Synthesis and Evaluation of the Antifungal Sensibility of Novel Thienopyridine 1,2,3-Triazole Derivatives
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.29356/jmcs.v68i1.1917Keywords:
Triazole, Antifungal, Cycloaddition, Azide-enolate, ThienopyridineAbstract
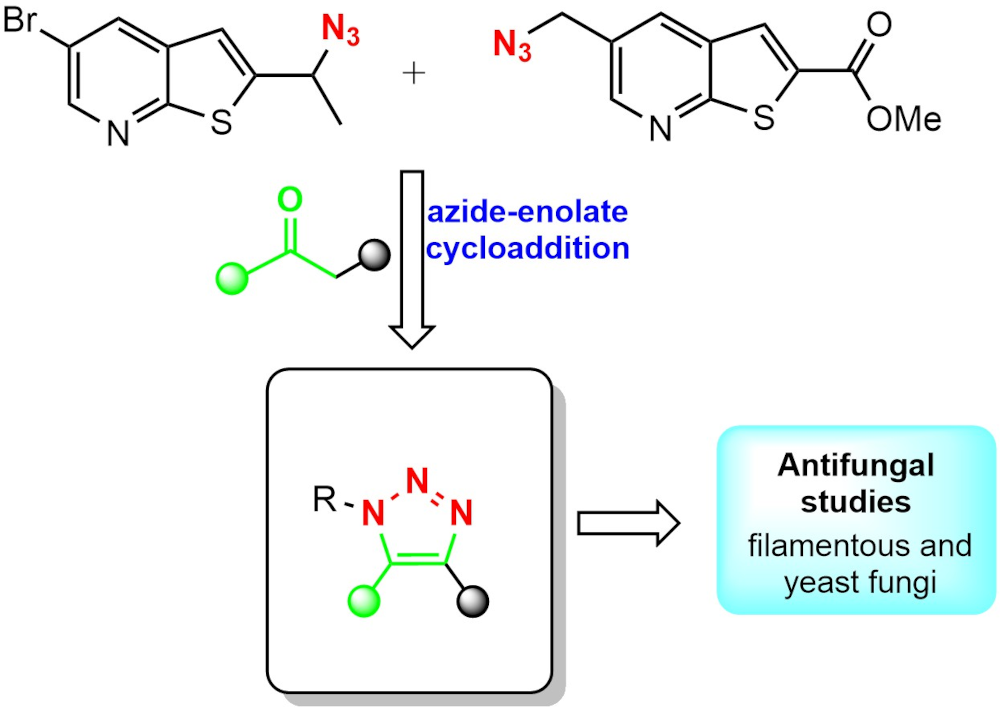
The family of compounds known as azoles are part of most of the antimicrobial drugs used for the treatment of infections. Within this family triazoles have been extensively studied as pharmacophores with very promising results. In this work, four novel trisubstituted 1,2,3-triazole compounds with a thienopyridine moiety (1a,b; 2a,b) were synthesized through an azide-enolate 1,3-dipolar cycloaddition. Their cheminformatic properties were calculated using simulation software available online such as Molinspiration, Molsoft, Osiris Property Explorer, pkCSM, SwissADME, and GUSA. The results provided important information which allowed us to consider the evaluation of the antifungal activity of these novel compounds. Therefore, the antifungal activity of these compounds was evaluated in vitro against four filamentous fungi, including Aspergillus fumigatus ATCC 16907, Trichosporon cutaneum ATCC 28592, Rhizopus oryzae ATCC 10329, and Mucor hiemalis ATCC 8690; as well as six species of yeast from the Candida genus; C. albicans ATCC 10231, C. utilis ATCC 9226, C. tropicalis ATCC 13803, C. parapsilosis ATCC 22019, C. glabrata ATCC 34138 and C. krusei ATCC 14243 The sensibility studies suggest that compounds 1b, 2a and 2b can be considered candidates for complementary biological studies due to the exhibited antifungal activity.
Resumen. La familia de compuestos conocidos como azoles forman parte de la mayoría de los medicamentos utilizados para el tratamiento de infecciones. Dentro de este grupo, los triazoles han sido extensamente estudiados como farmacóforos con resultados muy prometedores. En este trabajo, se sintetizaron cuatro nuevos 1,2,3-triazoles trisustituidos, que incluyen un anillo de tienopiridina en su estructura (1a,b; 2a,b) a través de una cicloadición 1,3-dipolar del tipo azida-enolato. Sus propiedades quimio informáticas fueron calculadas utilizando programas de simulación encontrados en línea como Molinspiration, Molsoft, Osiris Property Explorer, pkCSM, SwissADME y GUSAR. Los resultados obtenidos presentaron información importante que permitió considerar la evaluación de la actividad antifúngica de estos nuevos compuestos. Por lo tanto, esta actividad fue evaluada in vitro en cuatro cepas de hogos filamentosos, incluyendo Aspergillus fumigatus ATCC 16907, Trichosporon cutaneum ATCC 28592, Rhizopus oryzae ATCC 10329, and Mucor hiemalis ATCC 8690, así como también seis especies de levaduras del género Candida; C. albicans ATCC 10231, C. utilis ATCC 9226, C. tropicalis ATCC 13803, C. parapsilosis ATCC 22019, C. glabrata ATCC 34138 and C. krusei ATCC 14243. En estos estudios se observó que los compuestos 1a, 2a, y 2b pueden ser considerados para estudios posteriores de la evaluación biológica debido a la inhibición observada.
Downloads
References
Benhamou, R. I.; Bibi, M.; Steinbuch, K. B.; Engel, H.; Levin, M.; Roichman, Y.; Berman, J.; Fridman, M. ACS Chem. Biol. 2017, 12, 1769–1777. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/acschembio.7b00339.
(a) Zhang, Y.-Y.; Zhou, C.-H. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2011, 21, 4349–4352. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bmcl.2011.05.042. (b) Zhang, H.-Z.; Damu, G. L. V.; Cai, G.-X.; Zhou, C.-H. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2013, 64, 329–344. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejmech.2013.03.049.
(a) Guillon, R.; Pagniez, F.; Picot, C.; Hédou, D.; Tonnerre, A.; Chosson, E.; Duflos, M.; Besson, T.; Logé, C.; Le Pape, P. ACS Med. Chem. Lett. 2013, 4, 288–292. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/ml300429p. (b) Wang, S.; Zhang, L.; Jin, Y.; Tang, J. H.; Su, H.; Yu, S.; Ren, H. Asian J. Chem. 2014, 26, 2362–2364. DOI: https://doi.org/10.14233/ajchem.2014.15956.
Yao, B.; Ji, H.; Cao, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Zhu, J.; Lü, J.; Li, Y.; Chen, J.; Zheng, C.; Jiang, Y.; Liang, R.; Tang, H. J. Med. Chem. 2007, 50, 5293–5300. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/jm0701167.
(a) Lucas, S. C. C.; Moore, J. E.; Donald, C. S.; Hawkins, J. L. J. Org. Chem. 2015, 80, 12594–12598. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.joc.5b01735. (b) Elansary, A. K.; Moneer, A. A.; Kadry, H. H.; Gedawy, E. M. Arch. Pharm. Res. 2012, 35, 1909–1917. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12272-012-1107-6.
Leal, B.; Afonso, I. F.; Rodrigues, C. R.; Abreu, P. A.; Garrett, R.; Pinheiro, L. C. S.; Azevedo, A. R.; Borges, J. C.; Vegi, P. F.; Santos, C. C. C.; da Silveira, F. C. A.; Cabral, L. M.; Frugulhetti, I. C. P. P.; Bernardino, A. M. R.; Santos, D. O.; Castro, H. C. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2008, 16, 8196–8204. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bmc.2008.07.035.
(a) Fugel, W.; Oberholzer, A. E.; Gschloessl, B.; Dzikowski, R.; Pressburger, N.; Preu, L.; Pearl, L. H.; Baratte, B.; Ratin, M.; Okun, I.; Doerig, C.; Kruggel, S.; Lemcke, T.; Meijer, L.; Kunick, C. J. Med. Chem. 2013, 56, 264–275. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/jm301575n. (b) Verma, A. K.; Kotla, S. K. R.; Choudhary, D.; Patel, M.; Tiwari, R. K. J. Org. Chem. 2013, 78, 4386–4401. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/jo400400c.
Dayanandan, N.; Paulsen, J. L.; Viswanathan, K.; Keshipeddy, S.; Lombardo, M. N.; Zhou, W.; Lamb, K. M.; Sochia, A. E.; Alverson, J. B.; Priestley, N. D.; Wright, D. L.; Anderson, A. C. J. Med. Chem. 2014, 57, 2643–2656. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/jm401916j.
Jain, K. S.; Khedkar, V. M.; Arya, N.; Rane, P. V.; Chaskar, P. K.; Coutinho, E. C. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2014, 77, 166–175. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejmech.2014.02.066.
Serpi, M.; Ferrari, V.; Pertusati, F. J. Med. Chem. 2016, 59, 10343–10382. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jmedchem.6b00325.
McCarty, T. P.; White, C. M.; Pappas, P. G. Infect. Dis. Clin. North Am. 2021, 35, 389–413. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.idc.2021.03.007.
Pristov, K. E.; Ghannoum, M. A. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2019, 25, 792–798. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cmi.2019.03.028.
Earle, K.; Valero, C.; Conn, D. P.; Vere, G.; Cook, P. C.; Bromley, M. J.; Bowyer, P.; Gago, S. Virulence 2023, 14, 2172264. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1080/21505594.2023.2172264.
Khan, A. A.; Farooq, F.; Jain, S. K.; Golinska, P.; Rai, M. Microb. Ecol. 2022, 84, 1236–1244. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00248-021-01913-6.
Prakash, S.; Kumar, A. J. Basic Microbiol. 2023, 63, 119–127. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/jobm.202200334.
Dam, P.; Cardoso, M. H.; Mandal, S.; Franco, O. L.; Sağıroğlu, P.; Polat, O. A.; Kokoglu, K.; Mondal, R.; Mandal, A. K.; Ocsoy, I. Travel Med. Infect. Dis. 2023, 52, 102557. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tmaid.2023.102557.
Góralska, K.; Blaszkowska, J.; Dzikowiec, M. Infection 2018, 46, 443–459. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s15010-018-1152-2.
Ando, M.; Arima, K.; Yoneda, R.; Tamura, M. Am. Rev. Respir. Dis. 1991, 144, 765–769. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1164/ajrccm/144.4.765.
Hemalatha, K.; Selvin, J.; Girija, K. Asian J. Pharm. Res. 2018, 8, 125–132. DOI: https://doi.org/10.5958/2231-5691.2018.00022.9.
Hassan, M.; Ashraf, Z.; Abbas, Q.; Raza, H.; Seo, S.-Y. Interdiscip. Sci. Comput. Life Sci. 2018, 10, 68–80. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12539-016-0171-x.
Ramírez-Villalva, A.; González-Calderón, D.; Rojas-García, R. I.; González-Romero, C.; Tamaríz-Mascarúa, J.; Morales-Rodríguez, M.; Zavala-Segovia, N.; Fuentes-Benítes, A. Med. Chem. Comm. 2017, 8, 2258–2262. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1039/C7MD00442G.
Chandrasekaran, S. Click Reactions in Organic Synthesis, Ed., Wiley-VCH, 2016.
Vanjare, B. D.; Seok Eom, Y.; Raza, H.; Hassan, M.; Hwan Lee, K.; Ja Kim, S. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2022, 63, 116745. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bmc.2022.116745.
Rex, J. H. Reference Method for Broth Dilution Antifungal Susceptibility Testing of Yeats: Approved Standard, 3. ed., Ed., Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute, 2008.
Rex, J. H. Reference Method for Broth Dilution Antifungal Susceptibility Testing of Filamentous Fungi: Approved Standard, 2. ed., Ed., Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute, 2008.
Downloads
Additional Files
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2023 Alejandra Ramírez-Villalva, Claudia Cervantes-Rebolledo, Carlos A. González-González, Salvador Mastachi-Loza

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.
Authors who publish with this journal agree to the following terms:
- Authors retain copyright and grant the journal right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution License that allows others to share the work with an acknowledgement of the work's authorship and initial publication in this journal.
- Authors are able to enter into separate, additional contractual arrangements for the non-exclusive distribution of the journal's published version of the work (e.g., post it to an institutional repository or publish it in a book), with an acknowledgement of its initial publication in this journal.









