Enzyme Inhibitory and Mutagenicity Guided Investigation of Selected Medicinal Plants in Different Solvents
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.29356/jmcs.v66i3.1721Keywords:
Alpha glucosidase, acetylcholinesterase, solvent fractions , mutagenicityAbstract
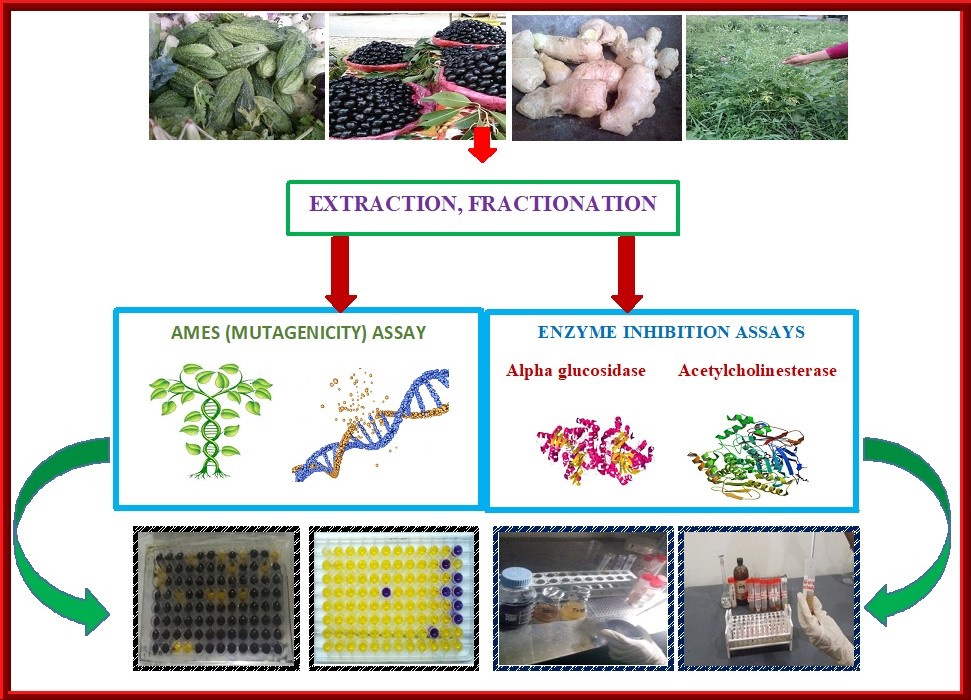
Abstract. Plants have developed the foundation of traditional systems of medicine that have been in existence for thousands of years due to the presence of vital bioactive constitutes. Aside from antioxidant, antimicrobial, hypoglycemic, anticarcinogenic and numerous activities of natural products, limited recognition regarding diverse therapeutic attributes of medicinal plants such as Momordica charantia, Syzygium cumini, Zingiber officinale and Parthenium hysterophorus exist. The current study was designed to explore the enzyme inhibitory (alpha glucosidase and acetylcholinesterase) and cytotoxicity capacities of solvent fractions of these indigenous plants. All the samples had inhibitory effects on alpha glucosidase, but methanolic fractionations of each plant exhibited greater inhibitory efficacy against enzyme action compared to other fractionations. Except for the methanolic extract of Parthenium hysterophorus (33.25 ± 0.43), all other studied plants, viz. Zingiber officinale (50.33 ± 0.99), S. cumini (73.91 ± 1.05) and Momordica charantia (72.30 ± 1.17) indicated more than 50% alpha glucosidase inhibitory potentials. Acetylcholinesterase inhibitions (percentage inhibition) by different fractions of P. hysterophorus, Z. officinale, S. cumini and M. charantia were in the range of 0.23 ± 0.14 to 11.40 ± 0.26, 13.04 ± 0.11 to 44.05 ± 0.76, 4.21 ± 0.15 to 71.55 ± 0.80 and 1.03 ± 0.09 to 50.12 ± 0.82 respectively. Among all studied plants, Momordica charantia, Syzygium cumini, and Zingiber officinale were non-mutagenic. Although slight variation in bioactivities was observed, all the botanical extracts are excellent sources of bioactive constituents with the potential to inhibit alpha glucosidase and acetylcholinesterase. Further research in this regard is warranted involving bioassay-guided assessment.
Resumen. Las plantas han desarrollado la base de los sistemas tradicionales de medicina que existen desde hace miles de años debido a la presencia de constituyentes bioactivos vitales. Además de las numerosas actividades antioxidantes, antimicrobianas, hipoglucemiantes, anticancerígenas y de los productos naturales, existe un reconocimiento limitado con respecto a los diversos atributos terapéuticos de las plantas medicinales como Momordica charantia, Syzygium cumini, Zingiber officinale y Parthenium hysterophorus. El estudio actual fue diseñado para explorar las capacidades inhibidoras de enzimas (alfa glucosidasa y acetilcolinesterasa) y citotóxicas de las fracciones solventes de estas plantas autóctonas. Todas las muestras tuvieron efectos inhibidores sobre la alfa glucosidasa, pero los fraccionamientos metanólicos de cada planta exhibieron una mayor eficacia inhibidora contra la acción enzimática en comparación con otros fraccionamientos. A excepción del extracto metanólico de Parthenium hysterophorus (33,25 ± 0,43), todas las demás plantas estudiadas, a saber. Zingiber officinale (50,33 ± 0,99), S. cumini (73,91 ± 1,05) y Momordica charantia (72,30 ± 1,17) indicaron más del 50 % de potenciales inhibidores de la alfa glucosidasa. Las inhibiciones de acetilcolinesterasa (porcentaje de inhibición) por diferentes fracciones de P. hysterophorus, Z. officinale, S. cumini y M. charantia estuvieron en el rango de 0,23 ± 0,14 a 11,40 ± 0,26, 13,04 ± 0,11 a 44,05 ± 0,76, 4,21 ± 0,15 a 71,55 ± 0,80 y 1,03 ± 0,09 a 50,12 ± 0,82 respectivamente. Entre todas las plantas estudiadas, Momordica charantia, Syzygium cumini y Zingiber officinale no fueron mutagénicas. Aunque se observó una ligera variación en las bioactividades, todos los extractos botánicos son excelentes fuentes de constituyentes bioactivos con el potencial de inhibir la alfa glucosidasa y la acetilcolinesterasa. Se justifica una mayor investigación a este respecto que involucre una evaluación guiada por bioensayo.
Downloads
References
Anand, U.; Tudu, C.K.; Nandy, S.; Sunita, K.; Tripathi, V.; Loake, G.J.; Dey, A.; Proćków. J Ethnopharmacol. 2022, 284, 114744. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jep.2021.114744
Ajayi, E. I. O.; Modo, E.U.; Kiakubu, O.T.; Molehin, O.R. Diabetes, 2019, 5, 545-558. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-813822-9.00035-7
Vinayagam, R.; Xiao, J., Xu, B. Phytochem. Rev. 2017, 16, 535-553. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11101-017-9496-2
Rahman, M.; Uddin, M.; Reza, A.S.M.; Tareq, A.M.; Emran, T.B.; Simal-Gandara, J. Plants. 2021, 10(4), 729. DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/plants10040729
Arya, A.; Abdullah, M.A.; Haerian, B.S.; Mohd, M.A. J. Chem. 2012, 9, 1196-1205. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1155/2012/103760
Hussain, F.; Shahid, M.; Zulfiqar, S.; Hafeez, J. J Mex Chem Soc. 2021, 6, 469-479. DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.29356/jmcs.v65i4.1532 DOI: https://doi.org/10.29356/jmcs.v65i4.1532
Alu’datt, M. H.; Rababah, T.; Alhamad, M.N.; Gammoh, S., Ereifej, K.; Johargy, A.; Kubow, S.; Almajwal, A.M.; Rawashdeh, M. Int. J. Food Prop. 2016, 19, 1303-1316. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1080/10942912.2015.1063066
Rahman, U. A.; Choudhary, M.I.; Thomsan, W.J. Int. J. Pharm. Tech. Res. 2001, 4, 369-374.
Khan, S.; Iqbal, I.; Ahmed, N.; Jamil, A. J. Animal Plant. Sci. 2015, 25, 1451-1456.
Seetaloo, A. D.; Aumeeruddy, M.Z.; Kannan, R.R.; Mahomoodally, M.F. S. Afr. J. Bot. 2019, 120, 3-24. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sajb.2018.05.015
Poovitha, S.; Parani, M. BMC Complement. Alt. Med. 2016, 16, 185. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s12906-016-1085-1
Sallau, A. B.; Yakubu, R.N.; Abdullahi, S.; Salihu, A.; Boniface, B,Y. Vitae. 2018, 25, 148-153. DOI: https://doi.org/10.17533/udea.vitae.v25n3a05
Nhiem, N. X.; Kiem, P.V.; Minh, C.V.; Ban, N.K.; Cuong, N.X.; Tung, N.H. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2010, 58, 720-724. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1248/cpb.58.720
Alagesan, K.; Thennarasu, P.; Kumar, V.; Sankarnarayanan, S.; Balsamy, T. Int. J. Pharm. Sci. Res. 2012, 3, 316-322.
Shinde, J.; Taldone, T.; Barletta, M.; Kunaparaju, N.; Hu, B.; Kumar, S. Carbohydr. Res. 2008, 343, 1278-1281. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carres.2008.03.003
Laoufi, H.; Benariba, N.; Adjdir, S.; Djaziri, R. J. Appl. Pharm. Sci. 2017, 7, 191-198
Kumar, N.; Goel, N. Biotechnol. Rep. 2019, 24, e00370. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.btre.2019.e00370
Bhatia, A.; Singh, B.; Arora, R.; Arora, S. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2019, 19, 74-82. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s12906-019-2482-z
Ajiboye, B. O.; Ojo, O.A.; Akuboh, O.S.; Okesola, M.A.; Idowu, O.T.; Oyinloye, B.E.; Talabi, J.Y. Jordan J. Biol. Sci. 2018, 11, 163-169.
Hafiz, Z. Z.; Amin, M.; James, J.R.M.; Teh, L.K.; Salleh, M.Z.; Adenan, M.I. Molecules. 2020, 25, 892. DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25040892
Kumaran, K. R.; Ahad, M.A.; Rawa, M.S.A.; Wahab, H.; Hassan, Z. Aust. Herb. Insight. 2019, 1, 022-027.
Al-Snafi, A. E. 2015. Int. J. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2015, 5, 177-192.
Oliveira, C.; Bagetta, D.; Cagide, F.; Teixeira, J.; Amorim, R.; Silva, T.; Garrido, J.; Remião, F.; Uriarte, E.; Oliveira, P.J.; Alcaro, S. Eur. J. Med. Chem.2019, 174, 116-129. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejmech.2019.04.026
Oboh, G.; Ademiluyi, A.O; Akinyemi, A.J. Exp. Toxicol. Pathol. 2012, 64, 315-319. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.etp.2010.09.004
El-Akabawy, G.; El-Kholy, W. Ann. Anat. 2014, 196, 119-128. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aanat.2014.01.003
Nagarani, G.; Abirami, A.; Siddhuraju, P. Food Sci. Human Wellness. 2014, 3, 36-46. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fshw.2014.02.003
Pitchakarn, P.; Suzuki, S.; Ogawa, K.; Pompimon, W.; Takahashi, S.; Asamoto, M.; Limtrakul, P.; Shirai, T. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2012, 50, 840-847. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fct.2012.01.009
Li, R. S.; Wang, X.B.; Hu, X.J.; Kong, L.Y. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2013, 23, 2636-2641. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bmcl.2013.02.095
Darusman, L. K.; Wahyuni, T.W.; Alwi. F. J. Biol. Sci. 2013, 13, 412-416. DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.3923/jbs.2013.412.416 DOI: https://doi.org/10.3923/jbs.2013.412.416
Alikatte, K. L.; Akondi, B.R.; Yerragunta, V.G.; Veerareddy, P.R.; Palle, S. Brain Dev. 2012, 34, 844-851. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.braindev.2012.02.008
Khan, H.; Amin, S.; Kamal, M.A.; Patel, S. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2018, 101, 860-870. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2018.03.007
Kong, X. P.; Liu, E.Y.L.; Chen, Z.C.; Xu, M.L.; Yu, A.X.D.; Wu, Q.Y.; Xia, Y.J.; Duan, R.; Dong, T.T.X.; Tsim, K.W.K. Molecules. 2019, 24, 4567. DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24244567
Balkrishna, A.; Pokhrel, S.; Tomer, M.; Verma, S.; Kumar, A.; Nain, P.; Gupta, A.; Varshney, A. Molecules. 2019, 24, 4175. DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24224175
Zahin, M.; Ahmad, I.; Aqil, F. Drug Chem. Toxicol. 2017, 40, 146-153. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1080/01480545.2016.1188397
Razak, M. F. A.; Aidoo, K.E. Asian J. Pharm. Clin. Res. 2011, 4, 23-27.
Roy, D. C.; Shaik, M. J. Med. Plants Stud. 2013, 1, 126-141.
Sahrawat, A.; Sharma, J.; Rahul, S.N.; Tiwari, S.; Rai, D.V. Int. J. Curr. Microbiol. App. Sci. 2018, 7, 3548-3557. DOI: https://doi.org/10.20546/ijcmas.2018.711.407
Abdillahi, H. S.; Verschaeve, L.; Finnie, J. F.; Staden, J.V. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2012, 139, 728-738. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jep.2011.11.044
Gautam, S.; Saxena, S.; Kumar, S. J. Food Chem. Nanotechnol. 2016, 2, 97-114. DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.17756/jfcn.2016-018 DOI: https://doi.org/10.17756/jfcn.2016-018
Birla, D.; Sonali, K.A.; Shaikh, A.; Khan, A.; Ghosi, A.; Pardeshi, P. Int. J. Health Med. 2017, 5, 81-3.
Abudayyak, M.; Nath, E.O.; Ozhan, G. Turk. J. Med. Sci. 2015, 45, 496-506. DOI: doi:10.3906/sag-1401-153 DOI: https://doi.org/10.3906/sag-1401-153
Plengsuriyakarn, T.; Viyanant, V.; Eursitthichai, V.; Tesana, S.; Chaijaroenkul, W.; Itharat, A.; Bangchang, K.N. Asian J. Cancer Prev. 2012, 13, 4597-4606. DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.7314/APJCP.2012.13.9.4597 DOI: https://doi.org/10.7314/APJCP.2012.13.9.4597
Stanisiere, J.; Mousset, P.Y.; Lafay, S. Foods. 2018, 7, 50-78. DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/foods7040050
Bekoe, E. O.; Agyare, C.; Boakye, Y.D.; Baiden, B.M.; Asase, A.; Sarkodie, J.; Nettey, H.; Adu, F.; Otu, P.B.; Agyarkwa, B.; Amoateng, P.; Asiedu-Gyekye, I.; Nyarko, A. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2020, 248, 112309. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jep.2019.112309
Islam, S.; Jalaluddin, M. Am. J. Food Sci. Health. 2019, 5, 25-31.
Adewumi, O. O.; Oladele, E.O.; Taiwo, I.A. Niger. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 3, 62-68. DOI: https://doi.org/10.36263/nijest.2019.01.0107
Aydin, G.; Kaya, E. Int. J. Tradit. Complement. Med. Res. 2020, 1, 79-95.
Ramos, A.; Rivero, R.; Victoria, M.C.; Visozo, A.; Piloto, J.; Garcıa, A. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2001, 77, 25-30. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/S0378-8741(01)00257-4
Khan, M. S.; Qais, F.A.; Ahmad, I.; Hussain, A.; Alajmi, M.F. Toxicol. Res. 2018, 7, 156-171. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1039/c7tx00269f

Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2022 JAVARIA HAFEEZ, FATMA HUSSAIN, MUHAMMAD SHAHID, AYSHA SAMEEN

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.
Authors who publish with this journal agree to the following terms:
- Authors retain copyright and grant the journal right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution License that allows others to share the work with an acknowledgement of the work's authorship and initial publication in this journal.
- Authors are able to enter into separate, additional contractual arrangements for the non-exclusive distribution of the journal's published version of the work (e.g., post it to an institutional repository or publish it in a book), with an acknowledgement of its initial publication in this journal.









