MTO Synthesis and Characterization of ZnAPO-34 and SAPO-34: Effect of Zn on the Acidity and Catalytic Activity in the MTO Reaction
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.29356/jmcs.v65i1.1261Keywords:
Methanol conversion, zeotypes, light olefins, CHA structure, SAPO-34, MeAPO-34Abstract
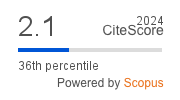
Abstract. SAPO-34 and ZnAPO-34 materials (Zn incorporated by isomorphic substitution in AlPO-34 material) were synthesized by hydrothermal synthesis using triethylamine (TEA) as the structure directing agent (SDA). The structure presented by both materials is isomorphic to the chabazite zeolite (CHA). However, they have different properties such as textural properties (Z34 and S34 presented a surface area of 485 and 603 m2/g, respectively), different crystal sizes and acid properties. The physicochemical properties of the zeotypes were studied using XRD (X-ray diffraction), N2 adsorption-desorption, temperature programmed desorption of NH3 and SEM (Scanning Electron Microscopy). The catalytic performance of these catalysts was studied in the MTO reaction at 400 °C and atmospheric pressure using a WHSV of 2.12 h-1 in a fixed bed reactor. The incorporation of Zn had an important effect on acidity, generating a higher density of acid sites, increasing selectivity to light olefins. It was observed that when the crystal size decreases (ZnAPO-34), 100 % mol methanol conversion is obtained at short reaction times. The ZnAPO-34 material had a smaller crystal size (0.5 µm) and selectivity for olefins of 78 mol %. On the other hand, the SAPO-34 catalyst showed a larger crystal size (1.5 µm) and lower selectivity to olefins (72 mol %). The Z34 catalyst was compared with a previously reported MeAPSO-36 material, the latter was selective for the formation of aromatic compounds and lower selectivity to olefins (35 % mol) due to the presence of larger channels and lower density of acid sites.
Resumen. En este trabajo se han sintetizado materiales SAPO-34 y ZnAPO-34 (Zn incorporado por sustitución isomórfica en material AlPO-34), mediante síntesis hidrotérmica usando trietilamina (TEA) como agente director de la estructura. La estructura presentada por ambos materiales es isomorfa a la de una zeolita chabazita. Sin embargo, ambos materiales tienen diferentes propiedades texturales (Z34 y S34 presentaron un área superficial de 485 y 603 m2/g, respectivamente), diferentes tamaños de cristal y distinta acidez. Las propiedades fisicoquímicas de los catalizadores se estudiaron mediante DRX (difracción de Rayos X), adsorción-desorción de N2, desorción programada a temperatura de NH3 y SEM (Microscopia electrónica de barrido). El rendimiento catalítico de los catalizadores se estudió en la reacción de transformación de metanol a olefinas (MTO) a 400 °C y presión atmosférica en un reactor de lecho fijo operando con un WHSV de 2.12 h-1. La incorporación de Zn tuvo un efecto importante en la acidez generando una mayor densidad de sitios ácidos y aumentando la selectividad a olefinas ligeras. Se observó que cuando el tamaño del cristal disminuye (ZnAPO-34), se obtiene una conversión de metanol del 100 % mol a tiempos cortos de reacción. El material ZnAPO-34 presentó un tamaño de cristal más pequeño (0.5 µm) y selectividad para olefinas de 78 % mol. Por otro lado, el catalizador SAPO-34 mostró un tamaño de cristal más grande (1.5 µm) y menos selectividad a olefinas (72 % mol). El catalizador Z34 fue comparado con un material MeAPSO-36 reportado anteriormente, que presentaba alta selectividad hacia la formación de compuestos aromáticos y menor selectividad a olefinas (35 % mol), debido a la presencia de canales de mayor tamaño y menor densidad de sitios ácidos.
Downloads
References
Dai, W.; Wang, X.; Wu, G.; Guan, N.; Hunger. M.; Li L. ACS Catal. 2011, 1, 292–299. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/cs200016u
Yahyazadeh-Saravi, S; Taghizadeh, M. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2019, 42, 1640–1662. DOI: https://doi.org/10.3906/kim-1804-26
Hashemi, F.; Taghizadeh, M.; Darzinezhad-Rami, M.; Micropor. Mesopor. Mater. 2020, 295, 109970 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micromeso.2019.109970
Stocker, M.; Micropor. Mesopor. Mater. 1999, 29, 3–48.
Tian, P.; Wei, Y.; Ye, M.; Liu, Z. ACS Catal. 2015, 5, 1922-1938. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/acscatal.5b00007
Álvaro-Muñoz, T.; Márquez-Álvarez, C.; Sastre, E. Catal. Today 2012, 179, 27-34.
Zhu, J.; Cui, Y.; Nawaz, Z.; Wang, Y.; Wei, F. Chin. J. Chem. Eng. 2010, 18, 979–987. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/S1004-9541(09)60156-7
Dai, W.; Wu, G.; Li, L.; Guan, N.; Hunger, M. ACS Catal. 2013, 3, 4, 588–596. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/cs400007v
Wilson, S.T.; Lok, B.M.; Messina, C.A.; Cannan, T.R.; Flanigen E.M. JACS 1982, 104, 1146-1147. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/ja00368a062
Makarova, M.; Ojo, A.; Al-Ghefaili, K.; Dwyer, J. In: Proceedings of the IX International Zeolite Conference. Montreal, Canada 1992, 2, 259. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-1-4832-8383-8.50116-1
Kumar-Saha, S.; Waghmode, S.B.; Maekawa, H.; Kawase, R.; Komura, K.; Kubota, Y.; Sugi, Y. Micropor. Mesopor. Mater. 2005, 81, 277–287. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micromeso.2005.02.008
Wilson, S.T.; Barger, P. Micropor. Mesopor. Mater. 1999, 29, 117–126. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/S1387-1811(98)00325-4
S?awi?ski, W.A.; Wragg, D.S.; Akporiaye, D.; Fjellvåg, H. Micropor. Mesopor. Mater. 2014, 195, 311-318. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micromeso.2014.04.024
Luo, M.; Zang, H.; Hu, B.; Wang, B.; Mao, G. RSC Advances 2016, 6, 17651- 17658. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1039/C5RA22424A
Dubois D.R.; Obrzut D.L.; Liu J.; Thundimadathil J.; Adekkanattu P. M.; Guin J.A.; Punnoose A.; Seehra M.S. Fuel Process. Technol. 2003, 83, 203–218 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/S0378-3820(03)00069-9
Kang, M. J. Mol. Catal. A Chem. 2000, 160, 437–444. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/S1381-1169(00)00281-8
Ristic, A.; Novak Tusar, N.; Arcon, I.; Thibault-Starzyic, F.; Hanzel, D.; Czyzniewska, J.; Kaucic, V. Micropor. Mesopor. Mater. 2002, 56, 303-315.
Salmasi, M.; Fatemi, S.; Najafabadi A.T. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2011, 17, 755–761. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jiec.2011.05.031
Sun, C.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Chen, H.; Wang, X.; Li, H.; Sun, L.; Fan, C.; Wang, C.; Zhang, X. Compt. Rendus Chim. 2018, 21, 61–70. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.crci.2017.11.006
Huang, H.; Mengyun, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Li C. Catal. Commun 2020, 137, 105932. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.catcom.2020.105932
Van Niekerk, M. J.; Fletcher, J. C. Q.; O Connor, C. T. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 1996, 138, 135–145. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/0926-860X(95)00240-5
Xu, L.; Liu, Z.M.; Du, A.P.; Wei, Y.X.; Sun, Z.G. Stud. Surf. Sci. Catal. 2004, 147, 445.
Sun, Q.; Xie, Z.; Yu, J. Natl. Sci. Rev. 2017, 0, 1–17.
Terasaka, K.; Imai, H.; Li, X. J. Adv. Chem. Eng. 2015, 5:4, 1000138.
Aghaei, E.; Haghighi, M.; Pazhohniya, Z.; Aghamohammadi, S, Micropor. Mesopor. Mater. 2016, 226, 331-343. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micromeso.2016.02.009
Benvindo, F.S.; de Sousa, R.C.; Fernandes, L.D. in: Anais do XX Simpósio IberoAmericano de Catálise, 2006, volume CDROM, 1–6.
Thommes, M.; Kaneko, K, Neimark, A, Olivier, J.P.; Rodriguez-Reinoso, F.; Rouquerol, J.; Sing, K. Pure Appl. Chem. 2015, 87, 1051–1069. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1515/pac-2014-1117
Wang, Q.; Chen, G.; Xu, S. Micropor. Mesopor. Mater. 2009, 119, 315–321. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micromeso.2008.11.004
Basina, G.; Shamia, D.A.; Polychronopoulou, K.; Tzitzios, V.; Balasubramanian, V.V.; Dawaymeh, F.; Karanikolosa, G.N.; Wahedi, Y.A. Surf. Coat. Tech. 2018, 353, 1-29. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.surfcoat.2018.08.083
Mirza, K.; Ghadiri, M.; Haghighi, M.; Afghan, A. Micropor. Mesopor. Mater. 2018, 260, 155–165. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micromeso.2017.10.045
Izadbakhsh, A.; Farhadi, F.; Khorasheh, F.; Sahebdelfar, S.; Asadi, M.; Zi-Feng, Y. Appl. Catal. A: Gen. 2009, 364, 48–56. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcata.2009.05.022
Zhu, Q.; Kondo, N.J.; Ohnuma, R.; Kubota, Y.; Yamaguchi, M.; Tatsumi, T. Micropor. Mesopor. Mater. 2008, 112, 153–161. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micromeso.2007.09.026
Álvaro-Muñoz, T.; Márquez-Álvarez, C.; Sastre, E. Catal. Today 2012, 179, 27-34. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cattod.2011.07.038
Wei, Y.; Zhang, D.; Xu, L.; Chang, F.; He, Y.; Meng, S.; Su, B.; Liu, Z. Catal. Today 2008, 131, 262–269. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cattod.2007.10.055
Xu, L.; Du, A.; Wei, Y.; Wang, Y.; Yu, Z.; He, Y.; Zhang, X.; Liu, Z. Microporor. Mesopor. Mater. 2008, 115, 332. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micromeso.2008.02.001
Izadbakhsh, A.; Farhadi, F.; Khorasheh, F.; Sahebdelfar, S.; Asadi, M.; Yan, Z.F. Micropor. Mesopor. Mater. 2009, 126, 1–7. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micromeso.2008.12.009
Calegario-Sena, F.; Figueirôa-de Souza, B.; Caroline-de Almeida, N.; Simonace-Cardoso, J.; Domiciano-Fernandes, L. Appl. Catal. A: Gen. 2011, 406, 59– 62. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcata.2011.08.010
Varzaneh, A.Z.; Towfighi, J.; Sahebdelfar, S. Micropor Mesopor Mater. 2016, 236, 1. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micromeso.2016.08.027
Sharifi-Pajaie, H.; Taghizadeh, M. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2015, 24, 59-70.
Huang, H.; Yu, M.; Zhang, Q.; Li, C. Micropor. Mesopor. Mater. 2020, 295, 109971. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micromeso.2019.109971
Zhong, J.; Han, J.; Wei, Y.; Xu, S.; Sun, T.; Guo, X.; Song, C.; Liu, Z. J. Energy Chem. 2019, 32, 174-181. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jechem.2018.07.017
Sun, Q.; Wang, N.; Bai, R.; Chen, G.; Shi, Z.; Zou, Y.; Yu, J. Chem Sus Chem. 2018, 11, 3812–3820. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/cssc.201801486
Song, W.; Haw, J.; Nicholas, J.; Heeneghan, C. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2000, 122, 10726–10727. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/ja002195g
Pajaie, H.S.; Taghizadeh, M. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2015, 24, 59–70. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jiec.2014.09.009
Tosheva L.; Valtchev V.P. Chem. Mater. 2005, 17, 2494-2513. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/cm047908z
García Ruiz, M.; Solís-Casados, D.A.; Aguilar-Pliego J.; Márquez-Álvarez, C.; Sastre de Andrés, E.; Sanjurjo-Tártalo, D.; Sánchez-Sánchez, M.; Grande-Casas M. Top Catal. 2020. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11244-020-01266-3
Akolekar, D.B.; Bhargava, S. J. Mol. Catal A. 2020, 122, 81–90. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/S1381-1169(97)00015-0

Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
License
Authors who publish with this journal agree to the following terms:
- Authors retain copyright and grant the journal right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution License that allows others to share the work with an acknowledgement of the work's authorship and initial publication in this journal.
- Authors are able to enter into separate, additional contractual arrangements for the non-exclusive distribution of the journal's published version of the work (e.g., post it to an institutional repository or publish it in a book), with an acknowledgement of its initial publication in this journal.