Copper-Zinc Superoxide Dismutase (CuZn-SOD) Electrochemical Catalytic Amplification Sensing at Pt Ultramicroelectrodes
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.29356/jmcs.v67i4.1963Keywords:
Electrochemical catalytic amplification, copper zinc superoxide dismutase (CuZnSOD), metalloproteins, Pt ultramicroelectrodesAbstract
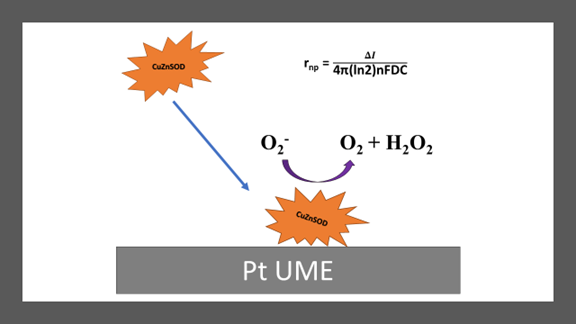
Abstract. Copper/zinc superoxide dismutase (CuZnSOD), a 32.5 kDa metalloprotein with a radius of ca. 2.1 nm, catalyses the superoxide to hydrogen peroxide and molecular oxygen. At the femtomolar concentration range, has been sensed through electrochemical catalytic amplification using a Pt ultramicroelectrode. During amperometric (i vs. t) analysis, cathodic and anodic current transitions peaks were seen, in agreement with the metalloprotein catalytic mechanism. The current amplitudes were analyzed and correspond to the CuZnSOD dimensions. Thermal treatment of metalloprotein samples at 80 °C showed larger current spikes suggesting aggregation without losing its catalytic capability. The size was confirmed by transmission electron microscopy.
Resumen. Cuprozinc superóxido dismutasa (CuZnSOD), es una metaloproteina de 32.5 kDa con un radio de aproximadamente 2.1 nm. Esta enzima cataliza la reacción de superóxido a peróxido y oxígeno molecular. Por primera vez, esta proteína es detectada a concentraciones femtomolares haciendo uso de la técnica electroquímica conocida como amplificación catalítica y la tecnología de ultra-microelectrodos de Pt. Durante un análisis amperométrico (curvas i vs. t), se observaron picos transitorios de corriente catódica y anódica que concuerdan con el mecanismo catalítico de la enzima. Al analizar la amplitud de la corriente, la misma concuerda con las dimensiones de CuZnSOD. Luego de exponer la proteína a un tratamiento térmico de 80 °C, CuZnSOD mostró picos de corriente transitorias que sugieren aglomeración de la enzima sin perder su capacidad catalítica. El tamaño fue confirmado por microscopía electrónica de transmisión.
Downloads
References
Rosa, A. C.; Corsi, D.; Cavi, N.; Bruni, N.; Dosio, F. Molecules. 2021, 26, 1844. DOI: 10.3390/molecules26071844 PubMed. DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26071844
Ge, B.; Scheller, F. W.; Lisdat, F. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2003, 18, 295-302. DOI: 10.1016/s0956-5663(02)00174-4 PubMed. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/S0956-5663(02)00174-4
Bakavayev, S.; Chetrit, N.; Zvagelsky, T.; Mansour, R.; Vyazmensky, M.; Barak, Z.; Israelson, A.; Engel, S. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 10826. DOI: 10.1038/s41598-019-47326-x. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-019-47326-x
Candas, D.; Li, J. J. Antioxid. Redox Signal 2014, 20, 1599-1617. DOI: 10.1089/ars.2013.5305 PubMed. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1089/ars.2013.5305
Yan, Z.; Spaulding, H. R. Redox Biol. 2020, 32, 101508. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.redox.2020.101508.
(Powers, K. M.; Oberley, L. W.; Domann, F. E. The Adventures of Superoxide Dismutase in Health and Disease: Superoxide in the Balance. In Oxidants in Biology: A Question of Balance, Valacchi, G., Davis, P. A. Eds.; Springer Netherlands, 2008; 183-201. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4020-8399-0_9
Altobelli, G. G.; Van Noorden, S.; Balato, A.; Cimini, V. C. Front. Med. 2020, 7 (183). DOI: 10.3389/fmed.2020.00183. DOI: https://doi.org/10.3389/fmed.2020.00183
Toh, Y.; Kuninaka, S.; Oshiro, T.; Ikeda, Y.; Nakashima, H.; Baba, H.; Kohnoe, S.; Okamura, T.; Mori, M.; Sugimachi, K. Int. J. Oncol. 2000, 17, 107-112. DOI: 10.3892/ijo.17.1.107 From NLM. DOI: https://doi.org/10.3892/ijo.17.1.107
Nadine, H.; Pauline, M. C.; Melendez, J. A. Anti-Cancer Agents Med. Chem. 2011, 11, 191-201. DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.2174/187152011795255911. DOI: https://doi.org/10.2174/187152011795255911
Chen, P. M.; Wu, T. C.; Shieh, S. H.; Wu, Y. H.; Li, M. C.; Sheu, G. T.; Cheng, Y. W.; Chen, C. Y.; Lee, H. Mol. Cancer Res. 2013, 11, 261-271. DOI: 10.1158/1541-7786.Mcr-12-0527 From NLM. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1158/1541-7786.MCR-12-0527
Dick, J. E.; Hilterbrand, A. T.; Boika, A.; Upton, J. W.; Bard, A. J. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U S A 2015, 112, 5303-5308. DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1504294112.PubMed. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1504294112
Dick, J. E.; Hilterbrand, A. T.; Strawsine, L. M.; Upton, J. W.; Bard, A. J. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U S A 2016, 113, 6403-6408. DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1605002113 PubMed. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1605002113
(Sekretareva, A. Sens. Actuators Rep. 2021, 3, 100037. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snr.2021.100037.
Andreescu, S.; Vasilescu, A. Curr. Opin. Electrochem. 2021, 30, 100820. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.coelec.2021.100820.
Dick, J. E. Chem. Comm. 2016, 52, 10906-10909. DOI: 10.1039/C6CC04515D. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1039/C6CC04515D
Tian, Y.; Mao, L.; Okajima, T.; Ohsaka, T. Anal. Chem. 2004, 76, 4162-4168. DOI: 10.1021/ac049707k. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/ac049707k
Xiao, X.; Bard, A. J. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2007, 129, 9610-9612. DOI: 10.1021/ja072344w PubMed. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/ja072344w
Bard, A. J.; Zhou, H.; Kwon, S. J. Israel J. Chem. 2010, 50, 267-276. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/ijch.201000014.
Sekretaryova, A. N.; Vagin, M. Y.; Turner, A. P. F.; Eriksson, M. Electrocatalytic Currents from Single Enzyme Molecules. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2016, 138, 2504-2507. DOI: 10.1021/jacs.5b13149. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/jacs.5b13149
Fan, F. R. F.; Demaille, C. Scanning Electrochemical Microscopy 2012, 75-110. DOI: 10.1201/b11850-4. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1201/b11850-4
Balamurugan, M.; Santharaman, P.; Madasamy, T.; Rajesh, S.; Sethy, N. K.; Bhargava, K.; Kotamraju, S.; Karunakaran, C. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2018, 116, 89-99. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2018.05.040.
Jamnongwong, M.; Loubiere, K.; Dietrich, N.; Hébrard, G. Chem. Eng. J. 2010, 165, 758-768. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2010.09.040.

Downloads
Additional Files
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2023 Annelis O. Sánchez-Álvarez, J. Andres Melendez, Mariena Silvestry-Ramos, Carlos R. Cabrera

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.
Authors who publish with this journal agree to the following terms:
- Authors retain copyright and grant the journal right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution License that allows others to share the work with an acknowledgement of the work's authorship and initial publication in this journal.
- Authors are able to enter into separate, additional contractual arrangements for the non-exclusive distribution of the journal's published version of the work (e.g., post it to an institutional repository or publish it in a book), with an acknowledgement of its initial publication in this journal.









