On the Pro-oxidant Activity of Curcumin in Lipid Media: A Theoretical Study
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.29356/jmcs.v66i3.1727Keywords:
Oxidative stress, kinetic, DFT, curcumin, pro-oxidantAbstract
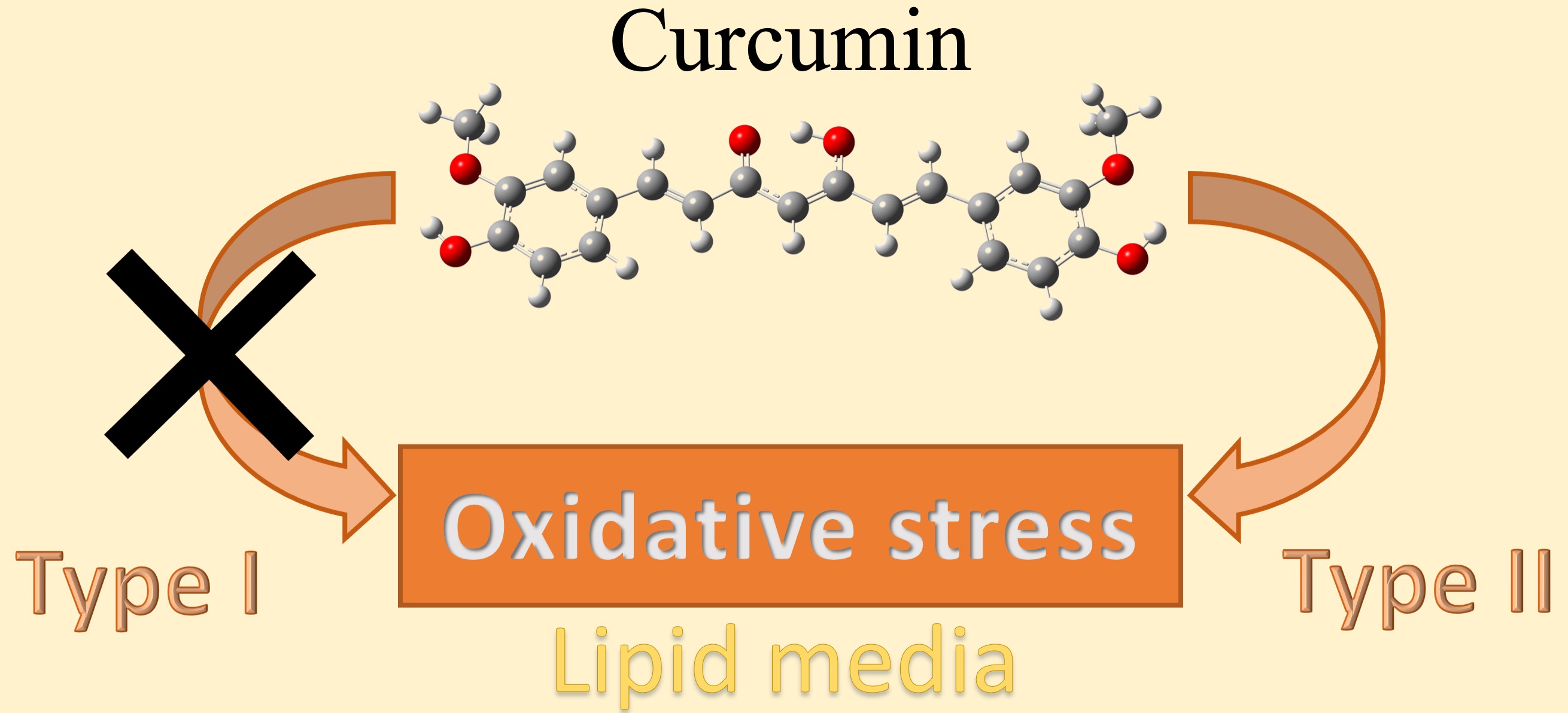
Abstract. In the scientific literature can be found experimental evidence on the pro-oxidant capacity of curcumin through its photosensitizer property; it has been related to biological activities such as the antibacterial and antitumor observed in this molecule; however, the pro-oxidant evidence, little is known about the reaction mechanism involved in the photosensitizing property of curcumin. Thus, it was carried out a study on the photosensitizer capacity of curcumin in lipid media employs the density functional theory. The thermodynamic results showed the remarkable capacity of curcumin to reduce itself through the single electron transfer mechanisms. The kinetic results showed that mechanism type II is the main mechanism, and it showed a total reaction rate constant calculated of 1.69 x 1010 M-1 s-1 on the photosensitizer capacity of curcumin in lipid media. The reactions related to the mechanism type I was not feasible; hence, these reactions were not contributed to the photosensitizer capacity of curcumin in lipid media. Finally, these results support the idea that the curcumin in lipid media is a pro-oxidant molecule capable of generating the 1O2 molecule and, consequently, could cause oxidative damage through the photooxidative reactions.
Resumen. En la literatura se puede encontrar evidencia experimental sobre la capacidad pro-oxidante de la curcumina a traves de su propiedad fotosensibilizadora, esta propiedad se ha relacionado con la actividad antibacteriana y antitumoral observada en esta molécula; a pesar de la evidencia experimental, poco se conoce sobre el mecanismo de reacción involucrado en la propiedad fotosensibilizadora de la curcumina. De acuerdo con lo anterior, se llevó a cabo el estudio de la capacidad fotosensibilizadora de curcumina en medio lipídico, empleando la teoría de funcionales de la densidad. Los resultados termodinámicos mostraron la extraordinaria capacidad de la curcumina para reducirse a través de reacciones de transferencia electrónica. Los resultados cinéticos mostraron que el mecanismo tipo II es el más importante en la capacidad fotosensibilizadora de la curcumina en medio lipídico, mostrando una constante de velocidad de 1.69 x 1010 M-1 s-1. La reacción relacionada con el mecanismo tipo I no se lleva a cabo; por lo tanto, estas reacciones no contribuyen en la capacidad fotosensibilizadora de la curcumina en medio lipídico. Finalmente, estos resultados apoyan la idea de que la curcumina en medio lipídico es una molécula prooxidante capaz de inducir el estrés oxidativo por la generación de la molécula de 1O2 y de esta forma, generar daño oxidativo a estructuras celulares importantes a través de reacciones de fotooxidación.
Downloads
References
Galano, A.; Mazzone, G.; Alvarez-Diduk, R.; Marino, T.; Alvarez-Idaboy, J. R.; Russo, N. Annu. Rev. Food Sci. Technol. 2016, 7, 335-52. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-food-041715-033206
Nimse, S. B.; Pal, D. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 27986-28006. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1039/C4RA13315C
Medina, M. E.; Galano, A.; Alvarez-Idaboy, J. R. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2015, 17, 4970-4976. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1039/C4CP05688D
Medina, M. E.; Galano, A.; Trigos, A. J. Phys. Org. Chem. 2015, 28, 504-508. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/poc.3449
Nikitaki, Z.; Hellweg, C. E.; Georgakilas, A. G.; Ravanat, J.-L. Front. Chem. 2015, 3, 35. DOI: https://doi.org/10.3389/fchem.2015.00035
Rahal, A.; Kumar, A.; Singh, V.; Yadav, B.; Tiwari, R.; Chakraborty, S.; Dhama, K. BioMed. Res. Int. 2014, 761264. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/761264
Schweitzer, C.; Schmidt, R. Chem. Rev. 2003, 103, 1685-1758. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/cr010371d
Espinoza, C.; Trigos, A.; Medina, M. E. J. Phys. Chem. A 2016, 120, 6103-6110. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jpca.6b03615
Medina, M. E.; Meza-Menchaca, T.; Trigos, A. J. Phys. Org. Chem. 2021, 34, e4167. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/poc.4167
Yu, S.; Wang, M.; Guo, X.; Qin, R. Med. Sci. Monit. 2018, 24, 2280-2286. DOI: https://doi.org/10.12659/MSM.909557
Khalil, O. A. K.; Oliveira, O. M. M.; Vellosa, J. C. R.; Quadros, A. U.; Dalposso, L. M.; Karam, T. K.; Mainardes, R. M.; Khalil, N. M. Food Chem. 2012, 133, 1001-1005. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2012.02.009
López-Lázaro, M. Mol. Nutr. Food. Res. 2008, 52, S103-S127.
Yang, F.; Lim, G. P.; Begum, A. N.; Ubeda, O. J.; Simmons, M. R.; Ambegaokar, S. S.; Chen, P.; Kayed, R.; Glabe, C. G.; Frautschy, S. A.; Cole, G. M. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 5892-5901. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M404751200
Oliveira, E. F.; Tosatic, J. V.; Tikekard, R. V.; Monteiroc, A. R.; Nitin, N. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2018, 137, 86-94. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.postharvbio.2017.11.014
Czekaj, R.; Majka, J.; Magierowska, K.; Sliwowski, Z.; Magierowski, M.; Pajdo, R.; Ptak-Belowska, A.; Surmiak, M.; Kwiecien, S.; Brzozowski, T. J. Gastroenterol. 2018, 53, 618-630. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00535-017-1385-3
Galano, A.; Álvarez-Diduk, R.; Ramírez-Silva, M. T.; Alarcón-Ángeles, G.; Rojas-Hernández, A. Chem. Phys. 2009, 363, 13-23. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemphys.2009.07.003
Jakubczyk, K.; Druzga, A.; Katarzyna, J.; Skonieczna-Zydecka, K. Antioxidants. 2020, 9, 1092. DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox9111092
Sharifi-Rad, J.; Rayess, Y. E.; Rizk, A. A.; Sadaka, C.; Zgheib, R.; Zam, W.; Sestito, S.; Rapposelli, S.; Neffe-Skocińska, K.; Zielińska, D.; Salehi, B.; Setzer, W. N.; Dosoky, N. S.; Taheri, Y.; Beyrouthy, M. E.; Martorell, M.; Ostrander, E. A.; Suleria, H. A. R.; Cho, W. C.; Maroyi, A.; Martins, N. Front. Pharmacol. 2020, 11, 1021. DOI: https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2020.01021
Hewlings, S. J.; Kalman, D. S. Foods. 2017, 6, 92. DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/foods6100092
Lagunes, I.; Trigos, A. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B Biol. 2015, 145, 30-34. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jphotobiol.2015.02.014
Lee, H.-J.; Kang, S.-M.; Jeong, S.-H.; Chung, K.-H.; Kim, B.-I. Photodiagnosis Photodyn. Ther. 2017, 20, 116-119. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pdpdt.2017.09.003
Xu, C.; Wang, M.; Guo, W.; Sun, W.; Liu, Y. Front. Oncol. 2021, 20, 672490.
Polat, E.; Kang, K. Biomedicines. 2021, 9, 584. DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines9060584
Eyring, H. J. Chem. Phys. 1935, 3, 107-115. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1063/1.1749604
Evans, M. G.; Polanyi, M. Trans. Faraday Soc. 1935, 31, 875-894. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1039/tf9353100875
Truhlar, D. G.; Hase, W. L.; Hynes, J. T. J. Phys. Chem. 1983, 87, 2664-2682. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/j100238a003
Marcus, R. A. Annu. Rev. Phys. Chem. 1964, 15, 155-196. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.pc.15.100164.001103
Marcus, R. A. Rev. Mod. Phys. 1993, 65, 599-610. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1103/RevModPhys.65.599
Marcus, R. A. Pure Appl. Chem. 1997, 69, 13-30. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1351/pac199769010013
Nelsen, S. F.; Weaver, M. N.; Luo, Y.; Pladziewicz, J. R.; Ausman, L. K.; Jentzsch, T. L.; O’Konek, J. J. J. Phys. Chem. A. 2006, 110, 11665-11676. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/jp064406v
Collins, F. C.; Kimball, G. E. J. Colloid Sci. 1949, 4, 425-437. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/0095-8522(49)90023-9
Smoluchowski, M. Z. Phys. Chem. 1917, 92, 129-168. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1515/zpch-1918-9209
Truhlar, D. G. J. Chem. Educ. 1985, 62, 104-106. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/ed062p104
Einstein, A. Ann. Phys. (Berlin, Ger.) 1905, 322, 549-560. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/andp.19053220806
Stokes, G. G. Mathematical and physical Papers; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, U.K., 1903; Vol. 3 (esp. section IV).
Frisch, M. J.; Trucks, G. W.; Schlegel, H. B.; Scuseria, G. E.; Robb, M. A.; Cheeseman, J. R.; Scalmani, G.; Barone, V.; Mennucci, B.; Petersson, G. A.; et al. Gaussian 09, Revision B.01; Gaussian, Inc.: Wallingford, CT, 2009.
Marenich, A. V.; Cramer, C. J.; Truhlar, D. G. J. Phys. Chem. B. 2009, 113, 6378-6396. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/jp810292n
Tiezza, M. D.; Hamlin, T. A.; Bickelhaupt, F. M.; Orian, L. Chem. Med. Chem. 2021, 16, 3763-3771. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/cmdc.202100546
Boulebd, H.; Pereira, D. M.; Khodja, I. A.; Hoa, N. T.; Mechler, A.; Vo, Q. V. J. Mol. Liq. 2022, 346, 118277. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2021.118277
Hoa, N. T.; Hang, D. T. N.; Hieu, D. P.; Truong, H. V.; Hoang, L. P.; Mechler, A.; Vo, Q. V. R. Soc. Open Sci. 2021, 8, 210626. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1098/rsos.210626
Zhao, Y.; Truhlar, D. G. J. Phys. Chem. A. 2008, 112, 1095-1099. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/jp7109127
Galano, A.; Alvarez-Idaboy, J. R. J. Comput. Chem. 2014, 35, 2019-2026. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/jcc.23715
Galano, A.; Alvarez-Idaboy, J. R. J. Comput. Chem. 2013, 34, 2430-2445. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/jcc.23409
Yang, I.; Jin, S. M.; Kang, J.; Ramanathan, V.; Kim, H. M.; Suh, Y. D.; Kim, S. K. Bull. Korean Chem. Soc. 2011, 32, 3090-3093. DOI: https://doi.org/10.5012/bkcs.2011.32.8.3090

Downloads
Additional Files
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2022 Manuel E. Medina, Ángel Trigos

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.
Authors who publish with this journal agree to the following terms:
- Authors retain copyright and grant the journal right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution License that allows others to share the work with an acknowledgement of the work's authorship and initial publication in this journal.
- Authors are able to enter into separate, additional contractual arrangements for the non-exclusive distribution of the journal's published version of the work (e.g., post it to an institutional repository or publish it in a book), with an acknowledgement of its initial publication in this journal.









