Green Synthesis, Characterization and Cholinesterase Inhibitory Potential of Gold Nanoparticles
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.29356/jmcs.v65i3.1479Keywords:
Green synthesis, morphology, gold nanoparticles, enzyme inhibition, bioactivityAbstract
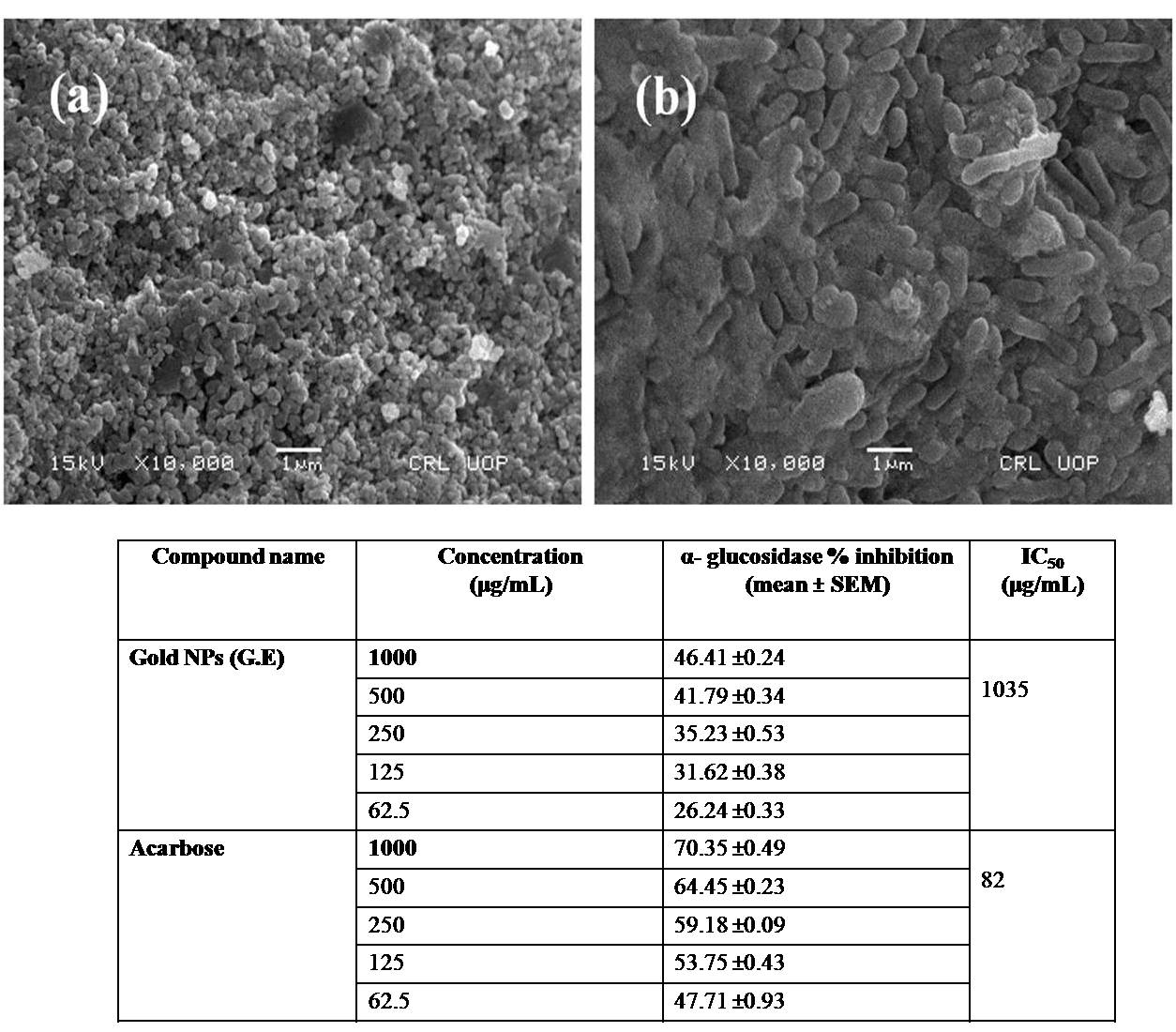
Abstract. The green synthesis of gold nanoparticles (Au NPs) from their precursor was carried out using Delphinium uncinatum and Erythrophyleum guineense plants extracts. The Au NPs obtained were characterized by various instrumental techniques such as scanning electron microscopy (SEM), energy dispersive X-ray (EDX), X-ray diffraction (XRD) and UV/Visible (UV/VIS) spectrophotometer. The SEM study presented that E. guineense (GE) and D. uncinatum (GN) synthesized gold nanoparticles was below 100 and 300 nm, respectively. The micrographs also presented that E. guineense (GE) synthesized gold particles had irregular round shaped while the D. uncinatum (GN) synthesized nanoparticles had cylindrical shaped. The XRD spectra presented peaks at about 38.1°, 44.43°, 64.6° and 77.64° can be indexed to (111), (200), (220) and (311) orientation, respectively, which confirmed the presence of gold nanoparticles. It means that both E. guineense (GE) and D. uncinatum (GN) synthesized gold nanoparticles are highly crystalline. The UV/VIS analysis presented that both plant extracts significantly reduced the gold slat and as a result high quantity of gold nanoparticles were formed. The E. guanense gold NP and D. uncinatum gold NPs were investigated for their in-vitro cholinesterases inhibitory potentials in 62.5-1000 µg/mL concentrations range. The bioactivity results presented that the loading of the test samples in gold NPs enhanced their AChE and BChE inhibitory potentials.
Resumen. La síntesis verde de nanopartículas de oro (NP de Au) se llevó a cabo mediante extractos de plantas de Delphinium uncinatum y Erythrophyleum guineense. Las NP de Au obtenidas se caracterizaron mediante diversas técnicas instrumentales como microscopía electrónica de barrido (SEM), dispersión de energía de rayos X (EDX), difracción de rayos X (XRD) y espectrofotómetro UV / Visible (UV / Vis). El estudio SEM reveló tamaños de las nanopartículas de oro sintetizadas por E. guineense (GE) y D. uncinatum (GN) por debajo de 100 y 300 nm, respectivamente. Las micrografías también mostraron que las partículas de oro sintetizadas por E. guineense (GE) tenían una forma redonda irregular, mientras que las nanopartículas sintetizadas por D. uncinatum (GN) tenían una forma cilíndrica. Los patrones XRD presentaron picos a aproximadamente 38.1 °, 44.43 °, 64.6 ° y 77.64 ° pueden indexarse a la orientación (111), (200), (220) y (311), respectivamente, lo que confirmó la presencia de nanopartículas de oro cristalinas. El análisis UV / Vis mostró que ambos extractos de plantas formaron nanopartículas de oro. Se investigaron las NP de oro como inhibidores de colinesterasas in vitro en un intervalo de concentraciones de 62.5 a 1000 µg / ml. Los resultados de la bioactividad mostraron que la carga de las muestras de prueba en NP de oro mejoró sus potenciales inhibidores de AChE y BChE.
Downloads
References
Ghaffari-Moghaddam, M.; Hadi-Dabanlou, R.; Khajeh, M.; Rakhshanipour, M.; Shameli, K. Korean. J. Chem. Eng. 2014, 3, 548-557.
Ahmed, S.; Ahmad, M.; Swami, B.L.; Ikram, S. J. Adv. Res. 2016, 7, 17–28.
Grimm, S.; Schultz, M.; Barth, S.; Müller, R. J. Mater. Sci. 1997, 32, 1083-1092.
Kim, E.H.; Lee, H.S.; Kwak, B.K.; Kim, B.-K. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2005, 289, 328.
Saeed, K.; Khan, I.; Shah, T.; Park, S.-Y. FiberPolym. 2015, 16, 1870-1875.
Lemine, O.M.; Omri, K.; Zhang, B.; El Mir, L.; Sajieddine, M.; Alyamani, A.; Bououdina,M. Superlattices Microstruct. 2012, 52, 793-799.
Song, J.Y.; Kwon, E.-Y.; Kim , B.S. Bioprocess Biosyst. Eng. 2010, 33, 159–164.
Ahamd, A.; Mukherjee, P.; Mandal, D.; Senapati, S.; Khan, M.I.; Kumar, R.; Sastry, M. J Am. Chem. Soc. 2002, 12441, 12108-12109.
Jang, E.; Ryu, B.H.; Shim, H.W.; Ju, H.; Kim, D.W.; Kim, T.D. Int. J.Biol. Macromol. 2014, 65, 188-192.
Lee, J.; Park, E.Y.; Lee, J. BioprocessBiosyst. Eng. 2014, 376, 983.
Shukla, R.; SNune, N.K.; Chanda, N.; Katti, K.; Mekapothula, S.; Kulkarni, R.R.; Welshons, W.V.; Kannan, R.; Katti, K.V. Small. 2008, 4, 1425-1436.
Suganya, A.; Murugan, K.; Kovendan, K.; Kumar, P.M.; Hwang, J.-S. Parasitol Res. 2013, 112, 1385–1397.
Song, J.Y.; Kwon, E.-Y.; Kim, B.S. Bioprocess Biosyst. Eng. 2010, 33, 159–164.
Rajasekharreddy, P.; Rani, P.U.; Sreedhar, B.. J. Nanopart. Res. 2010, 12, 1711.
Wang, L.; Natan, M.; Zheng, W.; Zheng, W.; Liu, S.; Jacobi, G.; Perelshtein, I.; Gedanken, A.; Banin, E.; Jiang, X. Nanoscale Adv. 2020, 2, 2293-2302.
Arief, S.; Nasution, F.W.; Zulhadjri; Labanni, A. J. Appl. Pharm. Sci. 2020, 10, 124-130.
Donga, S.; Bhadu, G.R.; Chanda, S. Artif. Cells, Nanomed., Biotechnol. 2020, 48, 1315-1325.
Botteon, C.E.A.; Silva, L.B.; Ccana-Ccapatinta, G.V.; Silva, T.S.; Ambrosio, S.R.; Veneziani, R.C.S.; Bastos, J.K.; Marcato, P.D. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11.
Singh, A.K.; Srivastava, O.N. Nanoscale. Res. Let. 2015, 10, 353.
ElMitwalli, O.S.;,Barakat, O.A.; Daoud, R.M.; Akhtar, S.; Henari, F.Z. J. Nanopart. Res. 2020, 22, 309.
State, R.; Papa, F.; Dobrescu, G.; Munteanu, C.; Atkinson, I.; Balint, I.; Volceanov, A. Environ. Eng. Manag. J. 2015, 14, 587-593.
Rajasekharreddy, P.; Rani, P.U.; Sreedhar, B. J Nanopart. Res. 2010, 12, 1711-1721.
Sett, A.; Gadewar, M.; Sharma, P.; Deka, M.; Bora, U. Adv. Nat. Sci.: Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2016, 7 025005.
Doan, V.D.; Thieu, A.T.; Nguyen, T.D.; Nguyen, V.C.; Cao, X.T.; Nguyen, T.L.H.; Le, V.T. J. Nanomater. 2020, 2020.
Association AS.Alzheimer’s disease facts and figures. Alzheimer's Dementia. 2012, 8, 131.
Jazayeri, S.B.; Amanlou, A.; Ghanadian, N.; Pasalar, P.; Amanlou, M. DARU J. Pharm. Sci. 2014, 22, 17.
International, ASD World Alzheimer report The global economic impact of dementia. Alzheimer's Dis. Int. 2010.
Penumala, M.; Zinka, R.B.; Shaik, J.B.; Gangaiah, D.A. BioMed. Res. Int. 2017, 1-12.
Schneider, J.A.; Arvanitakis, Z.; Bang, W.; Bennett, D.A. Neurology. 2007, 69, 2197-2204.
Owokotomo, I.A.; Ekundayo, O.; Abayomi, T.G.; Chukwuka, A.V. Toxicol. Rep. 2015, 2, 850-857.
Mukherjee, P.K.; Kumar, V.; Mal, M.; Houghton, P.J. Phytomedicine. 2007, 14, 289-300.
Duan, H.D.; Wang; Li, Y. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2015, 44, 5778.
Mukherjee, S.; Patra, C.R. Future Sci. 2017, 3, FSO203.
Rao, K.; Aziz, S.; Roome, T.; Razzak, A.; Sikandar, B.; Jamali, K.S.; Imran, M.; Jabri, T.; Shah, M.R. Artif. Cells Nanomed. Biotechnol. 2018. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1080/21691401.2018.1431653.
Singh, R.; Lillard, Jr J.W. Exp. Mol. Pathol. 2009, 86, 215-223.
Wang, Z.; Zhao, J.; Li, F.; Gao, D.; Xing, B. Chemosphere. 2009,77, 67-73.
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
License
Authors who publish with this journal agree to the following terms:
- Authors retain copyright and grant the journal right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution License that allows others to share the work with an acknowledgement of the work's authorship and initial publication in this journal.
- Authors are able to enter into separate, additional contractual arrangements for the non-exclusive distribution of the journal's published version of the work (e.g., post it to an institutional repository or publish it in a book), with an acknowledgement of its initial publication in this journal.









