Physicochemical Interpretation, with QSAR/SAR Analysis, of How the Barriers Of Pseudomonas Aeruginosa Bacteria Were Penetrated by Para-Substituted N-Arylbenzylimines: Synthesis, Characterization, and In Vitro Antibacterial Effect
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.29356/jmcs.v65i3.1481Keywords:
Antibacterial activity, E configuration, partition coefficient, electronic effects, QSAR/SARAbstract
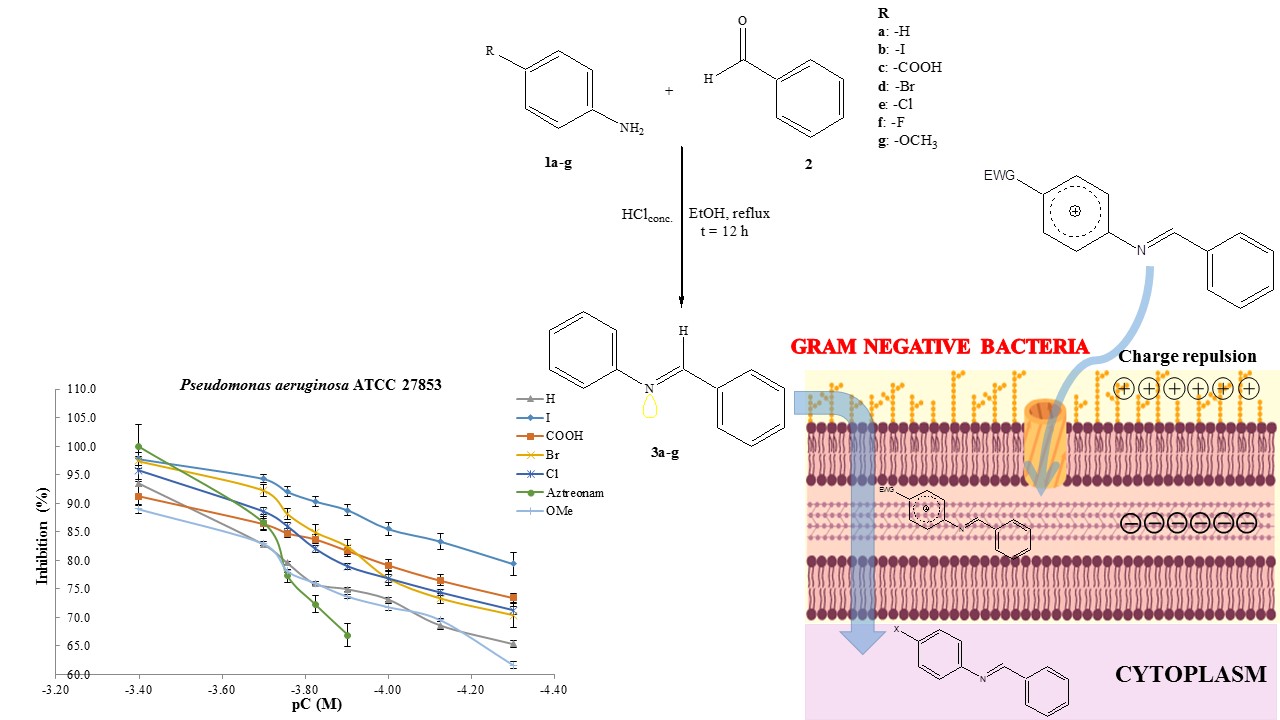
Abstract. Resistance to antibiotics is a growing problem that imposes limitations on current therapy around the world. The World Health Organization (WHO) recommends creating new antibacterial molecules to inhibit the most harmful bacteria by aiming at specific targets. Among such bacteria is multi-drug resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa, a Gram-negative bacterium responsible for 70% of invasive infections worldwide. The aim of this investigation was to synthesize N-arylbenzylimines, examine their antibacterial activity against P. aeruginosa ATCC 27853, and determine their physicochemical properties by quantitative structure-activity relationship (QSAR/SAR) analysis. Seven N-arylbenzylimines were synthesized with yields ≥50%, all with the E-configuration (as shown by NMR spectra and confirmed with X-ray diffraction). The in vitro microbiological evaluations were carried out with the Kirby-Bauer method, following the guidelines of the Clinical & Laboratory Standards Institute (CLSI). The N-arylbenzylimines produced a very good antibacterial effect on P. aeruginosa, with minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) values ranging from 198.47-790.10 µM, calculated by the Hill method. Based on the slopes of the concentration-response curves, the mechanism of action is different between the test compounds and aztreonam, the reference drug. The QSAR study performed with in vitro experimental data found that biological activity correlates most significantly with molecular size, followed by lipophilicity and electronic effects. According to the SAR analysis of antibacterial activity, molecules cross bacterial barriers differently if they bear substituents with resonance versus inductive electronic effects. The physicochemical data presently described are of utmost importance for designing and developing new molecules to combat the pathogenicity and resistance of P. aeruginosa.
Resumen. La resistencia a los antibióticos es un problema en aumento que impone limitaciones en la terapia actual a nivel mundial. La Organización Mundial de la Salud (OMS) recomienda crear nuevas moléculas antibacterianas para inhibir las bacterias más dañinas por medio de dianas específicas. Pseudomonas aeruginosa, entre estas bacterias, es Gram-negativa, resistente a múltiples fármacos, y responsable del 70% de las infeccione invasivas en el mundo. El objetivo de esta investigación fue sintetizar N-arilbenziliminas, examinar su actividad antibacteriana contra P. aeruginosa ATCC 27853, y determinar sus propiedades fisicoquímicas mediante análisis cuantitativo de relación estructura-actividad (QSAR/SAR). Todos los siete N-arilbenziliminas sintetizados tuvieron rendimientos ≥50% y la configuración E (de acuerdo con la espectroscopía de RMN y la difracción de rayos-X). Las pruebas microbiológicas in vitro se realizaron mediante el método Kirby-Bauer, siguiendo las directrices del Instituto de Estándares Clínicos y de Laboratorio (CLSI). Las N-arilbenziliminas mostraron efecto antibacteriano relevante sobre P. aeruginosa, con valores de la concentración mínima inhibitoria (MIC) en el rango de 198.47-790.10 µM, calculado por el método de Hill. Las pendientes de las curvas de concentración-respuesta sugieren que el mecanismo de acción es distinto entre las N-arilbenziliminas y aztreonam, el fármaco de referencia. El analisis QSAR de los datos experimentales indica que la actividad biológica se correlaciona de manera más significativa con el tamaño molecular, seguida de la lipofilicidad y los efectos electrónicos. Según el análisis SAR de la actividad antibacteriana, las moléculas cruzan las barreras bacterianas en forma diferente si portan sustituyentes con efectos electrónicos inductivos versus de resonancia. Estos datos fisicoquímicos son de suma importancia en el diseño y desarrollo de nuevas moléculas para combatir la infección y resistencia de P. aeruginosa.
Downloads
References
Carreño, A.; Rodríguez, L.; Páez-Hernández, D.; Martin-Trasanco, R.; Zúñiga, C.; Oyarzún, DP.; Gacitúa, M.; Schott, E.; Arratia-Pérez, R.; Fuentes, JA. Front. Chem. 2018, 6, 1-13. DOI: https://doi.org/10.3389/fchem.2018.00312
Arunachalam, S.; Padma-Priya, N.; Jayabalakrishnan, C.; Chinnusamy, V. Spectrochim. Acta A. 2009, 74, 591-596. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.saa.2009.06.061
Chonan, Z-H.; Scozzafava, A.; Supuran, C-T. J Enzyme Inhib. Med. Chem. 2003, 18, 259-263. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1080/1475636031000071817
Guevara-Salazar, J-A.; Morán-Díaz, J-R.; Ramírez-Segura, E.; Trujillo-Ferrara, J-G. Rev. Anti. Infect. Ther. 2020, 1-22. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1080/14787210.2021.1839418
Wise, R.; Hart, T.; Cars, O.; Streulens, M.; Helmuth, R.; Huovinen, P.; Sprenger, M. BMJ. 1998, 317, 609-610. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.317.7159.609
Beceiro, A.; Tomás, M.; Bou, G. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2013, 26, 185-230. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1128/CMR.00059-12
Shallcross, L.; Davies, D. Br. J. Gen. Pract. 2014, 64, 604-605. DOI: https://doi.org/10.3399/bjgp14X682561
Yelin, I.; Snitser, O.; Novich, G.; Katz, R.; Tal, O.; Parizade, M.; Chodick, G.; Koren, G.; Shalev, V.; Kishony, R. Nat. Med. 2019, 25, 1143-1152. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41591-019-0503-6
Aslam, B.; Wang, W.; Arshad, M.; Khurshid, M.; Muzammil, S.; Rasool, M.; Nisar, M.; Alvi, R.; Aslam, M.; Qamar. M.; Salamat, M.; Baloch, Z. Infect. Drug. Resist. 2018, 10, 1645-1658. DOI: https://doi.org/10.2147/IDR.S173867
Pang, Z.; Raudonis, R.; Glick, B.; Lin, T.; Cheng, Z. Biotechnol. Adv. 2018, 37, 177-19.2 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biotechadv.2018.11.013
Colomb-Cotinat, M.; Lacoste, J.; Brun-Buisson, C.; Jarlier, V.; Coignard, B.; Vaux, S. Antimicrob. Resist. Infect. Control. 2016, 5, 1-11. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s13756-016-0154-z
Kobayashi, S.; Ishitani, H. Chem. Rev. 1999, 99, 1069-1094. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/cr980414z
Tietze, O.; Schiefner, B.; Ziemer, Z.; Zschunke, A. Fresenius. J. Anal. Chem. 1997, 357, 477-481. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s002160050195
Bakkar, M.; Monshi, M.; Warad, I.; Siddiqui, M.; Bahajaj, A. J. Saudi. Chem. Soc. 2010, 14, 165-174. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jscs.2010.02.007
Corre, Y.; Lali, W.; Hamdaoui, M.; Trivelli, X.; Djukic, J.P.; Agbossou-Niedercorn, F.; Michon, C. Catal. Sci. Technol. 2015, 5, 1452-1458. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1039/C4CY01233J
Franz, D.; Sirtl, L.; Pöthig, A.; Inoue, S. Z. Anorg. Allg. Chem. 2016, 642, 1245-1250. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/zaac.201600313
Cainelli, G.; Panunzio, M.; Andreoli, P.; Martelli, G.; Spunta, G.; Giacomini, D.; Bandini, E. Pure & Appl. Chem. 1990, 62, 605-612. DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.1351/pac199062040605 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1351/pac199062040605
Mladenova, R.; Ignatova, M.; Manolova, N.; Petrova, T.; Rashkov, I. Eur. Polym. J. 2002, 38, 989-999. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/S0014-3057(01)00260-9
Geindy-Mohamed, G.; Mohamed-Omar, M.; Mohamed-Hindy, A. Turk. J. Chem. 2006, 30, 361-382.
Shi, L.; Mao, W-J.; Yang, Y.; Zhu, H-L. J. Coord. Chem. 2009, 62, 3471-3477. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1080/00958970903093694
Mohamed, G.; Omar, M.; Ibrahim, A. Spectrochim. Acta A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2010, 75, 678-685. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.saa.2009.11.039
Razieh, A.; Mohammad, A.; Tahereh, S. J. Mex. Chem. Soc. 2014, 58, 173-179. DOI: https://doi.org/10.29356/jmcs.v58i2.174
Bathia, MS.; Mulani, AK.; Choudhari, PB.; Ingale, KB.; Bathia, NM. Int. J. Drug. Discov. 2009, 1, 1-9. DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.9735/0975-4423.1.1.1-9 DOI: https://doi.org/10.9735/0975-4423.1.1.1-9
Yang, H.; Lou, C.; Sun, L.; Li, J.; Cai, Y.; Wang, Z.; Li, W.; Liu, G.; Tang, Y. BMC Bioinform. 2018, 35, 1067-1069. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/bty707
admetSAR http://lmmd.ecust.edu.cn/admetsar2/ accessed in April 2021
Daina, A.; Michelin, O.; Zoete, V. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2014, 54, 3284–3301. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/ci500467k
Daina, A.; Zoete, V. Chem. Med. Chem. 2016, 11, 1117-1121. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/cmdc.201600182
Daina, A.; Michielin, O.; Zoete, V. Sci. Rep. 2017, 3, 42717. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/srep42717
SwissADME http://www.swissadme.ch/ accessed in October 2020
Peach, M.; Zakharov, A.; Liu, R.; Pugliese, A.; Tawa, G.; Wallqvist, A.; Nicklaus, M. Future Med Chem. 2012, 4, 1907-1932. DOI: https://doi.org/10.4155/fmc.12.150
Olsen, L.; Montefiori, M.; Phuc-Tran, K.; Steen-Jorgensen, F. BMC Bioinform. 2019, 17, 3174-3175. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btz037
SMARTCyp : Site of Metabolism prediction for Cytochrome P450s https://smartcyp.sund.ku.dk/mol_to_som accessed in April 2021
ChemAxon-Marvin https://chemaxon.com/products/marvin accessed in April 2021
Guan-Yeow, Y.; Sie-Tiong, H.; Nobuo, I.; Katsumi, S.; Peng-Lim, B.; Mahmood, B.; Ahmad, W. J. Mol. Struct. 2003, 658, 87-99. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/S0022-2860(03)00453-8
Mandal, S.; Rout, A.; Pilet, G.; Bandyopadhyay, D. Transition. Met. Chem. 2009, 34, 719-724. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11243-009-9253-5
Altomare, A.; Cascarano, G.; Giacovazzo, C.; Guagliardi, A. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 1993, 26, 343-350. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1107/S0021889892010331
Sheldrick, G. Acta Cryst. 2008, 64, 112-122. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1107/S0108767307043930
Spek, A. L. Acta Cryst. D 2009, 65, 148–155. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1107/S090744490804362X
Harada, J.; Harakawa, M.; Ogawa, K. Acta Crystallogr B. 2004, 60, 578-588. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1107/S0108768104016532
These data can be obtained free of charge from the CCDC through the web page: https://www.ccdc.cam.ac.uk/structures/ (CCDC 2046921)
Kiehlbauch, J.; Hannett, G.; Salfinger, M.; Archinal, W.; Monserrat, C.; Carlyn, C. J Clin Microbiol. 2000, 38, 3341-3348. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1128/JCM.38.9.3341-3348.2000
Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute (2017) Performance Standards for Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing: 27th https://webstore.ansi.org/standards/clsi/clsim100s27 accessed in October 2020
Clinical Laboratory Standards Instutute (2018) Development of in vitro susceptibility testing criteria and quality controls parameters; approved guideline 5th ed. M23-Ed5E https://www.techstreet.com/standards/clsi-m23-ed5?product_id=2033354 accessed in October 2020
Baron, E.J. Classification. In Baron S. Medical microbiology.4th ed. Galveston (TX): University of Texas Medical Branch at Galveston. 1996
Marques de Cantú, M.J. Probabilidad y estadística para ciencias químico-biológicas. McGraw-Hill, México. 1998, 425-456, 471-486
Jaspers, S.; Aerts, M.; Verbeke, G.; Beloil, P-A. Stat. Med. 2014, 33, 289-303. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/sim.5939
Nguyen, M.; Brettin, T.; Long, S-W.; Musser, J-M.; Olsen, R-J.; Olson, R.; Shukla, M.; Stevens, R.L.; Xia, F.; Yoo, H.; Davis, J-J. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 1-11. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-18972-w
Liu, Y-Q.; Zhang, Y-Z.; Gao, P-J. Antimicrob. Agents. Chemother. 2004, 48, 3884-3891. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1128/AAC.48.10.3884-3891.2004
Ren, S.; Wang, R.; Komatsu, K.; Bonaz-Krause, P.; Zyrianov, Y.; McKenna, C.; Csipke, C.; Tokes, Z.; Lien, E. J. Med. Chem. 2002, 45, 410-419. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/jm010252q
Gertzen, C.; Gohlke, H. Mol. Inform. 2012, 31, 698-704. DOI: https://doi/org/10.1002/minf.201200015 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/minf.201200015
Ghose, AK.; Crippen, GM. J. Chem. Informat. Model. 1987, 27, 21-35. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/ci00053a005
Morán Díaz, J.R.; Jiménez Vázquez, H.A.; Gómez Pliego, R.; Arellano Mendoza, M.G.; Quintana Zavala, D.; Guevara-Salazar, J.A. Med. Chem. Res. 2019, 28, 1529-1546. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00044-019-02391-9
ACD/ChemSketch, Advanced Chemistry Development, Inc., Toronto, On, Canada, www.acdlabs.com accessed in September 2020
Hansch, C.; Leo, A. J. Pharm. Sci. 1980, 69, 1109 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/jps.2600690938
Hansch, C.; Fujita, T. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1964, 86, 1616-1626. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/ja01062a035
Williford, C.; Stevens, E. QSAR. Comb. Sci. 2004, 23, 495-505. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/qsar.200430863
Alipour, M.; Safari, Z. Chem. Phys. 2016, 18, 17917-17929. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1039/C6CP02750D
Schüürmann, G.; Ebert, R-U.; Chen, J.; Wang, B.; Kühne, R. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2008, 48, 2140-2145. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/ci800253u
Brunton, L.L.; Hidal-Dandan, R.; Knollmann, B. Goodman & Gilman's: The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics, 13rd ed. United State of America. 2018
Sultan, A.; Hoppenbrouwers, T.; Lemmens den, T.; Snijders, S.; van Neck, J.; Verbon, A.; de Maat, M.; van Wamel, W. Infect. Immun. 2019, 87, 00605-00619. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1128/IAI.00605-19
Crousilles, A.; Maunders, E.; Bartlett, S.; Fan, C.; Ukor, E-F.; Abdelhamid, Y.; Baker, Y.; Floto, A.; Spring, D-R.; Welch, M. Future Microbiol. 2015, 10, 1825-1836. DOI: https://doi.org/10.2217/fmb.15.100
Dewachter, L.; Verstraeten, N.; Fauvart, M.; Michiels, J. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2018, 42, 116-136. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1093/femsre/fuy005
Berti, T.; Ferrari, M.; Galla, F.; Scuka, M. Arch. Ital. Sci. Farmacol. 1965, 15, 203-208.
Bär H, Zarnack J. Pharmazie. 1970, 25, 10-22. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/j.2326-1951.1970.tb00048.x
Castillo-Vera, J.; Ribas-Aparicio, R-M.; Osorio-Carranza, L.; Aparicio, G. Bioquímica. 2006, 17, 41-48.
Dudley, M-N.; Ambrose, P-G.; Bhavnani, S-M.; Craig, W-A.; Ferraro, M-J.; Jones, R-N. Clin. Med. Microbiol. 2013, 56, 1301-1309. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1093/cid/cit017
Biedenbach, D-J.; Kazmierczak, K.; Bouchillon, S-K.; Sahm, D-F.; Brandford, P-A. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2015, 29, 4239-4248. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1128/AAC.00206-15

Downloads
Additional Files
Published
Issue
Section
License
Authors who publish with this journal agree to the following terms:
- Authors retain copyright and grant the journal right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution License that allows others to share the work with an acknowledgement of the work's authorship and initial publication in this journal.
- Authors are able to enter into separate, additional contractual arrangements for the non-exclusive distribution of the journal's published version of the work (e.g., post it to an institutional repository or publish it in a book), with an acknowledgement of its initial publication in this journal.









