO2-nanotube/Ti plates for UV-light Promoted Dye Degradation
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.29356/jmcs.v63i2.703Keywords:
Chemical modification, TiO2-nanotubes/Ti, Salicylic acid, Silver nanoparticles, Methylene orange, Photocatalyst.Abstract
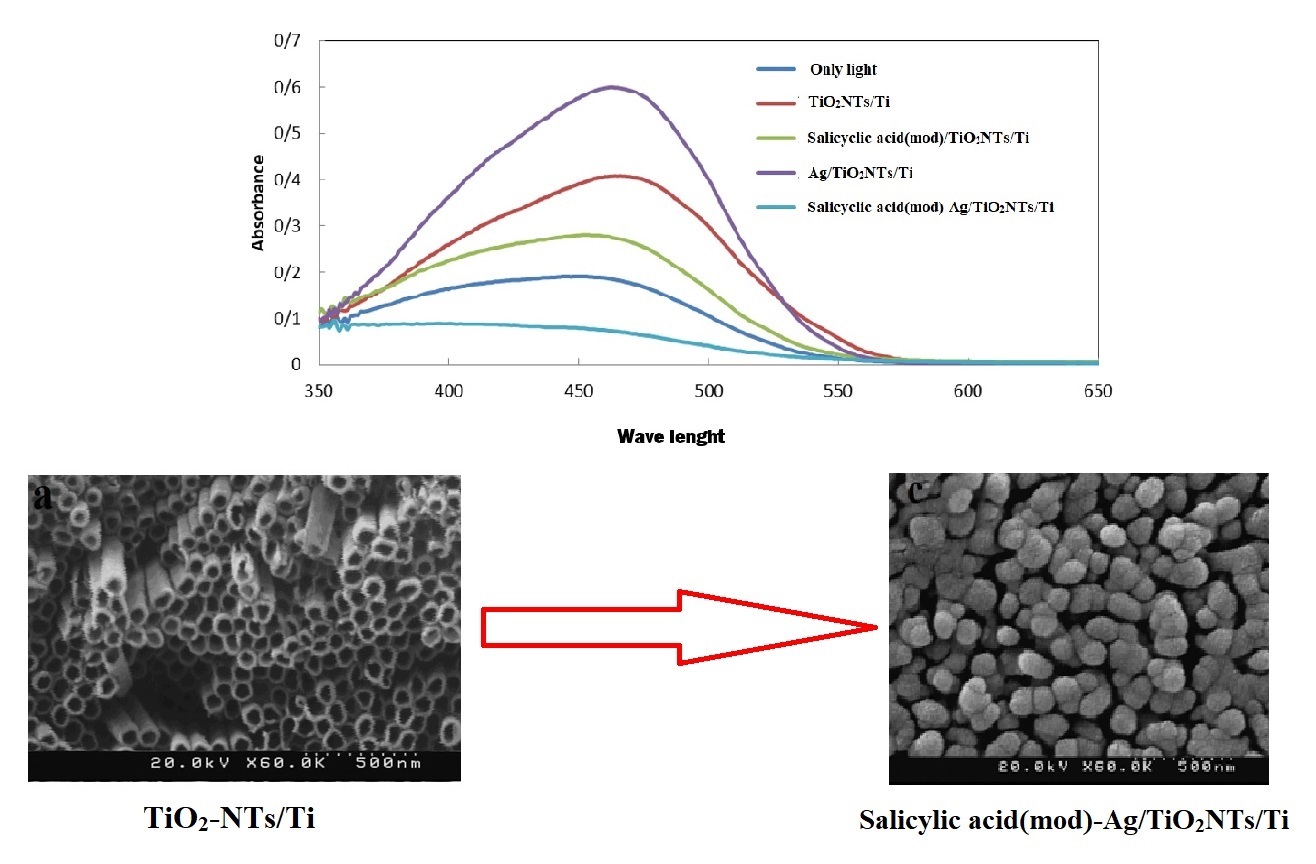
Abstract. Salicylic acid (mod)-Ag/TiO2NTs/Ti photocatalyst plates were prepared using chemical modification process of TiO2-nanotubes/Ti plates with salicylic acid and silver nanoparticles. Morphology studies exhibit that esterification between salicylic acid and -OH groups on TiO2 surface as well as deposition of Ag has been led to formation of uniform deposits on the walls of TiO2-nanotubes/Ti plates. The photocatalytic activity of the plates was tested on the degradation of Methylene Orange (MO) dye. The activity tests showed that the photodegradation efficiency for salicylic acid(mod)-Ag/TiO2NTs/Ti is higher than for Ag/TiO2NTs/Ti, salicylic acid(mod)/TiO2NTs/Ti and TiO2NTs/Ti plates, showing the integration the photocatalytic advantages of both Ag-TiO2 and salicylic acid-Mod-TiO2 composites. The modified plates can eliminate 96.6% of MO under UV light irradiation after 1 h, while can be recycled 4 times with 72.9% degradation ratio. Improved surface adsorption of MO, fast charge separation and slow electron-hole recombination are the main factors being responsible for the increase the photocatalytic activity of salicylic acid (mod)-Ag/TiO2-nanotubes/Ti plate.
Resumen. Se prepararon placas de fotocatalizador de ácido salicílico (mod)-Ag/TiO2NTs/Ti, utilizando un proceso de modificación química de placas de nanotubos/TiO2-TiO2, con ácido salicílico y nanopartículas de plata. Los estudios morfológicos muestran que la esterificación entre el ácido salicílico y los grupos -OH en la superficie de TiO2, así como la deposición de Ag, ha llevado a la formación de depósitos uniformes en las paredes de las placas de nanotubos de TiO2/ Ti. La actividad fotocatalítica de las placas se probó en la degradación del colorante naranja de metileno (MO). Las pruebas de actividad mostraron que la eficiencia de fotodegradación para el ácido salicílico (mod)-Ag /TiO2NTs/Ti es mayor que para las placas Ag/TiO2NTs/Ti, ácido salicílico (mod)/TiO2NTs/Ti y TiO2NTs/Ti, mostrando la integración de las ventajas fotocatalíticas de los compuestos de Ag-TiO2 y ácido salicílico-Mod-TiO2. Las placas modificadas pueden eliminar el 96.6% del MO bajo la irradiación con luz UV después de 1 h, mientras que pueden reciclarse 4 veces con una relación de degradación del 72.9%. La mejora de la adsorción superficial de MO, la rápida separación de la carga y la lenta recombinación del hueco de electrones son los principales factores responsables del aumento de la actividad fotocatalítica del ácido salicílico (mod)-Ag/TiO2-nanotubos/placa de Ti.
Downloads
References
Zhang, D.; Zeng, F. J. Iran Chem. Soc. 2017, 14, 2055-2066. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13738-017-1142-9
Tomova, D.; Iliev, V.; Rakovsky, S.; Anachkov, M.; Eliyas, A.; Puma, G. L. J. Photoch Photobio A. 2012, 231, 1-8. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jphotochem.2011.12.012
Zarei, A. R.; Rezaei-Vahidian, H.; Farajpour, T. J. Iran Chem. Soc. 2018, 15, 521-527. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13738-017-1252-4
Silva, R. M. E.; Thesing, A.; Deon, V. G.; Osório, A. G.; da S Noremberg, B.; Marins, N. H.; Orlandi, M. O.; da Motta, F. V.; do Nascimento, R. M.; Carreño, N. L. V. Bull. Mater Sci. 2017, 40, 499-504. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12034-017-1396-y
Song, M. S.; Vijayarangamuthu, K.; Han, E. J.; Jeon, K. J.; Seo, J. W. Korean J. Chem. Eng. 2016, 33, 2392-2395. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11814-016-0117-3
Golestanbagh, M.; Parvini, M.; Pendashteh, A. Catal. Lett. 2018, 148, 2162-2178. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10562-018-2385-5
Cui, E.; Lu, G. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy. 2014, 39, 8959-8968. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2014.03.258
Posa, V. R.; Annavaram, V.; Somala, A. R. Bull. Mater Sci. 2016, 39, 759-767. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12034-016-1215-x
Chen, C. J.; Liao, C. H.; Hsu, K. C.; Wu, Y. T.; Wu, J. C. S. Cata. Commun. 2011, 12, 1307-1310. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.catcom.2011.05.009
Feng, Z.; Lv, X.; Wang, T. J. Porous Mater. 2018, 25, 189-198. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10934-017-0432-z
Mohaghegh, N.; Faraji, M.; Gobal, F.; Gholami, M. R. RSC. Adv. 2015, 5, 44840-44846. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1039/C5RA03359D
Mumjitha, M.; Raj, V. Mater Sci. Eng. B-Adv. 2015, 198, 62-73. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mseb.2015.03.020
Shun-Xing, L.; Feng-Ying, Z.; Wen-Lian, C.; Ai-Qin, H.; Yu-Kun, X. J. Hazard Mater. 2006, 135, 431-436.
Li, S. X.; Zheng, F. Y.; Liu, X. L.; Wu, F.; Deng, N. S.; Yang, J. H. Chemosphere. 2005, 61, 589-594. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2005.02.054
Sboui, M.; Nsib, M. F.; Rayes, A.; Ochiai, T.; Houas, A. CR. Chim. 2017, 20, 181-189. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.crci.2015.12.007
Wang, X.; Zhao, H.; Quan, X.; Zhao, Y.; Chen, S. J. Hazard Mater. 2009, 166, 547-552. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2008.11.066
Faraji, M.; Mohaghegh, N. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2016, 288, 144-150. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.surfcoat.2016.01.022
Yang, G.; Yin, H.; Liu, W.; Yang, Y.; Zou, Q.; Luo, L.; Li, H.; Huo, Y.; Li, H. Appl. Catal B-Environ. 2018, 224, 175-182. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2017.10.052
Jiang, L.; Zhou, G.; Mi, J.; Wu, Z. Catal Commun, 2012, 24, 48-51. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.catcom.2012.03.017
Faraji, M.; Abedini, A. J. Photoch. Photobio. A, 2018, 361, 12-18. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jphotochem.2018.04.049
Sun, B.; Lu, N.; Su, Y.; Yu, H.; Meng, X.; Gao, Z. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2017, 394, 479-487. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2016.10.121
Wang, D.; Xu, Y.; Sun, F.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, P.; Wang, X. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2016, 377, 221-227. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2016.03.146
Bishnoi, A.; Chawla, H. M.; Rani, G. Inter. J. Adv. Chem. Eng. Bio. Sci. 2014, 1, 85-88.
Abanov, A. G. J. Phys. A: Math. Theor. 2013, 46, 292001-295301. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1088/1751-8113/46/29/292001
Huang, M.; Xu, C.; Wu, Z.; Huang, Y.; Lin, J.; Wu, J. Dyes Pigm, 2008, 77, 327-334. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dyepig.2007.01.026
Lu, J.; Wu, Z.; Li, Y. In 5th International Conference on Bioinformatics and Biomedical Engineering, 2011, 1-4. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1109/icbbe.2011.5781057
Talebi, S.; Chaibakhsh, N.; Moradi-Shoeili, Z. J. Appl. Res. Technol. 2017, 15, 378-385. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jart.2017.03.007

Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
License
Authors who publish with this journal agree to the following terms:
- Authors retain copyright and grant the journal right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution License that allows others to share the work with an acknowledgement of the work's authorship and initial publication in this journal.
- Authors are able to enter into separate, additional contractual arrangements for the non-exclusive distribution of the journal's published version of the work (e.g., post it to an institutional repository or publish it in a book), with an acknowledgement of its initial publication in this journal.