Determination of Sodium, Potassium, Calcium and Magnesium in Urine, Using Microwave Plasma - Atomic Emission Spectrometry and Multi-Energy Calibration
Determination by Na, K, Ca, Mg in Urine by MP-AES-MEC
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.29356/jmcs.v68i1.1906Keywords:
microwave plasma - atomic emission spectrometry (MP-AES), multi-energy calibration (MEC), urine, diabetesAbstract
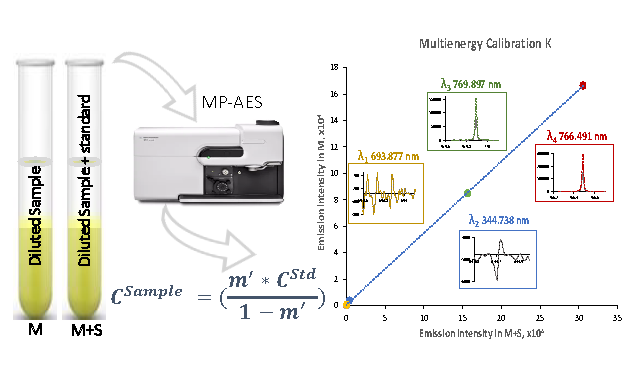
Microwave plasma - atomic emission spectrometry with multi-energy calibration (MP-AES-MEC) was used for the determination of four major elements in urine. In the family of atomic emission spectrometry, the distinctive features of MP-AES are: (i) nitrogen-based toroidal-shape plasma; (ii) good plasma tolerance to total solids; (iii) exceptionally low operating cost. On the other hand, due to relatively low plasma temperature, this technique is susceptible to spectral interferences and sample-to-sample fluctuating baseline is typical limitation, if previous acid digestion is not performed. MEC is a non-conventional quantification method, not requiring baseline correction and it has been selected in this work to achieve reliable determination of Na, K, Ca and Mg in simply diluted urine. The principle underlying MEC is the proportionality between signal intensity and analyte concentration, occurring at any emission line for given element. Accordingly, for each sample, only two solutions were prepared likewise in the one-point standard addition and two analytical runs were performed, yet four experimental points were generated for calibration according with the number of emission lines utilized. Based on the results obtained by analyzing urines from different subjects, the sample dilution fold was selected to adjust the analyte concentration below half of the calibration range (150 for K, 200 for Na, 50 for Ca and 25 for Mg), while the addition of standard was done roughly doubling natural concentration in the diluted sample. The evaluated instrumental limits of detection were: 0.009 ± 0.005 mg L-1 for K, 0.131 ± 0.011 mg L-1 for Na, 0.050 ± 0.014 mg L-1 for Ca and 0.059 ± 0.010 mg L-1 for Mg (five replicates in different days). Each analysis was performed in triplicate yielding percentage relative standard deviation £ 11 %. The percentage recoveries calculated taking the results obtained in acid-digested samples by external calibration as reference values were in the range: 83.3-102 % for K, 88.4-110 % for Na, 82.9-113 % for Ca and 85.8-108 % for Mg. The capability of the proposed MP-AES-MEC procedure for monitoring four elements in different clinical conditions was demonstrated by analyzing ten urines from diabetic patients and ten from non-diabetic control subjects; statistical differences between these two groups was found for Na and K.
Resumen. La espectrometría de emisión atómica con excitación en plasma de microondas y con el método de calibración multi-energéa (MP-AES-MEC) fueron empleados para la determinación de cuatro elementos mayoritarios en orina. Dentro de la familia de técnicas de espectrometría de emisión atómica, las características distintivas de MP-AES son las siguientes: (i) uso de plasma de nitrógeno con geometría toroidal; (ii) buena tolerancia del plasma a sólidos totales; (iii) excepcionalmente bajo costo de operación. Por otra parte, debido a la relativamente baja temperatura del plasma, una típica limitación de esta técnica es que es susceptible a interferencias espectrales y la fluctuación de línea base entre muestras si estas no son digeridas previamente. El método MEC es un método de cuantificación no-convencional, el cual no requiere corrección de linea base y fue seleccionado en este trabajo para lograr la determinación confiable de Na, K, Ca and Mg después de una simple dilución de orina. MEC se sustenta en la proporcionalidad entre intensidad de la señal y la concentración del analito existente en cualquier linea de emisión de un elemento dado. Para cada una de las muestras, se prepararon dos soluciones, igual que en el método de un punto de adición de estándar y se realizaron dos corridas analíticas, pero se generaron cuatro puntos experimentales para la calibración, correspondientes a cuatro líneas de emisión seleccionadas por elemento. Con base en los resultados obtenidos analizando orinas de diferentes sujetos, el factor de dilución de la muestra fue seleccionado para ajustar la concentración del analito por debajo de la mitad del rango de calibración (150 para K, 200 para Na, 50 para Ca, 25 para Mg), mientras que la adición de estándar se realizó subiendo aproximadamente al doble la concentración natural en la muestra diluida. Los límites de detección instrumentales fueron: 0.009 ± 0.005 mg L-1 para K, 0.131 ± 0.011 mg L-1 para Na, 0.050 ± 0.014 mg L-1 para Ca, 0.059 ± 0.010 mg L-1 para Mg (con base en cinco réplicas realizadas en diferentes días). Cada análisis se realizó por triplicado, obteniéndose valores de desviación estándar relativa £ 11 %. Los porcentajes de recuperación calculados considerando los resultados obtenidos en muestras digeridas con ácido mediante calibración externa convencional como valores de referencia fueron los siguientes: 83.3-102 % para K, 88.4-110 % para Na, 82.9-113 % para Ca, 85.8-108 % para Mg. La capacidad del procedimiento MP-AES-MEC para monitorear cuatro elementos en diferentes condiciones clínicas se demostró analizando orinas de pacientes diabéticos y orinas de sujetos en un grupo control, encontrándose diferencias estadísticamente significativas para Na y K.
Downloads
References
Maciel, A. T.; Vitorio, D.; Osawa, E. A. Front. Med. 2022, 9, 2186. DOI: https://doi.org/10.3389/fmed.2022.912877.
Moulin, F.; Ponte, B.; Pruijm, M.; Ackermann, D.; Bouatou, Y.; Guessous, I.; Ehret, G.; Bonny, O.; Pechère-Bertschi, A.; Staessen, J. A.; Paccaud, F.; Pierre-Yves, M.; Burnier, M.; Vogt, B.; Devuyst, O.; Bochud, M. Kidney Int. 2017, 92, 1536-1543.
Tietz, N. W. Tietz Clinical Guide to Laboratory. Elsevier, St. Louis MO, 1995.
Bazydlo, L. A.; Needham, M.; Harris, N. S. Lab. Med. 2014, 45, e44-e50.
Wróbel, K.; Wróbel, K.; López-de-Alba, P. L.; López-Martínez, L. Anal. Lett. 1997, 30, 717-737.
Parentoni, L. S.; Pozeti, R. C. S.; Figueiredo, J. F.; Faria, E. C. D. J. Braz. Patol. Med. Lab. 2001, 37, 235-238.
Agatemor, C.; Beauchemin, D. Anal. Chim. Acta 2011, 706, 66-83.
Krejcova, A.; Cernohorsky, T.; Curdova, E. J. Anal. At. Spectrom. 2001, 16, 1002–1005.
Balaram, V. Microchem. J. 2020, 159, 105483.
Espinoza Cruz, T. L.; Guerrero Esperanza, M.; Wrobel, K.; Barrientos, E. Y.; Acevedo-Aguilar, F. J.; Wrobel, K. Spectrochim. Acta Part B. 2020, 164, 105754.
Gonzalez Ibarra, A. A.; Yanez Barrientos, E.; Wrobel, K.; Corrales Escobosa, A. R.; Wrobel, K. J Plant Nutr. 2022, 1-17. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1080/01904167.2022.2071733.
Jung, M. Y.; Kang, J. H.; Choi, Y. S.; Lee, J. Y.; Park, J. S. Food Chem. 2019, 274, 20-25.
Virgilio, A.; Gonçalves, D. A.; McSweeney, T.; Neto, J. A. G.; Nóbrega, J. A.; Donati, G. L. Anal. Chim. Acta. 2017, 982, 31-36.
Jones, W. B.; Donati, G. L.; Calloway Jr, C. P.; Jones, B. T. Anal. Chem. 2015, 87, 2321-2327.
Barros, A. I.; Pinheiro, F. C.; Nóbrega, J. A. Anal. Methods. 2019, 11, 3401-3409.
Machado, R. C.; Silva, A. B. S.; Donati, G. L.; Nogueira, A. R. A. J. Anal. At. Spectrom. 2018, 33, 1168-1172.
Donati, G. L.; Amais, R. S. J. Anal. At. Spectrom. 2019, 34, 2353-2369.
Tognoni, E.; Hidalgo, M.; Canals, A.; Cristoforetti, G.; Legnaioli, S.; Salvettia, A.; Palleschi, V. Spectrochim. Acta Part B. 2007, 62, 435-443.
Virgilio, A.; Gonçalves, D. A.; McSweeney, T.; Neto, J. A. G.; Nóbrega, J. A.; Donati, G. L. Anal. Chim. Acta. 2017, 982, 31-36.
Guerrero-Esperanza, M.; Wrobel, K.; Wrobel, K.; Ordaz-Ortiz, J. J. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2023, 115, 104963.
Afridi, H. I.; Kazi, T. G.; Kazi, N.; Jamali, M. K.; Arain, M. B.; Jalbani, N.; Sarfaraz, R. A.; Shah, A.; Kandhro, G. A.; Shah, A. Q.; Baig, J. A. Biol. Tr. Elem. Res. 2008, 124, 206–224.
Liamis, G.; Evangelos, L.; Fotios, B.; Moses, E. World J. Clin. Cases. 2014, 2, 488–496.
Kim, H. W.; Park, J. T.; Yoo, T. H.; Lee, J.; Chung, W.; Lee, K. B.; Chae, D. W.; Ahn, C.; Kang, S. W.; Choi, K. H.; Han, S. H. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2019, 14, 330-340.
Araki, S.; Haneda, M.; Koya, D.; Kondo, K.; Tanaka, S.; Arima, H.; Kume, S.; Nakazawa, J.; Chin-Kanasaki, M.; Ugi, S.; Kawai, H.; Araki, H.; Uzu, T.; Maegawa, H. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2015, 10, 2152-2158.
Ekinci, E. I.; Clarke, S.; Thomas, M. C.; Moran, J. L.; Cheong, K.; MacIsaac, R. J.; Jerums, G. Diabetes Care 2011, 34, 703-709.
Perez, V.; Chang, E. T. Adv. Nutr. 2014, 5, 712-741.
Siddiqui, K.; Nahla, B.; Scaria Joy, S. The Scientific World Journal 2014, ID 461591. DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/461591.
Hattori, H.; Hirata, A.; Kubo, S.; Nishida, Y.; Nozawa, M.; Kawamura, K.; Hirata, T.; Kubota, Y.; Sata, M.; Kuwabara, K.; Higashiyama, A.; Kadota, A.; Sugiyama, D.; Miyamatsu, N.; Miyamoto, Y.; Okamura, T. Int. J. Environ. Pub. Health 2020, 17, 5811. DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17165811.
Carnevale, V.; Romagnoli, E.; D'Erasmo, E. Diabetes/Metab. Res. Rev. 2004, 20, 196-204.
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2023 Tania Lizeth Espinoza Cruz, Kazimierz Wrobel, Eunice Yanez Barrientos, Alma Rosa Corrales Escobosa, Ma Eugenia Garay-Sevilla, Francisco Javier AcevedoAguilar, Katarzyna Wrobel

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.
Authors who publish with this journal agree to the following terms:
- Authors retain copyright and grant the journal right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution License that allows others to share the work with an acknowledgement of the work's authorship and initial publication in this journal.
- Authors are able to enter into separate, additional contractual arrangements for the non-exclusive distribution of the journal's published version of the work (e.g., post it to an institutional repository or publish it in a book), with an acknowledgement of its initial publication in this journal.









