Experimental and Numerical Comparison of Dispersion and Sorption of Cr(VI) on Maize Cane Biomass
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.29356/jmcs.v68i2.1859Keywords:
Numerical simulation, hydrodynamic dispersion, sorption, porous mediaAbstract
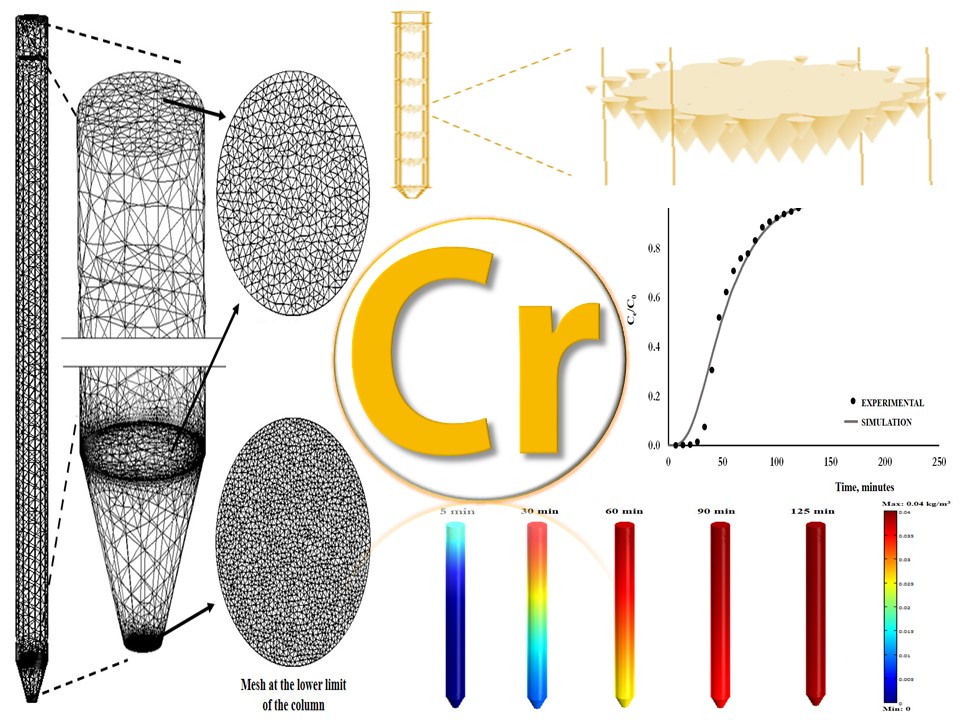
Abstract. Computational and theoretical modelling has become an important tool for the characterization, development, and validation of packed beds. Relevant breakthrough curves would provide much valuable information on designing a fixed bed adsorption process in field applications. In this study, the hydrodynamic properties involved in the Navier–Stokes flow equation, such as velocity, pressure, and permeability, in a packed bed were investigated. Experiments in natural porous media such as maize cane biomass for determining the sorption of Cr(VI) are compared with numerical simulations. The relevant ordinary partial equations were solved in COMSOL Multiphysics Software friendly and efficiently. The close agreement between the experimental and numerical results suggests that the theoretical model of advection-hydrodynamic dispersion can be used to model the transport of Cr(VI) in unsaturated porous media composed of maize cane biomass.
Resumen. El modelado computacional y teórico se ha convertido en una herramienta importante para la caracterización, desarrollo y validación de lechos empacados. Las curvas de avance relevantes proporcionarían información muy valiosa sobre el diseño de un proceso de adsorción de lecho fijo en aplicaciones de campo. En este estudio, se investigaron las propiedades hidrodinámicas involucradas en la ecuación de flujo de Navier-Stokes, como la velocidad, la presión y la permeabilidad, en un lecho empacado. Los experimentos en medios porosos naturales como la biomasa de caña de maíz para determinar la sorción de Cr(VI) se comparan con simulaciones numéricas. Las ecuaciones parciales ordinarias relevantes se resolvieron en COMSOL Multiphysics Software de manera amigable y eficiente. La estrecha concordancia entre los resultados experimentales y numéricos sugiere que el modelo teórico de dispersión hidrodinámica por advección puede usarse para modelar el transporte de Cr(VI) en medios porosos no saturados compuesta por biomasa de caña de maíz.
Downloads
References
Asuquo, E.D.; Martin, A. D. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2016, 4, 4207-4228.
Economou-Eliopoulos, M.; Frei, R.; Atsarou, C. Catena. 2014, 122, 216-228.
Polowczyk, I.; Urbano, B. F.; Rivas, B. L.; Bryjak, M.; Kabay, N. Chem. Eng. J. 2016, 284, 395-404.
Wang, S.; Choi, J. H. Applied Mathematical Modelling. 2013, 37, 102-111.
Owalude, S. O.; Tella, A. C. J. Basic Appl. Sci. 2016, 5, 377-388.
Usman, L. U.; Bharat, K. A.; Nakshatra, B. S.; Sushmita, B. J. Mol. Liq. 2022, 354, 118833.
Kavitha, B.; Deepa, R.; Sivakumar, S. Materials Today Sustainability. 2022, 18, 100124.
Ullah, I.; Nedeem, R.; Iqbal, M.; Manzoor, Q. Ecological Engineering. 2013, 60, 99-107.
Marín-Allende, M. J.; Romero-Guzmán, E. T.; Ramírez-García, J. J.; Reyes-Gutiérrez, L. R. Part. Sci. Technol. 2016, 35, 704–711.
COMSOL, Earth Science Module User’s Guide, ©1998–2008 by COMSOL AB.
Esfandian, H.; Samady-Maybodi, A.; Khoshandam, B.; Parvini, M. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2017, 75, 164-173.
Bird, R. B.; Stewart, W. E.; Lightfoot, E. N., in: Fenómenos de transporte. Editorial reverte, España, 2003, 4-29.
Qian, W.; Wu, J.; Yang, L.; Lin, X.; Chen, Y.; Chen X. Chem. Eng. J. 2012, 197, 424-434.
Basak, P. J. Irrig. Drain. Div., Am. Soc. Civ. Eng. 1977, 103, 459.
Volesky, B. Hydrometallurgy. 2003, 71, 179-190.
Naja, G. Volesky, B. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2006, 40, 3996-4003.
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2024 María de Jesús Marín-Allende, Elizabeth Teresita Romero-Guzmán, Carlos Enrique Alvarado-Rodríguez, Lázaro Raymundo Reyes-Gutiérrez

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.
Authors who publish with this journal agree to the following terms:
- Authors retain copyright and grant the journal right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution License that allows others to share the work with an acknowledgement of the work's authorship and initial publication in this journal.
- Authors are able to enter into separate, additional contractual arrangements for the non-exclusive distribution of the journal's published version of the work (e.g., post it to an institutional repository or publish it in a book), with an acknowledgement of its initial publication in this journal.









