Bioactive Lipids, Nutritional Benefits and Phytochemicals Present in Hura Crepitans Seed Oil
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.29356/jmcs.v68i3.1950Keywords:
Bioactive lipids, health benefits, Hura crepitans, phytochemicalsAbstract
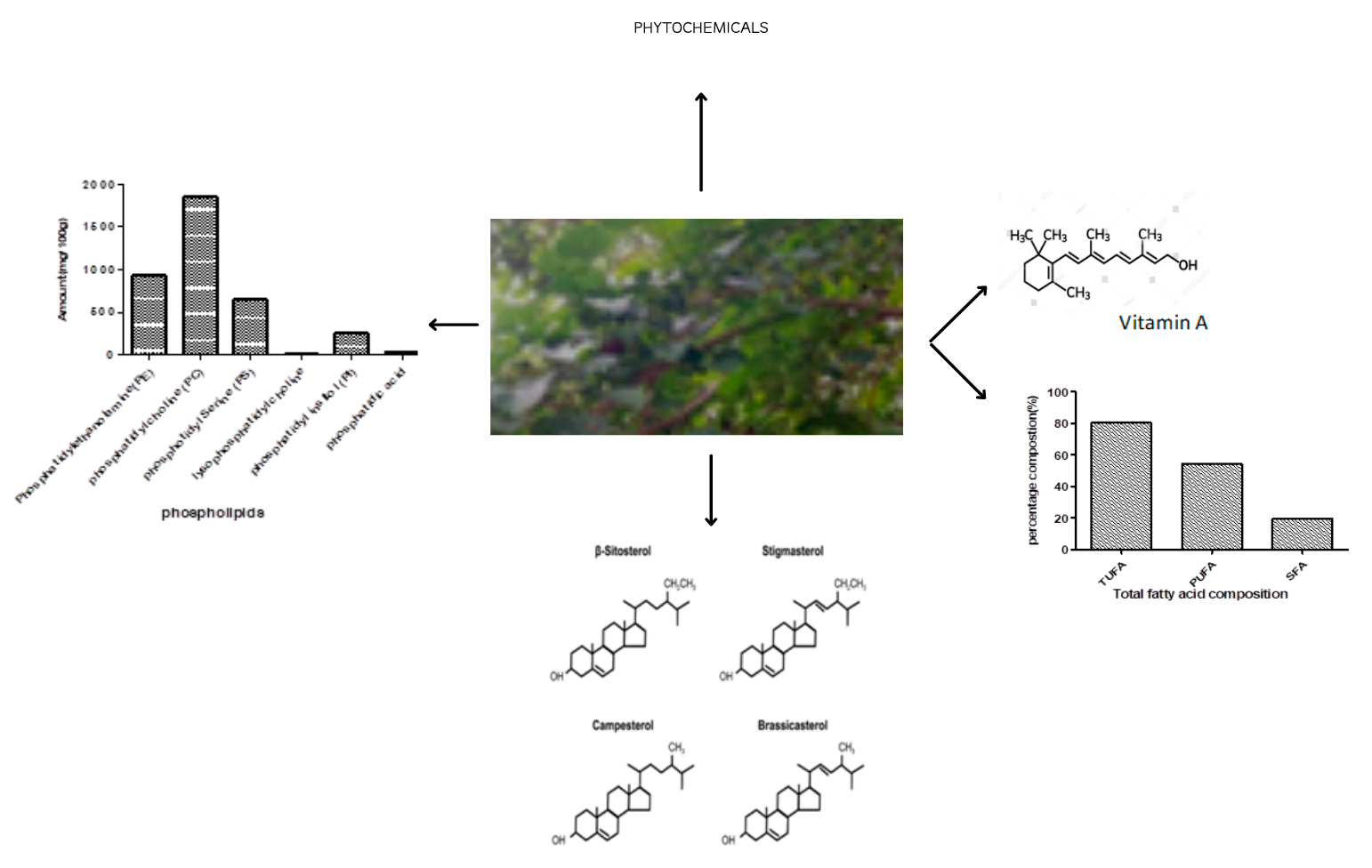
Abstract. Bioactive lipids are a group of lipids that can exhibit biological activity, prevent certain deadly diseases, and serve as sources of energy and nutrients for human’s daily activities. Thus, the need for their regular availability in the body system. The bioactive lipids (fat-soluble vitamins, phytosterol, and fatty acids), phospholipids, and phytochemicals present in Hura crepitans seed oil were investigated using standard analytical procedures. The nutritional, antinutritional, and physicochemical properties were also investigated. The result showed that the seed oil is rich in β sitosterol, campesterol, stigmasterol, and vitamin A. It also has a high percentage of linoleic acid and oleic acid, with a total unsaturated fatty acid of 80.31 %. The total phospholipid content was 3717.91 mg/100 g, with phosphatidylcholine and phosphatidylethanolamine being highly abundant in the seed oil. The sample has 1.63 and 2.714 mg/100 g of saponin and alkaloids, respectively, and 0.530 mg/100 g of oxalate. The oil has a high percentage of oil yield, ionization, and saponification values and a high amount of fat (37.5 %) and protein (27.31 %). Therefore, the oil from this underutilized plant could be of numerous applications in the pharmaceutical, cosmetics, and food industries as sources of important bioactive compounds.
Resumen. Los lípidos bioactivos son un grupo de lípidos que pueden exhibir actividad biológica, prevenir ciertas enfermedades mortales y servir como fuentes de energía y nutrientes para las actividades diarias del ser humano. De ahí la necesidad de su disponibilidad regular en el sistema corporal. Los lípidos bioactivos (vitaminas liposolubles, fitosterol y ácidos grasos), fosfolípidos y fitoquímicos presentes en el aceite de semilla de Hura crepitans se investigaron utilizando procedimientos analíticos estándar. También se investigaron las propiedades nutricionales, antinutricionales y fisicoquímicas. El resultado mostró que el aceite de semilla es rico en β sitosterol, campesterol, estigmasterol y vitamina A. También tiene un alto porcentaje de ácidos linoleico y oleico, con un total de ácidos grasos insaturados de 80.31 %. El contenido total de fosfolípidos fue de 3717.91 mg/100 g, siendo la fosfatidilcolina y la fosfatidiletanolamina, muy abundantes en el aceite de semilla. La muestra tiene 1.63 y 2.714 mg/100 g de saponina y alcaloides, respectivamente, y 0.530 mg/100 g de oxalato. El aceite tiene un alto porcentaje de rendimiento de aceite, valores de ionización y saponificación y una alta cantidad de grasa (37.5 %) y proteína (27,31 %). Por tanto, el aceite de esta planta subutilizada podría tener numerosas aplicaciones en las industrias farmacéutica, cosmética y alimentaria como fuente de importantes compuestos bioactivos.
Downloads
References
Olatunya, A. M.; Ajaja, A. K.; Akintayo, E. T. Sci. Study Res. Chem. Chem. Eng. Biotechnol. Food Ind. 2021, 22, 191–199.
Nagy, K.; Tiuca, I. D. in: Importance of Fatty Acids in Physiopathology of Human Body. In Catala A (ed) Fatty Acids; IntechOpen: London, 2017 ISBN 978-953-51-3302-5. DOI: https://doi.org/10.5772/67407
Olatunya, A. M.; Akintayo, E. T. Res. J. Chem. Environ. 2019, 23, 56–61.
Stone, N. J.; Robinson, J. G.; Lichtenstein, A. H.; Bairey Merz, C. N.; Blum, C. B.; Eckel, R. H.; Goldberg, A. C.; Gordon, D.; Levy, D.; Lloyd-Jones, D. M. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2014, 63, 2889–2934, http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.jacc.2013.11.002. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jacc.2013.11.002
Zhang, Y.; Zhang, T.; Liang, Y.; Jiang, L.; Sui, X. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2021, 69, 8929–8943. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jafc.1c01369
Ravisankar, P.; Reddy, A. A.; Nagalakshmi, B.; Koushik, O. S.; Kumar, B. V.; Anvith, P. S. IOSR J. Pharm. 2015, 5, 12–28.
https://www.verywellfit.com/fat-soluble-vitamins-2241991, accessed in September, 2022.
Olatunya, A. M.; Omojola, A.; Akinpelu, K.; Akintayo, E. T. Prev. Nutr. Food Sci. 2019, 24, 338–343. DOI: https://doi.org/10.3746/pnf.2019.24.3.338.
Jayaraman, T.; Kannappan, S.; Ravichandran, M. K.; Anuradha, C. V. Singapore Med. J. 2008, 49, 320.
Berger, A.; Jones, P. J.; Abumweis, S. S. Lipids Health Dis. 2004, 3, 1–19. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/1476-511X-3-5.
Abdulkadir, M. N.; Amoo, I. A.; Adesina, A. O. Int. J. Sci. Res. 2013, 2, 440–445.
Oyeleke, G. O.; Olayiwola, O. A.; Latona, D. F. IOSR J. Appl. Chem. 2012, 1, 10–13. DOI: https://doi.org/10.9790/5736-0111317
Udoh, A. P.; Udousoro, I. I.; Sunday, I. U. Niger. J. Chem. Res. 2019, 24, 15–25.
Fowomola, M. A.; Akindahunsi, A. A. J. Med. Food. 2007, 10, 159–164. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1089/jmf.2005.062
Raheja, R. K.; Kaur, C.; Singh, A.; Bhatia, I. S. J. Lipid Res. 1973, 14, 695–697. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/S0022-2275(20)36853-X
International Organisation for Standardization (ISO) Animal and Vegetable Fats and Oils- Determination of Composition of the Sterol Fraction - Method Using Gas Chromatography; International Organisation for Standardization: Switzerland, 1991.
Cocks, L. V.; Rede, C. V., in: Laboratory Handbook for Oil and Fat Analysts; London & New York: Academic Press, 1966.
Sebrell, W.; Harris, R. in: Descriptive Information on the Chemistry, Physicochemical Properties and Physiology of Vitamin A. In The Vitamins; Academic Press: New York, 1967; 1, 140.
AOAC Official Methods of Analysis of AOAC International; 18th ed.; AOAC International: Maryland USA, 2006.
Zeisel, S. H. J. Am. Coll. Nutr. 2004, 23, 621S-626S. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1080/07315724.2004.10719433.
Patel, D.; Witt, S. N. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2017, 2017, 4829180. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/4829180.
Küllenberg, D.; Taylor, L. A.; Schneider, M.; Massing, U. Lipids Health Dis. 2012, 11, 1–16. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/1476-511X-11-3.
Hartmann, P.; Szabó, A.; Eros, G.; Gurabi, D.; Horváth, G.; Németh, I.; Ghyczy, M.; Boros, M. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2009, 622, 58–64. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejphar.2009.09.012.
Eros, G.; Ibrahim, S.; Siebert, N.; Boros, M.; Vollmar, B. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2009, 11, 1–10. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/ar2651.
Salehi, B.; Quispe, C.; Sharifi-Rad, J.; Cruz-Martins, N.; Nigam, M.; Mishra, A. P.; Konovalov, D. A.; Orobinskaya, V.; Abu-Reidah, I. M.; Zam, W.; et al. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 11, 599959. DOI: https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2020.599959.
https://www.healthbenefitstimes.com/nutrition/campesterol, accessed in December, 2022.
Ezeh, I. E.; Umoren, S. A.; Essien, E. E.; Udoh, A. P. Ind. Crops Prod. 2012, 36, 94–99. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indcrop.2011.08.013.
Alabi, K. A.; Lajide, L.; Owolabi, B. J. Fountain J. Nat. Appl. Sci. 2013, 2, 32–37. DOI: https://doi.org/10.53704/fujnas.v2i2.28.
Okolie, P. N.; Uaboi-Egbenni, P. O.; Ajekwene, A. E. World J. Agric. Sci. 2012, 8, 359–365. DOI: https://doi.org/10.5829/idosi.wjas.2012.8.4.1119.
Liu, Q.; Zhang, J. Neurosci. Bull. 2014, 30, 331–345. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12264-013-1410-3.
Carrillo, C.; Cavia, M. D. M.; Alonso-Torre, S. R. Nutr. Hosp. 2012, 27, 1860–1865. DOI: https://doi.org/10.3305/nh.2012.27.6.6010.
Palomer, X.; Pizarro-Delgado, J.; Barroso, E.; Vázquez-Carrera, M. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2018, 29, 178–190. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tem.2017.11.009.
Akinyeye, R. O.; Olatunya, A. M. Med. Aromat. Plant Res. J. 2014, 2, 44–49.
Hamid, A. A. H.; Saleh, A.; Sidik, N. J.; Rahim, N.; Hadzir, N. M.; Ahmat, N. Malays. J. Chem. 2022, 24, 184–190.
Sharma, P.; Tyagi, A.; Bhansali, P.; Pareek, S.; Singh, V.; Ilyas, A.; Mishra, R.; Poddar, N. K. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2021, 150, 112075. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fct.2021.112075.
Eleazu, C. O.; Eleazu, K. C. Am. J. Food Technol. 2012, 7, 214–221. DOI: https://doi.org/10.3923/ajft.2012.214.221
Kurek, J. in: Alkaloids: Their Importance in Nature and Human Life; BoD–Books on Demand IntechOpen: UK, London, 2019. DOI: https://doi.org/10.5772/intechopen.85400
Heinrich, M.; Mah, J.; Amirkia, V. Molecules. 2021, 26, 1836. DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26071836.
Hassan, L. G.; Sokoto, A. M.; Ngaski, M. A.; Anka, S. A.; Chanchang, B. M.; Umar, K. J.; Ogbiko, C. Bayero J. Pure Appl. Sci. 2018, 11, 126–130. DOI: https://doi.org/10.4314/bajopas.v11i1.22.
Siener, R.; Bade, D. J.; Hesse, A.; Hoppe, B. J. Transl. Med. 2013, 11, 306. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/1479-5876-11-306.
Fredlund, K.; Isaksson, M.; Rossander-Hulthén, L.; Almgren, A.; Sandberg, A. S. J. Trace Elem. Med. Biol. 2006, 20, 49–57. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtemb.2006.01.003
Olatunya, A. M.; Olatunya, O. S.; Akintayo, E. T. Heliyon. 2017, 3, e00414. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2017. e00414. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2017.e00414
FAO Codex Standard of Fats and Oils from Vegetable Source; Food and Agriculture Organisation, 1999.
Dawodu, F. A. Electron. J. Environ. Agric. Food Chem. 2009, 8, 102–110.
Aremu, M. O.; Ibrahim, H.; Bamidele, T. O. Chem. Process Eng. Res. 2015, 32, 36–52.
Oyekunle, J. A. O.; Omode, A. A. Int. J. Food Prop. 2008, 11, 273–281. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1080/10942910701302598.
Umoren, S. A.; Ajibesin, K. K.; Bala, D. N. J. Nat. Appl. Sci. 2001, 1, 23–26.
Udoh, A. P.; Umoren, I. U.; Michael, E. P. J. Mater. Environ. Sci. 2020, 11, 157–165.
Ifijen, I.; Nkwor, A. Tanzan. J. Sci. 2020, 46, 817–827. DOI: https://doi.org/10.4314/tjs.v46i3.21

Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2024 Ayomadewa Mercy Olatunya, Adeolu Jonathan Adesina

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.
Authors who publish with this journal agree to the following terms:
- Authors retain copyright and grant the journal right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution License that allows others to share the work with an acknowledgement of the work's authorship and initial publication in this journal.
- Authors are able to enter into separate, additional contractual arrangements for the non-exclusive distribution of the journal's published version of the work (e.g., post it to an institutional repository or publish it in a book), with an acknowledgement of its initial publication in this journal.









