In-silico Studies of Phytochemicals of Ashwagandha, Harsingar, Meethi neem and Tulsi Against Covid-19
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.29356/jmcs.v66i2.1643Keywords:
COVID-19, SARS-CoV-2, Indian herbal plants, phytochemical compounds, docking, ADMET analysisAbstract
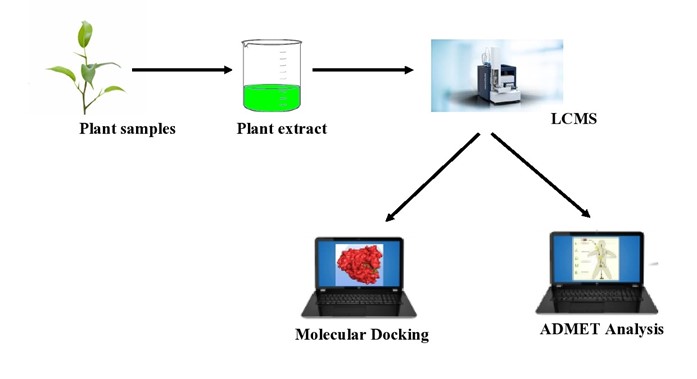
Abstract. The ongoing coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) has become a global pandemic and risk to the healthcare system of almost every nation around the world. The endocytic pathway has been considered as a key factor in viral infection. In the case of CoVs, several investigations have shown that these viruses mainly follow the clathrin-mediated endocytic pathway. As a result, inhibiting the clathrin-mediated endocytic pathway might be a useful therapeutic approach. In this study, bioactive components of Harsingar, Meethi neem, Tulsi and Ashwagandha extract was analyzed by HR-LCMS and among them 55 phytochemical compounds were selected based on antiviral and steroidal properties. 55 phytochemical compounds of four Indian herbal plants were used to analyze their binding with clathrin protein associated with COVID -19. Based on the molecular docking as well as ADMET analysis, Ashwagandha, Harsingar, Meethi neem and Tulsi were identified as potential herbal medicine candidates. We have found that the inhibition potentials of the Ashwagandha, Harsingar, Meethi neem and Tulsi are very promising with no side effects.
Resumen. La enfermedad provocada por el coronavirus 2019 (COVID-19) se ha convertido en una pandemia global y pone en riesgo a los sistemas de salud de casi cualquier nación en el mundo. Se ha considerado que la ruta endocítica es un factor clave en la infección viral. En el caso de CoVs, varias investigaciones han mostrado que estos virus siguen la ruta endocítica mediada por la clatrina. Como resultado, inhibir la ruta endocítica mediada por la clatrina puede ser una propuesta terapéutica útil. En este estudio, se analizaron extractos de componentes bioactivos de Harsingar, Meethi neem, Tulsi y Ashwagandha por HR-LCMS y entre ellos se seleccionaron 55 compuestos fitoquímicos basados en sus propiedades antivirales y esteroidales. Estos 55 compuestos obtenidos de 4 plantas herbáceas se utilizaron para analizar su interacción con la proteína clatrina asociada al COVID-19. Basados en el acoplamiento molecular así como en el análisis ADMET, se determinó que Harsingar, Meethi neem, Tulsi y Ashwagandha son candidatos potenciales de medicinas herbáceas. Hemos encontrado que los potenciales de inhibición de Harsingar, Meethi neem, Tulsi y Ashwagandha son muy promisorios y no muestran efectos colaterales.
Downloads
References
Huang, C.; Wang, Y.; Li, X.; Ren, L.; Zhao, J.; Hu, Y.; Zhang, L.; Fan, G.; Xu, J.; Gu, X. The Lancet. 2020, 395, 497-506. DOI: 10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30183-5 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30183-5
Li, Q.; Guan, X.; Wu, P.; Wang, X.; Zhou, L.; Tong, Y.; Ren, R.; Leung, K. S.; Lau, E. H.; Wong, J. Y. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020. DOI: 10.1056/NEJMoa2001316 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa2001316
Guo, Y. R.; Cao, Q. D.; Hong, Z. S.; Tan, Y. Y.; Chen, S. D.; Jin, H. J.; Tan, K. S.; Wang, D. Y.; Yan, Y. Mil. Med. Res. 2020, 7, 11. DOI: 10.1186/s40779-020-00240-0 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s40779-020-00240-0
Zou, L.; Ruan, F.; Huang, M.; Liang, L.; Huang, H.; Hong, Z.; Yu, J.; Kang, M.; Song, Y.; Xia, J. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 1177-1179. DOI: 10.1056/NEJMc2001737 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMc2001737
Cui, J.; Li, F.; Shi, Z. L. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2019, 17, 181–192. DOI: 10.1038/s41579-018-0118-9 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41579-018-0118-9
Finlay, B. B.; See, R. H.; Brunham, R. C. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2004, 2, 602–607. DOI: 10.1038/nrmicro930 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nrmicro930
de Haan, C. A.; Rottier, P. J. Adv. Virus Res. 2005, 64, 165-230. DOI: 10.1016/S0065-3527(05)64006-7 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/S0065-3527(05)64006-7
Millet, J. K.; Whittaker, G. R. Virology. 2018, 517, 3-8. DOI: 10.1016/j.virol.2017.12.015 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.virol.2017.12.015
Kuba, K.; Imai, Y.; Rao, S.; Gao, H.; Guo, F.; Guan, B.; Huan, Y.; Yang, P.; Zhang, Y.; Deng, W.; Bao, L. Nat. Med. 2005, 11, 875-879. DOI: 10.1038/nm1267 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nm1267
Hamming, I.; Timens, W.; Bulthuis, M. L. C.; Lely, A. T.; Navis, G. V.; van Goor, H. J. Pathol. 2004, 203, 631-637. DOI: 10.1002/path.1570 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/path.1570
Zumla, A.; Chan, J. F.; Azhar, E. I.; Hui, D. S.; Yuen, K. Y. Nat. Rev. Drug Discovery. 2016, 15, 327-347. DOI: 10.1038/nrd.2015.37 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nrd.2015.37
Yang, N.; Shen, H. M. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2020, 16, 1724. DOI: 10.7150/ijbs.45498 DOI: https://doi.org/10.7150/ijbs.45498
Stadler, K.; Ha, H. R.; Ciminale, V.; Spirli, C.; Saletti, G.; Schiavon, M.; Bruttomesso, D.; Bigler, L.; Follath, F.; Pettenazzo, A.; Baritussio, A. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2008, 39, 142-149. DOI: 10.1016/j.bbadis.2020.165889 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1165/rcmb.2007-0217OC
Pu, Y.; Zhang, X. J. Virol. 2008, 82, 8112-8123. DOI: 10.1128/JVI.00837-08 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1128/JVI.00837-08
Burkard, C.; Verheije, M. H.; Wicht, O.; van Kasteren, S. I.; van Kuppeveld, F. J.; Haagmans, B. L.; Pelkmans, L.; Rottier, P. J.; Bosch, B. J.; de Haan, C. A. PLoS Pathog. 2014, 10, 1004502. DOI: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1004502 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.ppat.1004502
Abiri, R.; Abdul-Hamid, H.; Sytar, O.; Abiri, R.; Bezerra de Almeida, E., Jr.; Sharma, S. K.; Bulgakov, V. P.; Arroo, R. R. J.; Malik, S. Molecules. 2021, 26, 3868. DOI: 10.3390/molecules26133868 DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26133868
Singh, R.; Sharma, R. R.; Kumar, S.; Gupta, R. K.; Patil, R. T. Bioresour. Tech. 2008, 99, 8507-8511. DOI: 10.1016/j.biortech.2008.03.034 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2008.03.034
Kumar, N.; Shala, A. Y.; Khurana, S. M. P. Int. J. Phytomed. Related Industries. 2021, 13, 229-236. DOI: 10.5958/0975-6892.2021.00026.5 DOI: https://doi.org/10.5958/0975-6892.2021.00026.5
Chikhale, R. V.; Gurav, S. S.; Patil, R. B.; Sinha, S. K.; Prasad, S. K.; Shakya, A.; Shrivastava, S. K.; Gurav, N. S.; Prasad, R. S. J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn. 2020, 39, 4510-4521. DOI: 10.1080/07391102.2020.1778539 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1080/07391102.2020.1778539
Desai, S. V.; Dhumal, A. S.; Chauhan, P. S. Int. J. Pharm. Technol. 2016, 8, 3611–3628.
Parekh, S.; Soni, A. J. Appl. Biol. Biotechnol. 2020, 8, 95-104. DOI: 10.7324/JABB.2020.80116 DOI: https://doi.org/10.7324/JABB.2020.80116
Gupta, P.; Bajpai, S. K.; Chandra, K.; Singh, K. L.; Tandon, J. S. Indian J. Exp. Biol. 2005, 43, 1156–60.
Samanta, S. K.; Kandimalla, R.; Gogoi, B.; Dutta, K. N.; Choudhury, P.; Deb, P. K.; Devi, R.; Pal, B. C.; Talukdar, N. C. Pharmacol. Res. 2017. DOI: 10.1016/j.phrs.2017.11.024 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phrs.2017.11.024
Gupta, P.; Nahata, A.; Dixit, V. K. J. Chin. Integr. Med. 2011, 9, 824-833. DOI: 10.4236/ajps.2014.519302 DOI: https://doi.org/10.3736/jcim20110803
Gholap, S.; Kar, A. Pharmazie. 2004, 59, 876–878. DOI:
Udupa, S. L.; Shetty, S.; Udupa, A. L.; Somayaji, S. N. Indian J. Exp. Biol. 2006, 44, 49–54.
Ghoke, S. S.; Sood, R.; Kumar, N.; Pateriya, A. K.; Bhatia, S.; Mishra, A. BMC Complementary Altern. Med. 2018, 18, 174. DOI: 10.1186/s12906-018-2238-1 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s12906-018-2238-1
Ahmad, S.; Zahiruddin, S.; Parveen, B.; Basist, P.; Parveen, A.; Gaurav; Parveen, R.; Ahmad, M. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 11, 578970. DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2020.578970 DOI: https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2020.578970
Rege, A.; Chowdhary, A. S. Int. J. Pharm. Sci. Rev. Res. 2014, 25, 315–318.
Hombalimath, V. S.; Shet, A. R. J. Adv. Bioinforma. Appl. Res. 2012, 3, 345–356.
Shivakumar, R.; Venkatarangaiah, K.; Shastri, S.; Naga¬raja, R. B.; Sheshagiri, A. Pharmacog. J. 2018, 10, 1221-1229. DOI: 10.5530/pj.2018.6.209 DOI: https://doi.org/10.5530/pj.2018.6.209
Ghildiyal, R.; Prakash, V.; Gabrani, R. Springer Nature 2020, 279-295. DOI: 10.1007/978-981-15-1761-7_12 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-15-1761-7_12
Singha, I.; Saxena, S.; Gautam, S.; Saha, A.; Das, S. K. Indian J. Biochem. Biophys. 2020, 57, 219.
Ganeshpurkar, A.; Saluja, A. Indian J. Biochem. Biophys. 2018, 55, 88. DOI: http://nopr.niscair.res.in/handle/123456789/44348
Tetko, I. V.; Tanchuk, V. Y. J. Chem. Inf. Comput. Sci. 2002, 42, 1136. DOI: 10.1021/ci025515j DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/ci025515j
Cheng, F.; Li, W.; Zhou, Y.; Shen, J.; Wu, Z.; Liu, G.; Lee, P. W.; Tang, Y. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2012, 52, 3099. DOI: 10.1021/ci300367a DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/ci300367a
Webster, D.; Taschereau, P.; Lee, T. D.; Jurgens, T. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2006, 106, 360–363. DOI: 10.1016/j.jep.2006.01.018 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jep.2006.01.018
Basu, A.; Sarkar, A.; Maulik, U.; Basak, P. Indian J. Biochem. Biophys. 2019, 56, 20. DOI: http://nopr.niscair.res.in/handle/123456789/45817
Bhal, S. K. Advanced Chemistry Development, Toronto, ON, Canada, 2007, 1-4.
Jorgensen, W. L.; Duffy, E. M. Bioor. Med. Chem. Lett. 2000, 10, 1155-1158. DOI: 10.1016/s0960-894x(00)00172-4 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/S0960-894X(00)00172-4

Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2022 Vandita Anand, Saumya Srivastava, Anjana Pandey

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.
Authors who publish with this journal agree to the following terms:
- Authors retain copyright and grant the journal right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution License that allows others to share the work with an acknowledgement of the work's authorship and initial publication in this journal.
- Authors are able to enter into separate, additional contractual arrangements for the non-exclusive distribution of the journal's published version of the work (e.g., post it to an institutional repository or publish it in a book), with an acknowledgement of its initial publication in this journal.