Development of a Composite Cu(II)-Selective Potentiometric Sensor Based on a Thiourea Derivative Symmetric Schiff Base
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.29356/jmcs.v68i2.1884Keywords:
potentiometric sensor, copper(II)-selective electrode, all-solid-state sensor, copper(II) determination, symmetric Schiff base, thiourea derivativeAbstract
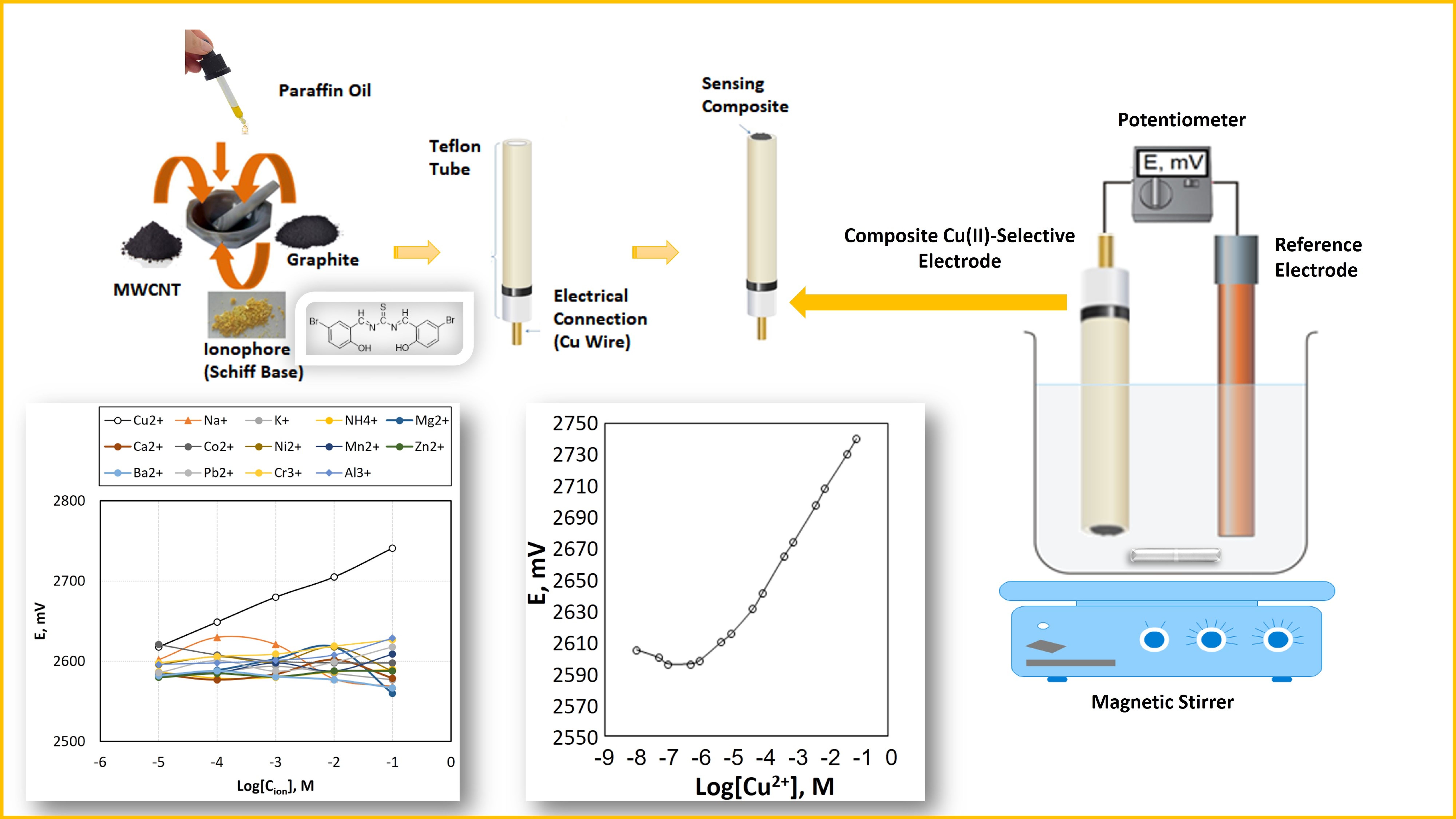
Abstract. In the present study, initially, a thiourea derivative symmetric Schiff base, (1E,3E)-1,3-bis(5-bromo-2-hydroxybenzylidene)thiourea, was synthesized and characterized by FTIR and SEM-EDX analysis. In addition, an all-solid-state composite Cu(II)-selective potentiometric sensor based on this synthesized compound as an electroactive substance was constructed. Optimization studies indicated that the composition of the optimum sensing composite exhibiting the best potentiometric characteristics was 3.0% Schiff base, 5.0 % multi-walled carbon nanotube (MWCNT), 20.0 % paraffin oil and 72.0% graphite by mass. The proposed sensor displayed a linear response in the concentration range of 5.0×10-6-1.0×10-1 M with a slope of 31.1 mV/decade and a detection limit of 5.0×10-7 M. The proposed sensor exhibited a fairly selective, stable (potential drift: 1.85 mV/h), and rapid (<10 s) response towards Cu(II) ions. Because of the magnitude of its potential drift, the sensor should be recalibrated along the analysis time at least half an hour apart. The sensor can employed safely in the samples with pHs in the range of 2.0-6.5. The lifetime of the fresh sensor surface was determined as 2 weeks. The most important advantage of the sensor is that the sensing composite surface is renewable (at least 10 times) and thus the sensor can be used many times for a long period of time. The analytical applications of the sensor were executed successfully by using the electrode in the potentiometric titration of Cu(II) ions with EDTA as an indicator electrode, in the direct determination of Cu(II) contents of spiked water samples, and in the determination of (w/w) Cu% content of a Turkish coin.
Resumen. En este estudio, inicialmente, se sintetizó una base de Schiff simétrica derivada de la tiourea, (1E,3E)-1,3-bis(5-bromo-2-hidroxibenciliden)tiourea, y se caracterizó mediante análisis FTIR y SEM-EDX. Además, se construyó un sensor potenciométrico selectivo de Cu(II) de estado sólido basado en este compuesto sintetizado como sustancia electroactiva. Los estudios de optimización indicaron que la composición del compuesto sensor óptimo que presentaba las mejores características potenciométricas fue con 3 % de base de Schiff, 5 % de nanotubos de carbono multipared (MWCNT), 20 % de aceite de parafina y 72 % de grafito en masa. El sensor propuesto mostró una respuesta lineal en el rango de concentración de 5×10-6 a 1×10-1 M con una pendiente de 31 mV/década y un límite de detección de 5×10-7 M. El sensor propuesto mostró una respuesta bastante selectiva, estable (deriva de potencial: 1.85 mV/h) y rápida (<10 s) hacia los iones Cu(II). Debido a la magnitud de su deriva de potencial, el sensor debe recalibrarse a lo largo del tiempo de análisis con un intervalo de al menos media hora. El sensor puede emplearse con seguridad en las muestras con pH en el rango de 2.0 a 6.5. La vida útil de la superficie fresca del sensor se determinó en 2 semanas. La ventaja más importante del sensor es que la superficie del compuesto sensor es renovable (al menos 10 veces) y, por tanto, el sensor puede utilizarse muchas veces durante un largo periodo de tiempo. Las aplicaciones analíticas del sensor se llevaron a cabo con éxito, utilizando el electrodo en la valoración potenciométrica de iones Cu(II) con EDTA como electrodo indicador, en la determinación directa del contenido de Cu(II) de muestras de agua enriquecidas y en la determinación del contenido (p/p) de Cu% de una moneda turca.
Downloads
References
Jaishankar, M.; Tseten, T.; Anbalagan, N.; Mathew, B.B.; Beeregowda, K.N. Interdiscip. Toxicol. 2014, 7, 60–72. DOI: https://doi.org/10.2478/intox-2014-0009.
Richardson, H.W., in: Handbook of Copper Compounds and Applications. Marcel Dekker, New York, 1997. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1201/9781482277463
Institute of Medicine (US) Panel on Micronutrients. Dietary Reference Intakes for Vitamin A, Vitamin K, Arsenic, Boron, Chromium, Copper, Iodine, Iron, Manganese, Molybdenum, Nickel, Silicon, Vanadium, and Zinc. Washington (DC): National Academies Press (US); 2001. 7, Copper. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK222312/
Hordyjewska, A.; Popiolek, L.; Kocot, J. Biometals. 2014, 27, 611–621. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10534-014-9736-5.
Schaefer, M.; Gitlin, G. D. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 1999, 276, G311–G314. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpgi.1999.276.2.G311.
Ali, A.; Shen, H.; Yin, X. Anal. Chim. Acta. 1998, 369, 215–223. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/S0003-2670(98)00252-9.
Bruno, P.; Caselli, M.; Daresta, B. E.; de Gennaro G.; de Pinto, V.; Ielpo, P.; Placentino C. M. J. Liq. Chromatogr. Relat. Technol. 2007, 30, 477–487. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1080/10826070601093762.
Yaseen, S.; Qasim, B.; Al-lame, N. Egypt. J. Chem. 2021, 64, 673–691. DOI: https://doi.org/10.21608/ejchem.2019.13907.1861.
Babayeva, K.; Demir, S.; Andac, M. J. Taibah Univ. Sci., 2017, 11, 808–814. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtusci.2017.02.001.
Arpa Şahin, Ç.; Tokgöz, İ. Anal. Chim. Acta 2010, 667, 83–87. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2010.04.012.
Bagherian, G.; Arab Chamjangali, M.; Shariati Evari, H.; Ashrafi, M. J. Anal. Sci. Technol. 2019, 10, 3. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s40543-019-0164-6.
Neri, T. S.; Rocha, D. P.; Muñoz, R. A. A.; Coelho, N. M. M.; Batista, A. D. Microchem. J., 2019, 147, 894–898. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.microc.2019.04.014.
Erdoğan, H. Düzce Üniversitesi Bilim ve Teknoloji Dergisi. 2021, 9, 1469–1482. DOI: https://doi.org/10.29130/dubited.884511.
Poosinuntakul, N.; Parnklang, T.; Sitiwed, T.; Chaiyo, S.; Kladsomboon, S.; Chailapakul, O.; Apilux, Microchem. J., 2020, 158, 105101. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.microc.2020.105101.
Clark, A. C.; Zhang, X.; Kontoudakis, N. Aust. J. Grape Wine Res. 2020, 26, 399–409. https://doi.org/10.1111/ajgw.12450.
Vasimalai, N.; Prabhakarn, A.; Abraham John, S. Nanotechnology. 2013, 24, 505503. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1088/0957-4484/24/50/505503.
He, L.; Bao, Z.; Zhang, K.; Yang, D.; Sheng, B.; Huang, R.; Zhao, T.; Liang, X.; Yang, X.; Yang, A.; Zhang, C.; Cui, P.; Zapien, J. A.; Zhou, H. Microchim. Acta. 2018, 185, 511. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-018-3043-8.
Chrastný, V.; Komárek, M. Chem. Pap. 2009, 63, 512–519. DOI: https://doi.org/10.2478/s11696-009-0057-z.
Yilmaz, V.; Arslan, Z.; Hazer, O.; Yilmaz, H. Microchem. J. 2014, 114, 66–72. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.microc.2013.12.002.
Ferreira, S. L.; Santos, H. C.; Ferreira, J. R.; Araujo, N. M.; Costa, A. C.; Jesus, D. S. J. Braz. Chem. Soc. 1998, 9, 525–530. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1590/S0103-50531998000600004.
Basheer, C.; Lee, H. K.; Electrophoresis. 2007, 28, 3520–3525. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/elps.200700248.
Ergün, E. G. C., Kenar, A. Turk. J. Chem. 2018, 42, 257–263. DOI: https://doi.org/10.3906/kim-1703-83.
Uesugi, K.; Kumagai, T.; Wada, S. Microchem. J. 1986, 33, 204-–208. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/0026-265X(86)90056-1.
Musa, D.; Sha’Ato, R.; Eneji, I.; Itodo, A. Open Access Library Journal. 2018, 5, 1–14. DOI: https://doi.org/10.4236/oalib.1104446.
Topcu, C.; Lacin, G.; Yilmaz, V.; Coldur, F.; Caglar, B.; Cubuk, O.; Isildak, I. Anal.Lett. 2018, 51, 1890–1910. DOI: 10.1080/00032719.2017.1395035. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1080/00032719.2017.1395035
Mohammadi, S.; Taher, M. A.; Beitollahi, H. Russ. J. Electrochem. 2021, 57, 1175–1185. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S1023193521100098.
Cui, Y.; Yang, C., in: 3rd International Conference on Bioinformatics and Biomedical Engineering, 2009, 1–4. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1109/ICBBE.2009.5162761.
Romero-Cano, L. A.; Zárate-Guzmán, A. I.; Carrasco-Marín, F.; González-Gutiérrez, L. V. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2019, 837, 22–29. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jelechem.2019.02.005.
Chong, J. M., Nor, A. Y., Shahrul Ainliah, A. A. Chemosensors. 2021, 9, 157. DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors9070157.
Khalil, S.; El-Sharnouby, M. Chemosensors. 2021, 9, 86. DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors9050086.
Mashhadizadeh, M. H.; Sheikhshoaie, I. Talanta. 2003, 60, 73–80. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/S0039-9140(03)00036-5.
Ganjali, M. R.; Emami, M.; Rezapour, M.; Shamsipur, M.; Maddah, M.; Salavat-Niasari, M.; Hosseini, M.; Talebpour, Z. Anal. Chim. Acta. 2003, 495, 51–59. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/S0003-2670(03)00921-8.
Malinowska, E. Analyst. 1990, 115, 1085–1087. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1039/AN9901501085.
Ganjali, M. R.; Roubollahi, A.; Mardan, A. R.; Hamzeloo, M.; Mogimi, A.; Shamsipur, M. Microchem. J. 1998, 60, 122–133. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1006/mchj.1998.1642.
Su, C. C.; Chang, M. C.; Liu, L. K. Anal. Chim. Acta. 2001, 423, 261–267. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/S0003-2670(00)01375-1.
Gupta, V. K.; Mangla, R.; Aggarwal, S. Electroanalysis. 2002, 14, 1127. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/1521-4109(200208)14:15/16<1127::AID-ELAN1127>3.0.CO;2-7
Bhat, V. S.; Ijeri, V. S.; Srivastava, A. K. Sens. Actuat. 2004, 99, 98–105. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2003.11.001.
Amini, M. K.; Mazloum, M.; Ensafi, A. A. Fresenius J. Anal. Chem. 1999, 364, 690–693. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s002160051415.
Srivastava, S. K.; Gupta, V. K.; Jain, S. Anal. Chem. 1996, 68, 1272–1275. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/ac9507000.
Ardakani, M. M.; Dehghani, H.; Jalayer, M. S.; Zare, H. R. Anal. Sci. 2004, 20, 1667–1672. DOI: https://doi.org/10.2116/analsci.20.1667.
Yagi, Y.; Masaki, S.; Iwata, T.; Nakane, D.; Yasui, T.; Yuchi, A. Anal. Chem. 2017, 89, 3937–3942. DOI: 10.1021/acs.analchem.6b03754. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.analchem.6b03754
Jain, A. K.; Singh, R. K.; Jain, S.; Raisoni, J. Transition Met. Chem. 2008, 33, 243–249. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11243-007-9022-2.
Schiff, H. Justus Liebigs Ann. Chem. 1864, 131, 118–119. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/jlac.18641310113.
Issaadi, S.; Douadi, T.; Zouaoui, A.; Chafaa, S.; Khan, M. A.; Bouet, G. Corros. Sci. 2011, 53, 1484–1488. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.corsci.2011.01.022.
Lashgari, M.; Arshadi, M. R.; Miandari, S. Electrochim. Acta. 2010, 55, 6058–6063. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2010.05.066.
Papic, S.; Koprivanac, N.; Grabaric, Z.; Parac-Osterman, D. Dyes Pigment. 1994, 25, 299–240. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/0143-7208(94)85012-7.
Dhar, D. N.; Taploo, C. L. J. Sci. Ind. Res. 1982, 41, 501–506.
Gupta, V. K.; Goyal R. N.; Pal, M. K.; Sharma, R. A. Anal. Chim. Acta. 2009, 653, 161–166. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2009.09.008.
Chaudhari, T. D.; Subnis, S. S. Bull. Haskine Inst. 1986, 4, 85–88.
Sharma, P. K.; Dubey, S. N. Ind. J.Chem. 2002, 33A, 1113–1115.
Ali, M. M.; Jesmin, M.; Salam, S. M. A.; Khanam, J. A.; Islam, M. F.; Islam, M. N. J. Sci. Res. 2009, 1, 641–646. DOI: https://doi.org/10.3329/jsr.v1i3.2585.
Fontana, R.; Marconi, P. C. R.; Caputo, A.; Gavalyan, V.B. Molecules. 2022, 27, 2740. DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27092740.
Irawan, C.; Islamiyati, D.; Utami, A.; Putri, I. D.; Perdana Putri, R.; Wibowo, S. Orient. J. Chem. 2020, 36, 577–580. DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.13005/ojc/360332. DOI: https://doi.org/10.13005/ojc/360332
Chaudhary, A.; Singh, A. Int. J. Curr. Res. Med. Sci. 2017, 3, 60–74. DOI: http://dx.doi.org10.22192/ijcrms.2017.03.06.009. DOI: https://doi.org/10.22192/ijcrms.2017.03.06.009
Crespo, G. A.; Macho, S.; Rius, F. X. Anal. Chem. 2008, 80, 1316–1322. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/ac071156l.
Parra, E. J.; Crespo, G. A.; Riu, J.; Ruiz, A.; Rius, F. X. Analyst. 2009, 134, 1905–1910. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1039/B908224G.
Xinde, Z.; Chenggang, W.; Zhiping, L.; Zhifeng, L.; Zishen, W. Synth. React. Inorg. Met.-Org. Chem. 1996, 26, 955–966. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1080/00945719608004346.
Buck, R. P.; Lindner, E. Pure Appl. Chem. 1994, 66, 2527–2536. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1351/pac199466122527.
Umezawa, Y.; Buhlmann, P.; Umezawa, K.; Tohda, K.; Amemiya, S. Pure Appl. Chem. 2000, 72, 1851–2082. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1351/pac200274060923. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1351/pac200072101851

Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2024 Ozden Yildirim, Fatih Çoldur, Cihan Topcu, Bulent Caglar

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.
Authors who publish with this journal agree to the following terms:
- Authors retain copyright and grant the journal right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution License that allows others to share the work with an acknowledgement of the work's authorship and initial publication in this journal.
- Authors are able to enter into separate, additional contractual arrangements for the non-exclusive distribution of the journal's published version of the work (e.g., post it to an institutional repository or publish it in a book), with an acknowledgement of its initial publication in this journal.