A Validation Model for Prediction of Kovats Retention Indices of Compounds Isolated from Origanum spp. and Thymus spp. Essential Oils
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.29356/jmcs.v65i4.1515Keywords:
Origanum spp., Thymus spp., QSRR, artificial neural networksAbstract
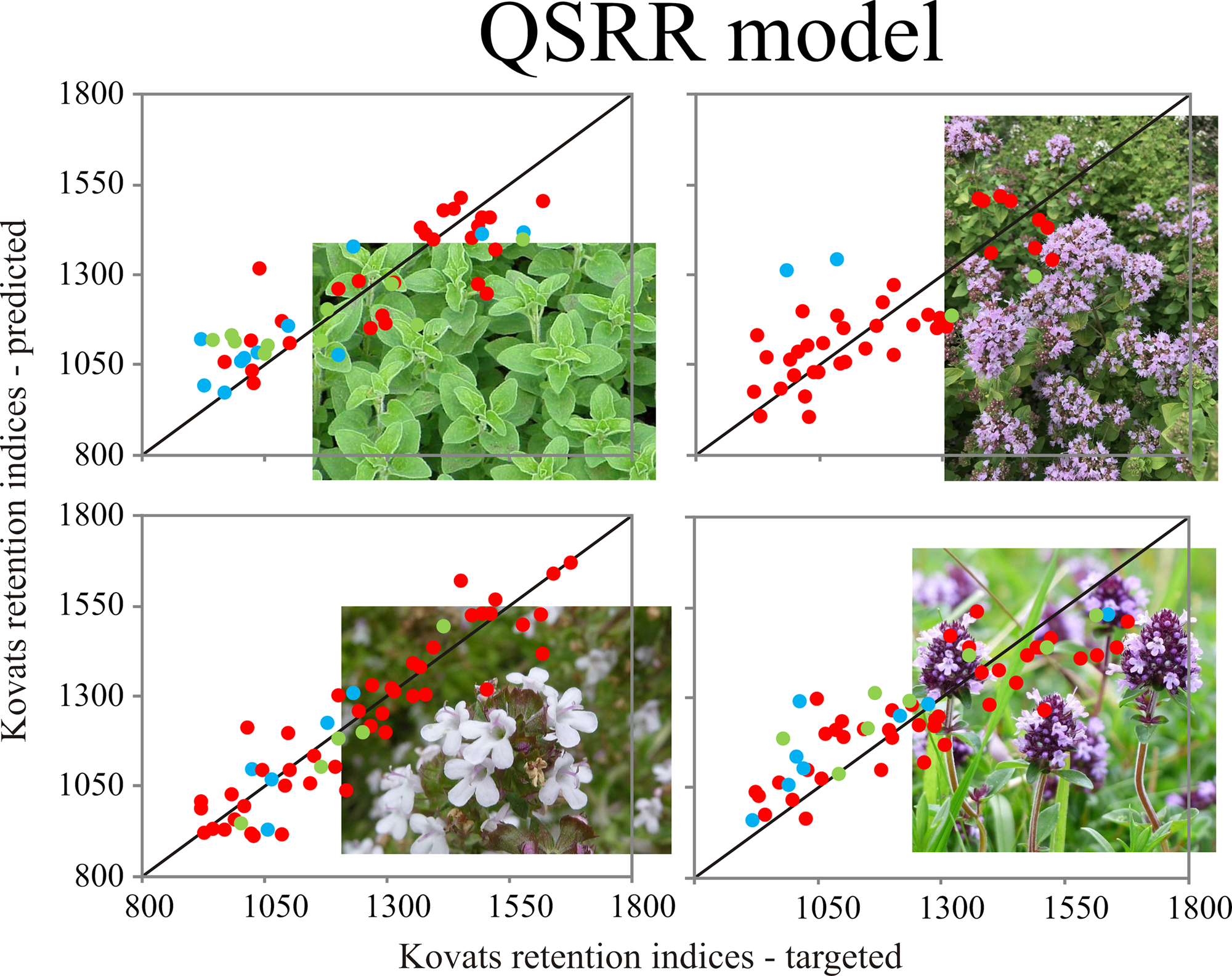
Abstract. This work aimed to obtain a validated model for the prediction of retention times of compounds isolated from Origanum heracleoticum, Origanum vulgare, Thymus vulgaris, and Thymus serpyllum essential oils. In total 68 experimentally obtained retention times of compounds, which were separated and detected by GC-MS were further used to build the prediction models. The quantitative structure–retention relationship was employed to foresee the Kovats retention indices of compounds acquired by GC-MS analysis, using eight molecular descriptors selected by a genetic algorithm. The chosen descriptors were used as inputs for the four artificial neural networks, to construct a Kovats retention indices predictive quantitative structure–retention relationship model. The coefficients of determination in the training cycle were 0.830; 0.852; 0.922 and 0.815 (for compounds found in O. heracleoticum, O. vulgare, T. vulgaris and T. serpyllum essential oils, respectively), demonstrating that these models could be used for prediction of Kovats retention indices, due to low prediction error and high r2.
Resumen. El objetivo de este trabajo es la obtención de modelos validados para la predicción del tiempo de retención de los compuestos aislados de aceites esenciales de Origanum heracleoticum, Origanum vulgare, Thymus vulgaris y Thymus serpyllum. Se han obtenido un total de 68 tiempos de retención de compuestos, separándose y detectándose por cromatografía de gases con detección por espectrometría de masas (GC-MS) con posterior desarrollo de modelos de predicción. La relación cuantitativa estructura-retención ha sido utilizada para predecir el índice de retención Kovats de los compuestos obtenidos por análisis de GC-MS, utilizando ocho descriptores moleculares seleccionados mediante algoritmo genético. Los descriptores seleccionados han sido utilizados como entrada para las cuatro redes neuronales artificiales y así elaborar los índices predictivos del modelo de relación cuantitativa estructura-retención. Los coeficientes de determinación en el ciclo de entrenamiento fueron de 0.830; 0.852; 0.922 y 0.815 (para los compuestos identificados en los aceites esenciales del O. heracleoticum, O. vulgare, T. vulgaris y T. serpyllum respectivamente) demostrando así que estos modelos son útiles en la predicción de los índices de retención de Kovats con un error de bajo predicción y alta r2.
Downloads
References
Dreger, M.; Wielgus, K. Herba Pol. 2013, 59, 142-156.
Nikoli?, M.; Glamo?lija, J.; Ferreira, I.; Calhelha, R.C.; Fernandes, Â.; Markovi?, T.; Markovi?, D.; Giweli, A.; Sokovi?, M. Ind. Crop. Prod. 2014, 52, 183-190.
García-Beltrán, J.M.; Esteban, M.Á. SM J. Biol. 2016, 2, 1006. https://smjournals.com/biology/fulltext/smjb-v2-1006.pdf
Marrelli, M.; Araniti, F.; Abenavoli, M.R.; Stattia, G.; Confortia, F. Nat. Prod. Commun. 2018, 13, 1183-1187.
Marrero-Ponce, Y.; Barigye, S.J.; Jorge-Rodríguez, M.E. Tran, T.T. Chem. Pap. 2017, 72, 57–69. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11696-017-0257-x
Qin, L.T.; Liu, S.S.; Chen, F.; Xiao, Q.F.; Wu, Q.S. Chemosphere. 2013,90, 300-305.
Liu, J.J.; Alipuly, A.; B?czek, T.; Wong, M.W.; Žuvela, P. Int J Mol Sci. 2019, 20, 3443.
Metivier-Pignon, H.; Faur, C.; Le Cloirec, P. Chemosphere, 2017, 66, 887-893.
Dong, P. P.; Ge, G. B.; Zhang, Y. Y.; Ai, C. Z.; Li, G. H.; Zhu, L. L.; Luan, H. W.; Liu, X. B.; Yang L. J. Chromatogr. A. 2009, 1216, 7055-7062.
Héberger, K. J. Chromatogr. A. 2007, 1158, 273-305.
Kaliszan, R.; Ba? czek, T.; Buci?ski, A.; Buszewski, B.; Sztupecka, M. J. Sep. Sci. 2003, 26, 271-282.
Khodadoust, S.; Ghaedi, M.; Hadjmohammadi, M.R. Talanta, 2013, 116, 637-646.
Wolfender, J.L.; Martia, G.; Thomas, A.; Bertranda, S. J. Chromatogr. A. 2015, 1382, 136-164.
Zisi, C.; Sampsonidis, I.; Fasoula, S.; Papachristos, K.; Witting, M.; Gika, H.G.; Nikitas, P.; Pappa Louisi A. Metabolites. 2017, DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo7010007
Adams, R.P. Identification of Essential Oil Components by Gas Chromatography/Mass Spectrometry, 4th ed.; Allured Publishing Corporation: Carol Stream, IL, USA, 2007.
Automated Mass Spectral Deconvolution and Identification System software (AMDIS ver. 2.1 National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST), Standard Reference Data Program, Gaithersburg, MD, USA, 2005.
Yap, C.W. J. Comput. Chem. 2011, 32, 1446-1474.
https://dev.heuristiclab.com/trac.fcgi. accessed in December 2018
Goldberg, D.E. Genetic algorithms in search, optimisation and machine learning. Addison-Wesley, Massachusetts, Boston, USA, 1989.
Gramatica, P. QSAR Comb. Sci. 2007, 26, 694-701 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/qsar.200610151
Statistica 10 software (StatSoft, Inc. STATISTICA, ver. 10, data analysis software system), accessed in December 2018.
Hu, X.; Weng, Q. Remote Sens. Environ. 2009, 113, 2089-2102.
Wang D.; Yuan Y.; Duan S.; Liu R.; Gu S.; Zhao S.; Liu L.; Xu J. Chemometr. Intell. Lab. 2015, 143, 7-15.
Kojic, P.; Omorjan, R. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2018, 125, 398-407.
Yoon, Y.; Swales, G.; Margavio, T.M. J. Oper. Res. Soc. 2017, 44, 51-60.
Al-Asmari A.K.; Athar M.T.; Al-Faraidy A.A.; Almuhaiza M.S. Asian Pac. J. Trop. Biomed. 2017, 7, 147-150.
Rostro-Alanis M.J.; Báez-González J.; Torres-Alvarez C.; Parra-Saldívar R.; Rodriguez-Rodriguez J.; Castillo S. Molecules, 2019, 24, 1904. DOI: https://doi:10.3390/molecules24101904
Dzamic, A.; Sokovic, M.; Ristic, M.S. et al. Chemical composition and antifungal activity of Origanum heracleoticum essential oil. Chem. Nat. Compd. 2008, 44, 659–660 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10600-420 008-9162-4
?abarkapa, I.; ?olovi?, R.; ?uragi?, O.; Popovi?, S.; Koki?, B.; Milanov, D.; Pezo, L. Biofouling. 2019, 35, 361-375.
Alizadeh, A.; Alizadeh, O.; Amari, G.; Zare, M. J. Essent. Oil. Bear. Pl. 2013, 16, 59-70.
Andrade-Ochoa, S.; Nevárez-Moorillón, G.V.; Sánchez-Torres, L.E.; Villanueva-García, M., Sánchez Ramírez, B.E.; Rodríguez-Valdez, L.M.; Rivera-Chavira, B.E. BMC Complem. Altern. M. 2015, 15, 332 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s12906-015-0858-2
Owen, L.; Laird, K.; Wilson, P.B. Mol. Cell. Probe. 2018, 38, 25-30.
Nekoei, M.; Mohammadhosseini, M.; Pourbasheer, E. Med. Chem. Res. 2015, 24), 3037–3046.
Nekoei, M.; Salimi, M.; Dolatabadi, M.; Mohammadhosseini, M. Chem. Mont. 2011, 142, 943 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00706-011-0510-x
Todeschini, R.; Consonni, V. Handbook of Molecular Descriptors, Methods and Principles in Medicinal Chemistry. Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH, Weinheim, Germany, 2000.
Driouche, Y.; Messadi, D. J. Serb. Chem. Soc. 2019, 84, 405-416.
Bodor, N.; Buchwald, P.; Huang, M.J. J. Theor. Comput. Chem. 1999, 8, 569-618.
Noorizadeh, H.; Farmany, A.; Noorizadeh, M. Quím. Nova. 2011, 34, 242-249.
Azar, P. A.; Nekoei, M.; Riahi, S.; Ganjali, M. R.; Zare, K. J. Serb. Chem. Soc. 2011, 76, 891-902.
Arsenovi?, M.; Pezo, L.; Stankovi?, S.; Radojevi?, Z. 2015. Appl. Clay Sci. 2015, 115, 108-455 114.

Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
License
Authors who publish with this journal agree to the following terms:
- Authors retain copyright and grant the journal right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution License that allows others to share the work with an acknowledgement of the work's authorship and initial publication in this journal.
- Authors are able to enter into separate, additional contractual arrangements for the non-exclusive distribution of the journal's published version of the work (e.g., post it to an institutional repository or publish it in a book), with an acknowledgement of its initial publication in this journal.









