Green Synthesis of Nickel Nanoparticles using Fruit Peels of Citrus Paradise for Remediation of Congo Red Dye
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.29356/jmcs.v65i4.1572Keywords:
Congo red direct dye, grapefruit peel, Ni nanoparticles, remediation.Abstract
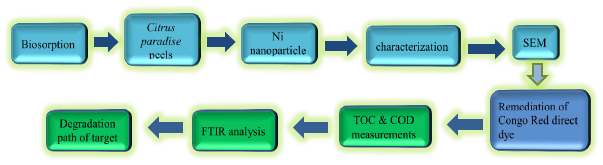
Abstract. Biosorption is a cost-effective excellent tool for removing problematic dyes. The present work was focused on the utilization of Citrus paradise (grapefruit) peels aqueous extract for synthesis of nickel nanoparticles. The prepared nanoparticles were characterized by SEM and were used for the remediation of congo red direct dye. The decolorization of Congo Red direct dye was measured using UV/Visible spectrophotometer following the optimization of experimental factors. Maximum decolorization was observed at a dye concentration of 0.02 %, pH 6, at 50 °C temperature, and catalyst dose was 0.01 g/L. TOC and COD values were found to be 79.89 % and 78.23 %. Agriculrural waste could be used for the remediation of other synthetic dyes as well; hence helps in cleaning our natural environment.
Resumen. La biosorción es una excelente herramienta rentable para eliminar colorantes problemáticos. El presente trabajo se centró en la utilización del extracto de cáscaras de Citrus paradise (pomelo) para la síntesis de nanopartículas de níquel. Las nanopartículas preparadas se caracterizaron por microscopía electrónica de barrido (MEB) y se utilizaron para la remediación del colorante directo rojo de Congo. La decoloración del colorante directo Rojo Congo se midió mediante espectrometría siguiendo la optimización de factores experimentales. Se observó una decoloración máxima a una concentración de colorante de 0.02 %, pH 6, y una temperatura de 50 °C; la dosis del catalizador fue de 0.01 g/L. Se determinó que los valores de TOC y DQO eran 79.89 % y 78.23 %, respectivamente. Los residuos agrícolas también podrían utilizarse para la remediación de otros tintes sintéticos y con ello ayudar a limpiar nuestro entorno natural.
Downloads
References
Edison, T.; Atchudan, R.; Sethuraman, M. G.; Lee, Y. R. Photobiol. B: Biol. 2016, 162, 604-610. DOI: 10.1016/j.jphotobiol.2016.07.040. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jphotobiol.2016.07.040
Kiran, S.; Adeel, S.; Nosheen, S.; Hassan, A.; Usman, M.; Rafique, M. A. Adv. Mater. Wastewater Treat. 2017, 29, 29-49. DOI: 10.1002/9781119407805. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/9781119407805.ch2
Naseer, A.; Nosheen, S.; Kiran, S.; Kalam, S.; Javaid, M. A.; Mustafa, M.; Tahir, A. Desalin. Water Treat. 2016, 57, 24070-24082. DOI: 10.1080/19443994.2016.1138145. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1080/19443994.2016.1138145
Gulzar, T.; Huma, T.; Jalal, F.; Iqbal, S.; Abrar, S.; Kiran, S.; Rafique, M. A. Molecules. 2016, 22, 2244. DOI: 1420-3049/22/12/2244. DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules22122244
Chatha, S.; Kiran, S.; Gulzar, T., Kamal, S.; Ghaffar, A.; Chatha, M. N. Oxid. Commun. 2016, 39, 1604-1614
Gulzar, T.; Kiran, S.; Abrar, S.; Rahmat, M.; Haque, A.; Nosheen, S.; Ahmad, A.; Rasul, S. J. J. Chem. Soc. Pak. 2019, 41, 509 DOI: https://doi.org/10.52568/000755/JCSP/41.03.2019
Kiran, S.; Nosheen, S.; Iqbal, S.; Abrar, S.; Jalal, F.; Gulzar, T.; Mukhtar, A.; Maqsood, S., Ahmad, W., Nasreen, N. Chiang Mai J. Sci. 2018, 45, 2730-2739. DOI: 6653943832/64235.
Kiran, S.; Gulzar, T.; Iqbal, S.; Habib, N.; Hassan, A.; Naz, S. Integ. Green Chem. Sust. Eng. 2019, 473-525. DOI: 10.1002/9781119509868. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/9781119509868.ch15
Haque, A.; Kiran, S.; Nosheen, S.; Afzal, G.; Gulzar, T.; Ahmad, S.; Rehman, S.; Tariq, M. H. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 2020, 29, 609-616. DOI: 10.15244/pjoes/104663. DOI: https://doi.org/10.15244/pjoes/104663
Abid, P.; Farzi, A.; Karimi, A. J. Tai. Inst. Chem. Engng. 2017, 71, 137-144. DOI: 10.1016/j.jtice.2016.11.022. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtice.2016.11.022
Kiran, S.; Ali, S.; Asgher, M.; Shahid, S. A. J. Environ. Sci. Water Resour. 2012, 1, 267-275
Rasheed, A.; Nosheen, S.; Kiran, S.; Bhatti, H. N.; Kamal, S.; Shamim, F.; Rafique, M. A. Oxid. Commun. 2016, 39, 1716-1726
Wang, B.; Dong, F.; Chen, M.; Zhu, J.; Tan, J.; Fu, X.; Chen, S. Procedia. Environ. Sci. 2016, 31, 12-17. DOI: 10.1016/j.proenv.2016.02.002. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.proenv.2016.02.002
Kiran, S.; Huma, T.; Jalal, F.; Farooq, T.; Hameed, A.; Gulzar, T.; Bashir, A.; Rahmat, M.; Rahmet, R.; Rafique, M. A. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 2019, 28, 1749-1757. DOI: 10.15244/pjoes/89575. DOI: https://doi.org/10.15244/pjoes/89575
Manikprabhu, D.; Lingappa, K. J. Pharm. Res. 2013, 6, 255-260. DOI: 10.1016/j.jopr.2013.01.022. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jopr.2013.01.022
Adeoye, A. O.; Lateef, A.; Gueguim-kana, E. B. Biocatal. Agricul. Biotechnol. 2015, 4, 568-574. DOI: 10.1016/j.bcab.2015.08.004. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bcab.2015.08.004
Rosales, E.; Meijide, J.; Tanvares, T.; Pazos, M.; Sanroman, M. A. Process Saf. Environ. Protection. 2016, 101, 61-71. DOI: 10.1016/j.psep.2016.03.006. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.psep.2016.03.006
Fang, R.; Chen, K., Yin, L.; Sun, Z.; Li, F.; Cheng, H. M. Adv. Mater. 2019, 31, 1800863. DOI: 10.1002/adma.201800863. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.201970066
Sharma, A.; Siddiqui, Z. M.; Dhar, S.; Mehta, P.; Pathania, D. Sep. Sci. Technol. 2019, 54, 916-929. DOI: 10.1080/01496395.2018.1524908.
Kuchelar, S.; Dhag, P.; Gaikwad, V.; Aher, H.; Han, S. Chem. Sci. 2018, 7, 696. DOI: 10.7589/cst2018.1537.
Greenberg, A. E.; Trussell, R. L.; Clesceri, L. S. Standard Methods for the examination of water and wastewater. 20th Ed., 1985.
Steel, R. G.; Torrie, O.; Dickey, D. A. Principles and procedures of Statistics: A Biochemical Approach, 3rd Ed.; McGraw Hill, New York, USA, 1997.
Santhosh, A. M.; Yogendra, K.; Mahadevan, K. M.; Madhusudhana, N. Int. J. Adv. Res. Sci .Engng. 2017, 6, 51-64.
Kiran, S.; Rafique, M. A.; Iqbal, S.; Nosheen, S.; Naz, S. and Rasheed, A. Environ. Sci. Poll. Res., 2020, 27, 32998-33007. DOI: 10.1007/s11356-020-09510-9. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-09510-9
Foster, S.L.; Estoque, K.; Voecks, M.; Rentz, N.; Greenlee, L. F. J. Nanomater. 2019, 1, 1-12. DOI: 10.1155/2019/9807605. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1155/2019/9807605
Zhu, C.; Wang, L.; Kong, L.; Yang, X.; Zheng, S.; Chen, F.; Maizhi, F.; Zong, H. Chemosphere. 2000, 41, 303-309. DOI: 10.1016/S0045-6535(99)00487-7. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/S0045-6535(99)00487-7
Chowdhury, S.; Bhattacharyya, K. G. J. Appl. Sci. 2019, 1, 87 DOI: 10.1007/s42452-018-0094-8. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42452-019-1261-2
Da Silva, B. C.; Zanutto, A.; Pietrobelli, J. M. Adsorpt. Sci. Technol. 2019, 37, 236–259. DOI: 10.1177/0263617418823995. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1177/0263617418823995
Sharma, A.; Siddiqui, Z. M.; Dhar, S.; Mehta, P.; Pathania, D. Sep. Sci. Technol. 2019, 54, 916-929. DOI: 10.1080/01496395.2018.1524908. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1080/01496395.2018.1524908
Yasmin, S.; Nouren, S.; Bhatti, H. N.; Iqbal, D. N.; Iftikhar, S.; Majeed, J.; Mustafa, R.; Nisar, N.; Nisra, J., Nazir, A.; Iqbal, M.; Rizvi, H. Green Process. Synth. 2020, 9, 87-96. DOI: 10.1515/gps-2020-0010. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1515/gps-2020-0010
Viana, D. F.; Salazar-banda, G. R.; Leite, M. S. Sep. Sci. Technol. 2018, 53, 2647-2661. DOI: 10.1080/01496395.2018.1463264. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1080/01496395.2018.1463264
Ferraz, E.; Oliveira, G.; Grando, M. D.; Lizier, T. M.; Zanoni, M.; Oliveria, D. P. J. Environ. Manag. 2013, 124, 108-114. DOI: 10.1016/j.jenvman.2013.03.033. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2013.03.033
Muneer, M.; Saeed, M.; Bhatti, I. A.; Haq, A. U.; Khosa, M. K.; Jamal, M. A.; Ali, S. Nukleonika 2019, 64, 49-53. DOI: 10.2478/nuka-2019-0006. DOI: https://doi.org/10.2478/nuka-2019-0006
Harun, N. H.; Rahman, M.; Kamarudin, W.; Irwan, Z.; Muhammud, A.; Akhir, N.; Yaafar, M. R. J. Fund. Appl. Sci. 2018, 10, 832-846.

Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
License
Authors who publish with this journal agree to the following terms:
- Authors retain copyright and grant the journal right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution License that allows others to share the work with an acknowledgement of the work's authorship and initial publication in this journal.
- Authors are able to enter into separate, additional contractual arrangements for the non-exclusive distribution of the journal's published version of the work (e.g., post it to an institutional repository or publish it in a book), with an acknowledgement of its initial publication in this journal.