Alpha-glucosidase and Alpha-amylase Inhibitors Derived from Naturally Occurring Prenylated Isoflavones
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.29356/jmcs.v68i1.2129Keywords:
Diabetes mellitus, α-Glucosidase, α-Amylase, Prenylated isoflavones, PyranoisoflavonesAbstract
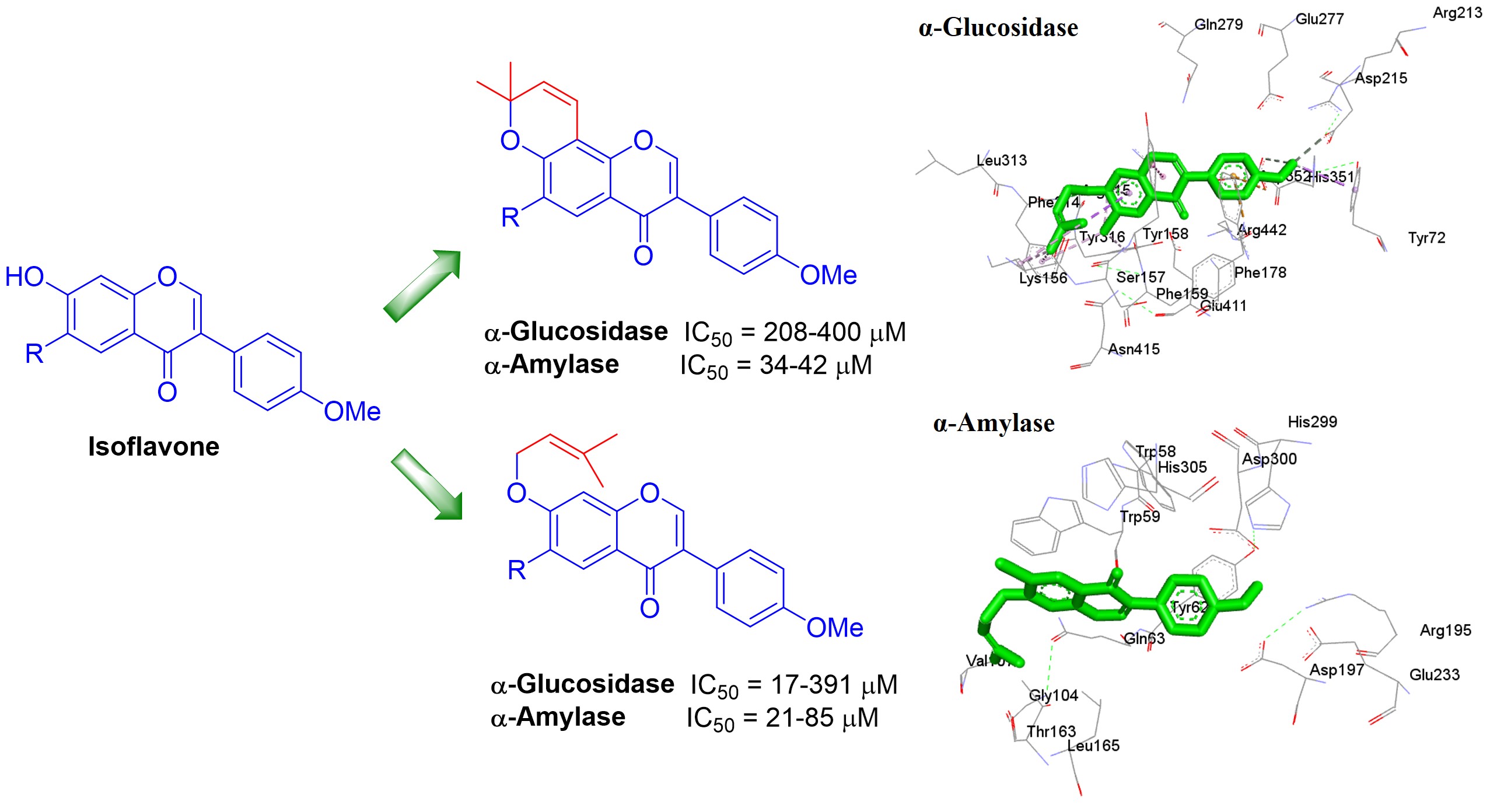
A series of prenylated isoflavones were synthesized to evaluate their inhibitory effect against α-glucosidase and α-amylase enzymes, analyzing the bioisosteric effect of the linear or cyclized prenyl moiety in these benzopyran derivatives. Compound 5a exhibited higher α-glucosidase inhibition (IC50 = 60.5 µM) and lower α-amylase inhibition (IC50 = 85.0 µM) compared to acarbose (IC50 = 527.5 µM for α-glucosidase and 20.1 µM for α-amylase). In contrast, prenylated isoflavone 5c showed higher inhibition in both enzymes (IC50 = 17.6 µM for α-glucosidase and 21.2 µM for α-amylase). This suggests that the attachment of a prenyl moiety to the 7-hydroxy group of isoflavone provides higher inhibition in the enzymes α-glucosidase and α-amylase. Docking studies of compounds 5a and 5c displayed key interactions towards both enzymes. The type of inhibition for 5c was analyzed, where the results indicate a competitive inhibition of both α-glucosidase and α-amylase. Finally, ADMET studies support that compounds 5a and 5c are candidates for the design of novel isoflavones derivatives with antidiabetic potential.
Resumen. Una serie de isoflavonas preniladas se sintetizaron para evaluar su efecto inhibidor sobre las enzimas α-glucosidasa y α-amilasa, analizando el efecto bioisotérico del fragmento prenilo tipo lineal o ciclado en estos benzopiranos derivados. El compuesto 5a exhibió una inhibición alta de α-glucosidasa (CI50 = 60.5 µM) y una inhibición más baja de α-amilasa (CI50 = 85.0 µM, respectivamente) en comparación con acarbosa (CI50 = 527.5 y 20.1 µM). La isoflavona prenilada 5c mostró mayor inhibición en ambas enzimas (CI50 = 17.7 µM para α-glucosidasa y 21.2 µM para α-amilasa). Esto sugiere que la unión del fragmento prenilo al hidroxilo de la posición 7 de la isoflavona ocasiona una mayor inhibición en las enzimas α-glucosidasa y α-amilasa. Los compuestos 5a y 5c mostraron interacciones clave hacia el sitio activo de ambas enzimas, de acuerdo con los cálculos de acoplamiento. Se analizó el tipo de inhibición para 5c, donde los resultados indican una inhibición competitiva tanto de α-glucosidasa como de α-amilasa. Finalmente, los estudios ADMET respaldan que los compuestos 5a and 5c son candidatos para el diseño de nuevos derivados de isoflavonas con potencial antidiabético.
Downloads
References
World Health Organization. Diabetes (who.int), accessed in February 2023.
Proenca, C.; Ribeiro, D.; Freitas, M.; Fernandes, E. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nut. 2022. 62, 3137-3207. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1080/10408398.2020.1862755.
Upadhyay, J.; Polyzos, S. A.; Perakakis, N.; Thakkar, B.; Paschou, S. A.; Katsiki, N.; Underwood, P.; Park, K-H.; Seufert, J.; Kang, E. S.; Sternthal, E.; karagiannis, A.; Mantzoros, C. S. Metabolism. 2018, 78, 13-42. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.metabol.2017.08.10 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.metabol.2017.08.010
Jo, Y. H.; Lee, S.; Yeon, S. W.; Ryu, S. H.; Turk, A.; Hwang, B. Y.; Han, Y. K.; Lee, K. Y.; Lee, M. K. Phytochemistry. 2022, 194, 113016. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phytochem.2021.113016.
Ahmed, Q. U.; Ali, A. H. M.; Mukhtar, S.; Alsharif, M. A.; Parveen, H.; Sabere, A. S. M.; Nawi, M. S. M.; Khatib, A.; Siddiqui, M. J.; Umar, A.; Alhassan, A. M. Molecules. 2020, 25, 5491. DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25235491.
Hu, W.; Wu, X.; Tang, J.; Zhao, G.; Xiao, N.; Zhang, L.; Li, S. J. Cell Mol. Med. 2019, 23, 3505-3511. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1111/jcmm.14248.
Wei, Z.; Yang, Y.; Xie, C.; Li, C.; Wang, G.; Ma, L.; Xiang, M.; Sun, J.; Wei, Y.; Chen, L. Fitoterapia. 2014, 97, 172-183. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fitote.2014.06.002.
Ndemangou, B.; Sielinou, V. T.; Vardamides, J. C.; Ali, M. S.; Lateef, M.; Iqbal, L.; Afza, N.; Nkengfack, E. J. Enzyme Inhib. Med. Chem. 2013, 28, 1156-1161. DOI: https://doi.org/10.3109/14756366.2012.719025.
Cardullo, N.; Muccilli, V.; Pulvirenti, L.; Tringali, C. J. Nat. Prod. 2021, 84, 654-665. DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.1021/acs.jnatprod.0c01387. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jnatprod.0c01387
Demir, Y.; Durmaz, L.; Taslimi, P.; Gulçin, I. Biotechnol. Appl. Biochem. 2019, 781-786. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/bab.1781.
Sun, H.; Li, Y.; Zhang, X.; Lei, Y.; Ding, W.; Zhao, X.; Wang, H.; Song, X.; Yao, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Ma, Y.; Wang, R.; Zhu, T.; Yu, P. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2015, 25, 4567-4571. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bmcl.2015.08.059.
Wu, C.; Tu, Y-B.; Li, Z.; Li, Y-F. Bioorg. Chem. 2019, 88, 102949. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bioorg.2019.102949.
Polbuppha, I.; Suthiphasilp, V.; Maneerat, T.; Charoensup, R.; Limtharakul, T.; Cheenpracha, S.; Pyne, S. G.; Laphookhieo, S. Phytochemistry. 2021, 187, 112773. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phytochem.2021.112773.
Jo, Y. H.; Lee, S.; Yeon, S. W.; Turk, A.; Lee, J. H.; Hong, S. M.; Han, Y. K.; Lee, K. Y.; Hwang, B.; Y.; Kim, S. Y.; Lee, M. K. Bioorg. Chem. 2021, 114, 105098. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bioorg.2021.105098.
Lv, H-W.; Wang, Q-L.; Luo, M.; Zhu, M-D.; Lian, H-M.; Li, W-J.; Cai, H.; Zhou, Z-B.; Wang, H.; Tong, S-Q.; Li, X-N. Arch. Pharm. Res. 2023, 46, 207-272. DOI: http://doi.org/10.1007/s12272-023-01443-4. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12272-023-01443-4
Wen, R.; Lv, H.; Jiang, Y.; Tu, P. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2018, 28, 1050-1055. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bmcl.2018.02.026.
Hikita, K.; Salgusa, S.; Takeuchi, Y.; Matsuyama, H.; Nagai, R.; Kato, K.; Murata, T.; Tanaka, H.; Wagh, Y. S.; Asao, N.; Kaneda, N, Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2020, 28, 115490. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bmc.2020.115490.
Buyinza, D.; Yang, L. J.; Derese, S.; Ndakala, A.; Coghi, P.; Heydenreich, M.; Wong, V. K. W.; Moller, H. M.; Yenesew, A. Nat. Prod. Res. 2021, 35, 2744-2747. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1080/14786419.2019.1660335.
Chang, S. K.; Jiang, Y.; Yang, B. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 108, 197-213. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tifs.2020.12.022.
Dirir, A.M.; Daou, M.; Yousef, A.; Yousef, L. F. Phytochem Rev. 2022, 21, 1049-1079. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11101-021-09773-1.
Park, M-H.; Ju, J-W.; Park, M-J.; Han, J-S. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2013, 712, 48-52. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejphar.2013.04.047.
Aguila-Muñoz, D. G.; Cervantes-Espinoza, E.; Escalante, C. H.; Gutiérrez, R. U.; Cruz-López, M. C.; Jiménez-Montejo, F. E.; Villa-Ruano, N.; Gómez-García, O.; Tamariz, J.; Mendieta-Moctezuma, A. Med. Chem. Res. 2022, 31, 1298-1312. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00044-022-02910-1.
Yenesew, A.; Midiwo, J. O.; Waterman, P. G. J. Nat. Prod. 1997, 60, 806-807. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/np9605955.
Yao, H.; Xu, F.; Wang, G.; Xie, S.; Li, W.; Yao, H.; Ma, C.; Zhu, Z.; Xu, J.; Xu, S. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2019, 167, 485-498. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejmech.2019.02.014.
Do, L. T. M.; Huynh, T. T. N.; Sichaem, J. Molecules. 2022. 27, 4624. DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27144624.
Chokki, M.; Cudalbeanu, M.; Zongo, C.; Dah-Nouvlessounon, D.; Ghinea, I. O.; Furdui, B.; Raclea, A.; Savadogo, A.; Baba-Moussa, L.; Avamescu, S. M.; Dinica, F. M.; Baba-Moussa, F. Foods. 2020, 9, 434. DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/foods9040434.
Morris, G. M.; Huey, R.; Lindstrom, W.; Sanner, M. F.; Belew, R. K.; Goodsell, D. S.; Olson, A. J. J. Comput. Chem. 2009, 30, 2785-2791. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/jcc.21256.
Bioinformatics and Molecular Design Research Center. Seul, South Corea, 2004. PreADMET Program. Available from: https://preadmet.webservice.bmdrc.org, accessed in June 2023.
BIOVIA, Dassault Systèmes, Discovery Studio Visualizer v20.1.0.19295, San Diego: Dassaul Systèmes (2020).
Choudhury, M. K.; Shiferaw, Y.; Sur, K. R.; Dey, D.; Debnathan, S.; Ghosh, S.; Ray, R.; Hazra, B. J. Coast. Life Med. 2016. 4, 556-563. DOI: https://doi.org/10.12980/jclm.4.2016J6-84.
Deyou, T.; Marco, M.; Heydenreich, M.; Pan, F.; Gruhonjic, A.; Fitzpatrick, P. A.; Koch, A.; Derese, S.; Pelletier, J.; Rissanen, K.; Yenesew, A.; Erdélyi, M. J. Nat. Prod. 2017. 2060-2066. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jnatprod.7b00255.
Na, Z.; Fan, Q-F.; Song, Q-S.; Hu, H-B. Phytochem. Lett. 2017. 19, 215-219. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phytol.2017.02.002.
Do, L. T. M.; Huynh, T. T. N.; Tran, Q. H. N.; Nguyen, H. T. M.; Nguyen, T. T. A.; Nguyen, T. T. N.; Nguyen, P. H. H.; Sichaem, J. Nat. Prod. Res. 2022. 1-7. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1080/14786419.2022.2110092.
Aguila-Muñoz, D. G.; Vázquez-Lira, G.; Sarmiento-Tlale, E.; Cruz-López, M. C.; Jiménez-Montejo, F. E.; López y López, V. E.; Escalante, C. H.; Andrade-Pavón, D.; Gómez-García, O.; Tamariz, J.; Mendieta-Moctezuma, A. Molecules. 2023. 28, 4180. DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28104180.

Downloads
Additional Files
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2023 Brandón Hernández, María del Carmen Cruz, Omar Gómez, Elvia Becerra, Fabiola Eloisa Jiménez, Aaron Mendieta

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.
Authors who publish with this journal agree to the following terms:
- Authors retain copyright and grant the journal right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution License that allows others to share the work with an acknowledgement of the work's authorship and initial publication in this journal.
- Authors are able to enter into separate, additional contractual arrangements for the non-exclusive distribution of the journal's published version of the work (e.g., post it to an institutional repository or publish it in a book), with an acknowledgement of its initial publication in this journal.









