Diketopiperazines from Alternaria dauci
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.29356/jmcs.v64i4.1228Keywords:
Daucus carota, Alternaria dauci, phytopathogen, phytotoxicity, diketopiperazineAbstract
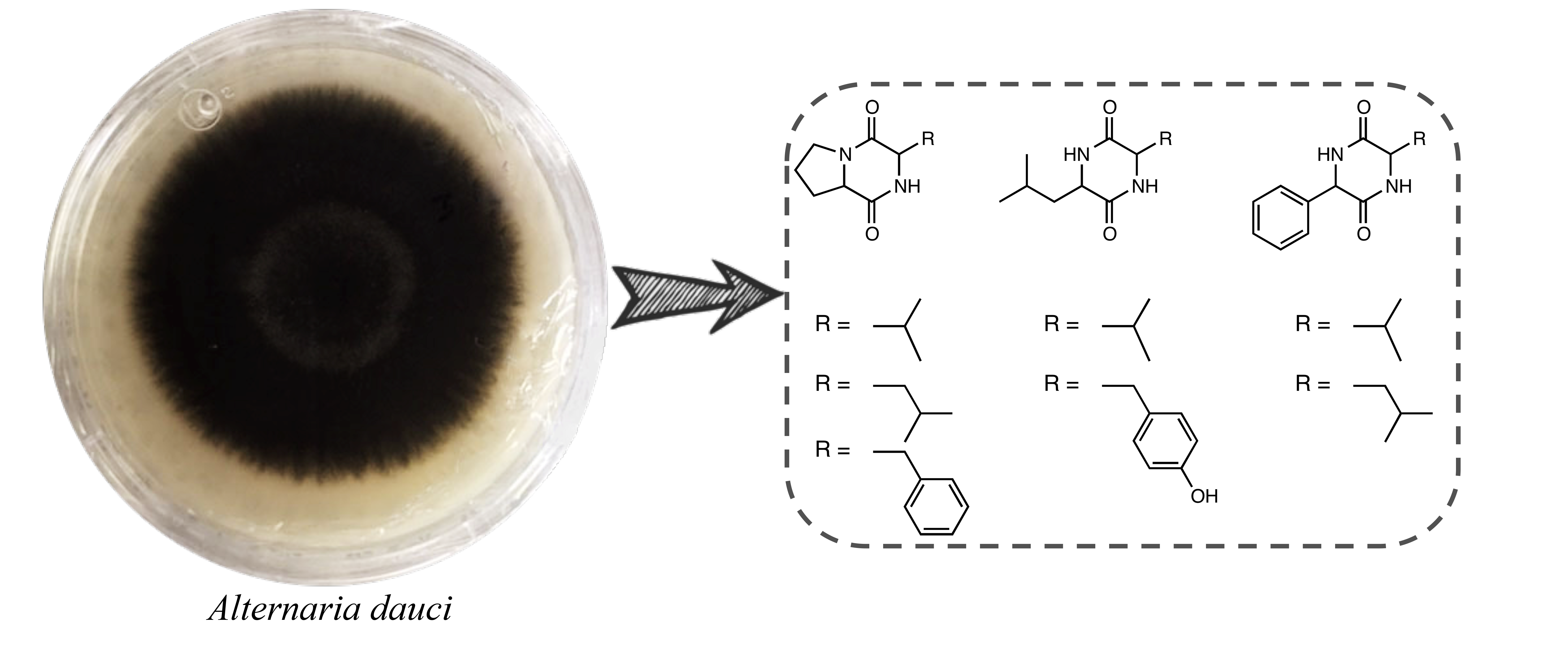
Abstract. Alternaria dauci is the causal agent of Alternaria leaf blight (ALB), a foliar disease of carrot crops (Daucus carota) around the world. In terms of phytotoxic metabolites production, A. dauci has received limited attention. Previous studies carried out on the secondary metabolites involved in the pathogenicity of this fungus have only reported the isolation of a ubiquitous non-selective phytotoxin known as zinniol. Because of this, the aim of this research is directed towards the isolation and identification of secondary metabolites involved in the plant-pathogen interaction process. A. dauci was cultured in the Czapek-Dox medium, and the culture filtrate was extracted with ethyl acetate. The leaf-spot assay of fractions resulting from the partition process showed a phytotoxic effect in the ethyl acetate fraction. The chromatographic separation of ethyl acetate fraction allowed the isolation of seven diketopiperazines, identified as cyclo-(pro-val) (1), cyclo-(pro-leu) (2), cyclo-(pro-phe) (3), cyclo-(val-leu) (4), cyclo-(val-phe) (5), cyclo-(leu-phe) (6) and cyclo-(leu-tyr) (7). The structures of the different metabolites were established by comparing their spectroscopic (1H NMR) and spectrometric (GC-MS) data with those reported in the literature.
Resumen. Alternaria dauci es el agente causal del tizón de la hoja (ALB), una enfermedad foliar que afecta los cultivos de zanahoria (Daucus carota) alrededor del mundo. En términos de producción de metabolitos fitotóxicos, A. dauci ha recibido una atención muy limitada. Estudios previos llevados a cabo sobre los metabolitos secundarios involucrados en la patogenicidad de este hongo, solo han reportado el aislamiento de una fitotoxina no selectiva y ubicua conocida como zinniol. Debido a lo anterior, el objetivo de esta investigación se dirige al aislamiento e identificación de metabolitos secundarios implicados en la interacción planta-patógeno. Para esto el fitopatógeno se cultivó en medio Czapek-Dox y el filtrado del cultivo se extrajo con acetato de etilo. La evaluación de las fracciones resultantes de la partición, en el ensayo de manchas foliares en hojas, mostró un efecto fitotóxico en la fracción de acetato de etilo. La separación cromatográfica de la fracción de acetato de etilo permitió el aislamiento de siete dicetopiperazinas identificadas como ciclo-(pro-val) (1), ciclo-(pro-leu) (2), ciclo-(pro-phe) (3), ciclo-(val-leu) (4), ciclo-(val-phe) (5), ciclo-(leu-phe) (6) y ciclo-(leu-tyr) (7). Las estructuras de los diferentes metabolitos se establecieron comparando sus datos espectroscópicos (1H RMN) y espectrométricos (CG-EM) con los reportados en la literatura.
Downloads
References
Lou, J.; Fu, L.; Peng, Y.; Zhou, L. Molecules 2013, 18, 5891–5935. DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules18055891
Narain, U.; Kant, S.; Chand, G., in: Crop Diseases and Their Management - Integrated Approaches, Chand, G., Kumar, S., Eds. CRC Press, Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2016.
Evans, N.; Mcroberts, N.; Hill, R.A.; Marshall, G. Ann Appl Biol, 1996, 129, 415–431. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1744-7348.1996.tb05765.x
Buchwaldt, L.; Green, H. Plant Pathol. 1992, 41, 55–63. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-3059.1992.tb02316.x
Sanodiya, B.S.; Thakur, G.S.; Baghel, R.K.; Pandey, A.K.; Bhogendra, G.; Prasad, K.S.; Bisen, P.S. J. Plant Prot. Res. 2010, 50, 133–139. DOI: https://doi.org/10.2478/v10045-010-0023-3
Barash, I.; Mor, H.; Netzer, D.; Kashman, Y. Physiol. Plant Pathol. 1981, 19, 7–16. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/S0048-4059(81)80003-3
Tietjen, K.G.; Schaller, E.; Matern, U. Physiol. Plant Pathol. 1983, 23, 387–400. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/0048-4059(83)90023-1
Cotty, P.J.; Misaghi, I.J. Phytopathology 1984, 74, 785–788. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1094/phyto-74-785
Stierle, A.; Hershenhorn, J.; Strobel, G. Phytochemistry 1993, 32, 1145–1149. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/S0031-9422(00)95080-5
Gamboa-Angulo, M.M.; Escalante-Erosa, F.; Garcia-Sosa, K.; Alejos-Gonzalez, F.; Delgado-Lamas, G.; Peña-Rodríguez, L.M. J. Agr. Food Chem. 2002, 50, 1053–1058. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/jf010641t
Stierle, A.C.; Cardellina II, J.H.; Strobel, G.A. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 1988, 85, 8008–8011. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.85.21.8008
Boedo, C.; Benichou, S.; Berruyer, R.; Bersihand, S.; Dongo, A.; Simoneau, P.; Lecomte, M.; Briard, M.; Le Clerc, V.; Poupard, P. Plant Pathol. 2012, 61, 63–75. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-3059.2011.02494.x
Lecomte, M.; Hamama, L.; Voisine, L.; Gatto, J.; Hélesbeux, J.J.; Séraphin, D.; Peña-Rodríguez, L.M.; Richomme, P.; Boedo, C.; Yovanopoulos, C.; Gyomlai, M.; Briard, M.; Simoneau, P.; Poupard, P.; Berruyer, R. PLoS One 2014, 9. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0101008
Farrar, J.J.; Pryor, B.M.; Davis, R.M. Plant Dis. 2004, 88, 779–784. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1094/PDIS.2004.88.8.776
Freeman, G.G. Phytochemistry 1966, 5, 719–725. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/S0031-9422(00)83652-3
Qui, J.A.; Castro-Concha, L.A.; García-Sosa, K.; Miranda-Ham, M.L.; Peña-Rodríguez, L.M. J. Gen. Plant Pathol. 2010, 76, 94–101. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10327-010-0222-9
Chu, M.; Mierzwa, R.; Truumees, I.; Gentile, F.; Patel, M.; Gullo, V.; Chan, T.M.; Puar, M.S. Tetrahedron Lett. 1993, 34, 7537–7540. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/S0040-4039(00)60393-3
Elkahoui, S.; Rahim, H.A.; Tabbene, O.; Shaaban, M.; Limam, F.; Laatsch, H. Nat. Prod. Res. 2013, 27, 108–116. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1080/14786419.2012.660635
Kodaira, Y. Agric. Biol. Chem 1961, 25, 261–262. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1080/00021369.1961.10857803 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1271/bbb1961.25.261
Adamczeski, M.; Reed, A.R.; Crews, P. J. Nat. Prod. 1995, 58, 201–208. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/np50116a007
Dashti, Y.; Grkovic, T.; Abdelmohsen, U.R.; Hentschel, U.; Quinn, R.J. Mar. Drugs 2014, 12, 3046–3059. DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/md12053046
Trigos, A.; Reyna, S.; Cervantes, L. Nat. Prod. Lett. 1995, 6, 241–246. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1080/10575639508043166
Degrassi, G.; Aguilar, C.; Bosco, M.; Zahariev, S.; Pongor, S.; Venturi, V. Curr. Microbiol. 2002, 45, 250–254. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00284-002-3704-y
Ginz, M.; Engelhardt, U.H. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2001, 213, 8–11. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s002170100322
Chen, M.Z.; Dewis, M.L.; Kraut, K.; Merritt, D.; Reiber, L.; Trinnaman, L.; Da Costa, N.C. J. Food Sci. 2009, 74, 100–105. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1750-3841.2009.01062.x
Campbell, J.; Lin, Q.; Geske, G.D.; Blackwell, H.E. ACS Chem. Biol. 2009, 4, 1051–1059. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/cb900165y
Wong, J.W.J.; McPhail, L.T.; Brastianos, H.C.; Andersen, R.J.; Ramer, M.S.; O’Connor, T.P. Exp. Neurol. 2008, 214, 331–340. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.expneurol.2008.08.020
Chen, J.H.; Lan, X.P.; Liu, Y.; Jia, A.Q. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2012, 22, 3177–3180. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bmcl.2012.03.045
Hirsch, S.; Miroz, A.; McCarthy, P.; Kashman, Y. Tetrahedron Lett. 1989, 30, 4291–4294. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/S0040-4039(01)80713-9
Rhee, K.H. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2004, 24, 423–427. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2004.05.005
Li, X.; Kim, S.K.; Nam, K.W.; Kang, J.S.; Choi, H.D.; Son, B.W. J.Antibiot. 2006, 59, 248–250. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/ja.2006.35
Gomez-Monterrey, I.; Campiglia, P.; Carotenuto, A.; Stiuso, P.; Bertamino, A.; Sala, M.; Aquino, C.; Grieco, P.; Morello, S.; Pinto, A.; Ianelli, P.; Novellino, E. J. Med. Chem. 2008, 22, 2924–2932. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/jm7013056
Furukawa, T.; Akutagawa, T.; Funatani, H.; Uchida, T.; Hotta, Y.; Niwa, M.; Takaya. Y. Bioorgan. Med. Chem. 2012, 20, 2002–2009. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bmc.2012.01.050
Shou Zheng, T.; Xiang, P.; Guoyong, L.; Li-Xing, Z.; Li-Hua, X.; Wen-Jun, L.; Yinggang, L. J. Agr. Food Chem. 2013, 61, 3006–3012. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/jf400718w
Cronan, J.M.; Davidson, T.R.; Singleton, F.L.; Colwell, R.R.; Cardellina, J.H. Nat. Prod. Lett. 1998, 11, 271–278. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1080/10575639808044959
Borthwick, A.D. Chem Rev. 2012, 112, 3641?3716. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/cr200398y
Pedras, M.S.C.; Smith, K.C.; Taylor, J.L. Phytochemistry 1998, 49, 1575–1577. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/s0031-9422(98)00271-4
Strobel, G.; Kenfield, D.; Bunkers, G.; Sugawara, F.; Clardy, J. Cell Mol. Life Sci. 1991, 47, 819–826. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01922462
King, R.R.; Calhoun, L.A. Phytochemistry 2009, 70, 833–841. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phytochem.2009.04.013
Scheible, W.R.; Fry, B.; Kochevenko, A.; Schindelasch, D.; Zimmerli, L.; Somerville, S.; Loria, R.; Somerville, C.R. Plant Cell 2003, 15, 1781–1794. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.013342
Trigos, A.; Reyna, S.; Gutierrez, M.L.; Sanchez, M. Nat. Prod. Lett. 1997, 11, 13–16. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1080/10575639708043751

Downloads
Additional Files
Published
Issue
Section
License
Authors who publish with this journal agree to the following terms:
- Authors retain copyright and grant the journal right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution License that allows others to share the work with an acknowledgement of the work's authorship and initial publication in this journal.
- Authors are able to enter into separate, additional contractual arrangements for the non-exclusive distribution of the journal's published version of the work (e.g., post it to an institutional repository or publish it in a book), with an acknowledgement of its initial publication in this journal.